
Contributions
Abstract: EP986
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Patients (pts) with multiple myeloma (MM) often relapse and become refractory to successive lines of therapy, warranting better treatment options. The Phase 3 IKEMA study (NCT03275285) demonstrated that isatuximab (Isa) plus carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd) significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) compared with Kd in pts with relapsed MM (RMM) (HR 0.53; 99% CI 0.32–0.89; P=0.0007).
Aims
Evaluate the efficacy and/or safety of Isa-Kd by number of prior lines of therapy (1 vs >1) and refractoriness to lenalidomide (Len) or bortezomib (Bor).
Methods
Pts were randomized (3:2) to Isa-Kd (n=179) or Kd (n=123). Isa (10 mg/kg IV) was given weekly for 4 weeks, then every 2 weeks. K (20 mg/m² days 1-2, then 56 mg/m²) was given twice-weekly 3 of 4 weeks, and d (20 mg) twice-weekly. The primary endpoint was PFS; key secondary endpoints were very good partial response or better (≥VGPR), minimum residual disease negativity (MRD-), and complete response (CR) rates.
Results
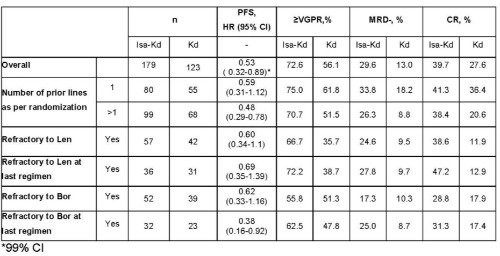
Of the 302 randomized pts, 44.7% had 1 prior line, 55.3% had >1 prior line, 32.8% were Len-refractory, and 30.1% were Bor-refractory. PFS was improved with Isa-Kd vs Kd in pts who received 1 prior line and >1 prior line, as well as in pts refractory to Len, Len at last regimen, Bor, or Bor at last regimen (Table). The addition of Isa to Kd improved depth of response (≥VGPR, MRD-, and CR rates) in all subpopulations analyzed by prior treatment. Grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were generally similar between the prior line subgroups (77.2% [Isa-Kd] vs 64.8% [Kd], 1 prior line; 76.5% [Isa-Kd] vs 69.1% [Kd], >1 prior line) and the overall safety population (76.8% [Isa-Kd] vs 67.2% [Kd]). Serious AEs were 62.0% vs 48.1% in the 1 prior line subgroup, and 57.1% vs 64.7% in the >1 prior line subgroup; TEAEs leading to discontinuations were 8.9% vs 11.1%, 1 prior line and 8.2% vs 16.2%, >1 prior line.
Conclusion
The addition of Isa to Kd improved PFS and depth of response, irrespective of prior lines of therapy or refractory status, consistent with the benefit observed in the overall IKEMA study population. Isa-Kd had a manageable safety profile regardless of number of prior lines. Isa-Kd is a potential new treatment option for pretreated pts with RMM.
Keyword(s): CD38, Monoclonal antibody, Multiple myeloma, Phase III
Abstract: EP986
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Patients (pts) with multiple myeloma (MM) often relapse and become refractory to successive lines of therapy, warranting better treatment options. The Phase 3 IKEMA study (NCT03275285) demonstrated that isatuximab (Isa) plus carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd) significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) compared with Kd in pts with relapsed MM (RMM) (HR 0.53; 99% CI 0.32–0.89; P=0.0007).
Aims
Evaluate the efficacy and/or safety of Isa-Kd by number of prior lines of therapy (1 vs >1) and refractoriness to lenalidomide (Len) or bortezomib (Bor).
Methods
Pts were randomized (3:2) to Isa-Kd (n=179) or Kd (n=123). Isa (10 mg/kg IV) was given weekly for 4 weeks, then every 2 weeks. K (20 mg/m² days 1-2, then 56 mg/m²) was given twice-weekly 3 of 4 weeks, and d (20 mg) twice-weekly. The primary endpoint was PFS; key secondary endpoints were very good partial response or better (≥VGPR), minimum residual disease negativity (MRD-), and complete response (CR) rates.
Results
Of the 302 randomized pts, 44.7% had 1 prior line, 55.3% had >1 prior line, 32.8% were Len-refractory, and 30.1% were Bor-refractory. PFS was improved with Isa-Kd vs Kd in pts who received 1 prior line and >1 prior line, as well as in pts refractory to Len, Len at last regimen, Bor, or Bor at last regimen (Table). The addition of Isa to Kd improved depth of response (≥VGPR, MRD-, and CR rates) in all subpopulations analyzed by prior treatment. Grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were generally similar between the prior line subgroups (77.2% [Isa-Kd] vs 64.8% [Kd], 1 prior line; 76.5% [Isa-Kd] vs 69.1% [Kd], >1 prior line) and the overall safety population (76.8% [Isa-Kd] vs 67.2% [Kd]). Serious AEs were 62.0% vs 48.1% in the 1 prior line subgroup, and 57.1% vs 64.7% in the >1 prior line subgroup; TEAEs leading to discontinuations were 8.9% vs 11.1%, 1 prior line and 8.2% vs 16.2%, >1 prior line.

Conclusion
The addition of Isa to Kd improved PFS and depth of response, irrespective of prior lines of therapy or refractory status, consistent with the benefit observed in the overall IKEMA study population. Isa-Kd had a manageable safety profile regardless of number of prior lines. Isa-Kd is a potential new treatment option for pretreated pts with RMM.
Keyword(s): CD38, Monoclonal antibody, Multiple myeloma, Phase III


