
Contributions
Abstract: EP985
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Daratumumab (Dara), ixazomib (I), carfilzomib (K), bortezomib (V), and elotuzumab (Elo) plus Rd, as well as Rd alone, are among the standards of care for RRMM treatment. In phase 3 RRMM trials, these regimens have been given as long-term/continuous therapy, with median DOTs ranging from 10.1 to 34.3 months. Longer DOT is associated with improved outcomes; however, the lengthy DOTs seen in clinical trials do not always translate to the real-world setting due to multiple pt- and treatment-related factors, emphasizing the importance of real-world data collection to aid in treatment decisions.
Aims
To estimate DOT with Rd-based regimens in RRMM pts in the global, prospective, observational INSIGHT MM study (NCT02761187).
Methods
From July 2016 to June 2019, INSIGHT MM enrolled 4307 pts from 15 countries, including 1939 pts with ≥2 prior lines of therapy (LOT). Prospective follow-up of ≥2 years/pt is ongoing. DOT was defined as time from Rd-based treatment initiation within a LOT (index regimen) to time of discontinuation of index regimen. Kaplan-Meier analyses were used to determine DOT for each Rd-based regimen reported, overall, and by LOT and region (Europe+Israel [EUR]; North America [NA]). Exposure to prior therapies and reasons for treatment discontinuation were also examined.
Results
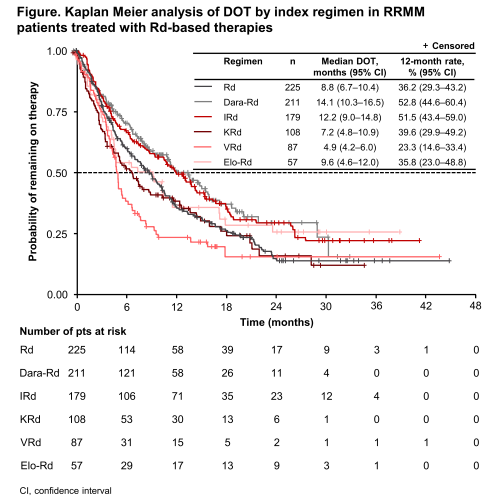
In total, 821 pts received 867 Rd-based LOT for RRMM (225 Rd, 211 Dara-Rd, 179 IRd, 108 KRd, 87 VRd, and 57 Elo-Rd; pts could be included more than once if they received an Rd-based treatment in >1 LOT), including 464/262/150 in 2nd/3rd/≥4th line (134/70/24 Rd, 115/58/39 Dara-Rd, 58/82/40 IRd, 67/25/18 KRd, 57/16/15 VRd, and 33/11/14 Elo-Rd; 9 pts received the same regimen >once). Overall, median DOT was longest with Dara-Rd and IRd (14.1 and 12.2 months); the proportions of pts in treatment at 12 months (12-month DOT rate) were 52.8% and 51.5%, respectively (Figure). Analysis by region showed higher 12-month DOT rates in EUR vs NA with Dara-Rd (57.1 vs 43.7%), IRd (55.3 vs 34.2%), and KRd (41.0 vs 30.7%), a lower rate in EUR with VRd (11.0 vs 30.7%), and similar rates with Rd (40.8 vs 40.0%) and Elo-Rd (37.0 vs 33.6%). These rates were not analyzed in Latin America and Asia-Pacific regions due to small pt numbers. Among 2nd/3rd/≥4th-line pts, 12-month DOT rates with Dara-Rd were 58.8%/56.1%/31.1%; with IRd, 49.8%/56.6%/47.4%; with KRd, 41.3%/44.3%/35.3%; with Elo-Rd, 40.8%/30.0%/27.7%; with Rd, 36.8%/36.2%/28.1%; and with VRd, 25.0%/40.0%/0%. Most regimens received immediately prior to Rd-based treatment were V-based (n=504, 58.1%). Overall, common prior regimens received included VCd (20.6%), VRd (10.3%), VTd (9.1%), Vd (8.9%), Rd (6.6%), and VMP (5.9%), used primarily as 1st and 2nd line. Prior therapies were more diverse in pts receiving Rd-based treatment beyond 3rd vs in earlier lines. Overall, 555/867 (64.0%) of the reported LOT were in R-naïve pts and 312 (36.0%) were in pts exposed to R in any line prior to Rd-based treatment. At data cutoff, 530/867 (61.1%) Rd-based individual LOT had been discontinued; overall reasons for discontinuation (multiple reasons could be provided per LOT) included relapse in 224 pts (42.3% of 530), adverse events in 78 (14.7%), death in 33 (6.2%), and other reasons in 207 (39.1%).
Conclusion
DOT with Rd-based treatment in the real-world setting of INSIGHT MM generally appeared shorter than in clinical trials. The longest DOTs were seen in 2nd and 3rd LOT with Dara-Rd and IRd. Thirty six percent of the reported LOT were in pts who received R in any prior line, while the most common therapies immediately prior to Rd-based therapy were V-based.
Keyword(s): Immunomodulation, Multiple myeloma, Proteasome inhibitor, Treatment
Abstract: EP985
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Daratumumab (Dara), ixazomib (I), carfilzomib (K), bortezomib (V), and elotuzumab (Elo) plus Rd, as well as Rd alone, are among the standards of care for RRMM treatment. In phase 3 RRMM trials, these regimens have been given as long-term/continuous therapy, with median DOTs ranging from 10.1 to 34.3 months. Longer DOT is associated with improved outcomes; however, the lengthy DOTs seen in clinical trials do not always translate to the real-world setting due to multiple pt- and treatment-related factors, emphasizing the importance of real-world data collection to aid in treatment decisions.
Aims
To estimate DOT with Rd-based regimens in RRMM pts in the global, prospective, observational INSIGHT MM study (NCT02761187).
Methods
From July 2016 to June 2019, INSIGHT MM enrolled 4307 pts from 15 countries, including 1939 pts with ≥2 prior lines of therapy (LOT). Prospective follow-up of ≥2 years/pt is ongoing. DOT was defined as time from Rd-based treatment initiation within a LOT (index regimen) to time of discontinuation of index regimen. Kaplan-Meier analyses were used to determine DOT for each Rd-based regimen reported, overall, and by LOT and region (Europe+Israel [EUR]; North America [NA]). Exposure to prior therapies and reasons for treatment discontinuation were also examined.
Results
In total, 821 pts received 867 Rd-based LOT for RRMM (225 Rd, 211 Dara-Rd, 179 IRd, 108 KRd, 87 VRd, and 57 Elo-Rd; pts could be included more than once if they received an Rd-based treatment in >1 LOT), including 464/262/150 in 2nd/3rd/≥4th line (134/70/24 Rd, 115/58/39 Dara-Rd, 58/82/40 IRd, 67/25/18 KRd, 57/16/15 VRd, and 33/11/14 Elo-Rd; 9 pts received the same regimen >once). Overall, median DOT was longest with Dara-Rd and IRd (14.1 and 12.2 months); the proportions of pts in treatment at 12 months (12-month DOT rate) were 52.8% and 51.5%, respectively (Figure). Analysis by region showed higher 12-month DOT rates in EUR vs NA with Dara-Rd (57.1 vs 43.7%), IRd (55.3 vs 34.2%), and KRd (41.0 vs 30.7%), a lower rate in EUR with VRd (11.0 vs 30.7%), and similar rates with Rd (40.8 vs 40.0%) and Elo-Rd (37.0 vs 33.6%). These rates were not analyzed in Latin America and Asia-Pacific regions due to small pt numbers. Among 2nd/3rd/≥4th-line pts, 12-month DOT rates with Dara-Rd were 58.8%/56.1%/31.1%; with IRd, 49.8%/56.6%/47.4%; with KRd, 41.3%/44.3%/35.3%; with Elo-Rd, 40.8%/30.0%/27.7%; with Rd, 36.8%/36.2%/28.1%; and with VRd, 25.0%/40.0%/0%. Most regimens received immediately prior to Rd-based treatment were V-based (n=504, 58.1%). Overall, common prior regimens received included VCd (20.6%), VRd (10.3%), VTd (9.1%), Vd (8.9%), Rd (6.6%), and VMP (5.9%), used primarily as 1st and 2nd line. Prior therapies were more diverse in pts receiving Rd-based treatment beyond 3rd vs in earlier lines. Overall, 555/867 (64.0%) of the reported LOT were in R-naïve pts and 312 (36.0%) were in pts exposed to R in any line prior to Rd-based treatment. At data cutoff, 530/867 (61.1%) Rd-based individual LOT had been discontinued; overall reasons for discontinuation (multiple reasons could be provided per LOT) included relapse in 224 pts (42.3% of 530), adverse events in 78 (14.7%), death in 33 (6.2%), and other reasons in 207 (39.1%).

Conclusion
DOT with Rd-based treatment in the real-world setting of INSIGHT MM generally appeared shorter than in clinical trials. The longest DOTs were seen in 2nd and 3rd LOT with Dara-Rd and IRd. Thirty six percent of the reported LOT were in pts who received R in any prior line, while the most common therapies immediately prior to Rd-based therapy were V-based.
Keyword(s): Immunomodulation, Multiple myeloma, Proteasome inhibitor, Treatment


