
Contributions
Abstract: EP996
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Cardiac disease is one of the most common complications of multiple myeloma (MM), which seriously affects the survival and prognosis of patients. Several studies have revealed that circular RNAs (circRNAs) might play some roles in the initiation and progression of MM. Exosomes participate in the growth and drug resistance of many tumors via delivering bioactive molecules contained in them. However, the clinical significance of most serum exosome-derived circRNAs (exo-circRNAs) in MM-related cardiac complications is rarely studied.
Aims
To provide evidence for exo-circRNAs as novel potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets for MM-related cardiac diseases.
Methods
We collected serum samples from 21 MM patients which cardiac complications and 5 matched healthy control people as total samples. Then, we used the ExoQuick exosome precipitation kit to separate the exosomes, after which transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was applied to observe the precipitates. Subsequently, 6 serum samples from MM patients and 5 control samples were sent for high-throughput sequencing. According to p value and fold changes, the top 6 significantly up-regulated and 10 down-regulated exo-circRNAs were selected for quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) in total samples. Finally, we statistically analyzed the data with SPSS STATISTICS 26.0. ROC curves and Kaplan Meier survival curves were performed to evaluate the diagnostic and prognostic performance of the relative circRNA in MM-related cardiac diseases.
Results
1.Characterization of serum exosomes
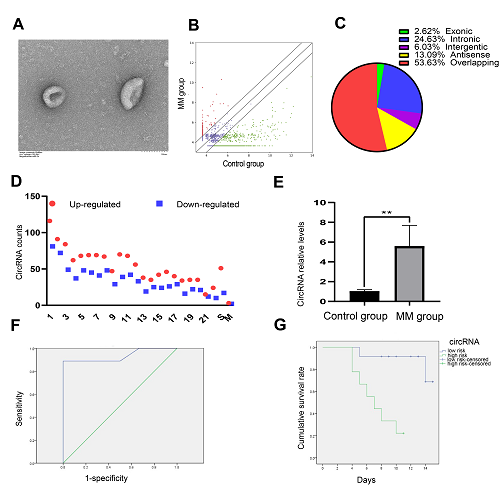
Under the TEM, oval extracellular vesicles less than 100 nm diameter were observed (Fig 1A), which demonstrated that the separated granules were true exosomes.
2. High throughput RNA sequencing
We identified 16106 differentially expressed exo-circRNAs via high-throughput sequencing. Taking FC ≥ 2.0 and P ≤ 0.05 as the criteria, 2,052 exo-circRNAs were selected with significant differences compared with the control group. Then they were visualized by a Scatter plot (Fig 1B). Further analysis showed that most of the up-regulated ones were sense overlapping, while most of the down-regulated ones were exonic (Fig 1C), and they were widely distributed in 22 pairs of autosomes, sex chromosomes and mitochondria (Fig 1D).
3.qRT-PCR validation
The results showed that one of the up-regulated circRNAs chr22: 37076154-37076351 - was derived from the intron of CACNG2 locus, named it as “circ-CACNG2”, with the data of 5.55 ± 2.15 in MM, which was more than five times that in the control group (Fig 1E, P<0.01). It proved that circ-CACNG2 was highly expressed in the exosomes of MM patients.
4.Correlation between circ-CACNG2 and clinicopathological characteristics
The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis indicated that circ-CACNG2 had high sensitivity and specificity as a prognostic indicator. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.935 (P=0.001, Fig 1F), and the optimal critical value of circ-CACNG2 is 4.95 (sensitivity = 88.9% and specificity =100%, Fig 1F). Furthermore, Kaplan Meier survival curve analysis demonstrated that there was a significant difference in survival time between circ-CACNG2 high risk (≥ 4.95) and low risk (< 4.95) (P = 0.001, Fig 1G).
Conclusion
Exosome-derived circ-CACNG2 has the potential to be a novel independent diagnostic factor and prognostic indicator of MM-related cardiac diseases. And it may be an effective therapeutic target in the future.
Keyword(s): Multiple myeloma
Abstract: EP996
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Cardiac disease is one of the most common complications of multiple myeloma (MM), which seriously affects the survival and prognosis of patients. Several studies have revealed that circular RNAs (circRNAs) might play some roles in the initiation and progression of MM. Exosomes participate in the growth and drug resistance of many tumors via delivering bioactive molecules contained in them. However, the clinical significance of most serum exosome-derived circRNAs (exo-circRNAs) in MM-related cardiac complications is rarely studied.
Aims
To provide evidence for exo-circRNAs as novel potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets for MM-related cardiac diseases.
Methods
We collected serum samples from 21 MM patients which cardiac complications and 5 matched healthy control people as total samples. Then, we used the ExoQuick exosome precipitation kit to separate the exosomes, after which transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was applied to observe the precipitates. Subsequently, 6 serum samples from MM patients and 5 control samples were sent for high-throughput sequencing. According to p value and fold changes, the top 6 significantly up-regulated and 10 down-regulated exo-circRNAs were selected for quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) in total samples. Finally, we statistically analyzed the data with SPSS STATISTICS 26.0. ROC curves and Kaplan Meier survival curves were performed to evaluate the diagnostic and prognostic performance of the relative circRNA in MM-related cardiac diseases.
Results
1.Characterization of serum exosomes
Under the TEM, oval extracellular vesicles less than 100 nm diameter were observed (Fig 1A), which demonstrated that the separated granules were true exosomes.
2. High throughput RNA sequencing
We identified 16106 differentially expressed exo-circRNAs via high-throughput sequencing. Taking FC ≥ 2.0 and P ≤ 0.05 as the criteria, 2,052 exo-circRNAs were selected with significant differences compared with the control group. Then they were visualized by a Scatter plot (Fig 1B). Further analysis showed that most of the up-regulated ones were sense overlapping, while most of the down-regulated ones were exonic (Fig 1C), and they were widely distributed in 22 pairs of autosomes, sex chromosomes and mitochondria (Fig 1D).
3.qRT-PCR validation
The results showed that one of the up-regulated circRNAs chr22: 37076154-37076351 - was derived from the intron of CACNG2 locus, named it as “circ-CACNG2”, with the data of 5.55 ± 2.15 in MM, which was more than five times that in the control group (Fig 1E, P<0.01). It proved that circ-CACNG2 was highly expressed in the exosomes of MM patients.
4.Correlation between circ-CACNG2 and clinicopathological characteristics
The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis indicated that circ-CACNG2 had high sensitivity and specificity as a prognostic indicator. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.935 (P=0.001, Fig 1F), and the optimal critical value of circ-CACNG2 is 4.95 (sensitivity = 88.9% and specificity =100%, Fig 1F). Furthermore, Kaplan Meier survival curve analysis demonstrated that there was a significant difference in survival time between circ-CACNG2 high risk (≥ 4.95) and low risk (< 4.95) (P = 0.001, Fig 1G).

Conclusion
Exosome-derived circ-CACNG2 has the potential to be a novel independent diagnostic factor and prognostic indicator of MM-related cardiac diseases. And it may be an effective therapeutic target in the future.
Keyword(s): Multiple myeloma


