
Contributions
Abstract: EP978
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Ciltacabtagene autoleucel (cilta-cel; JNJ-68284528) is a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy with two BCMA–targeting, single-domain antibodies designed to confer avidity. In the phase 1b/2 CARTITUDE-1 single arm study (NCT03548207), a single infusion of cilta-cel yielded early, deep, and durable responses with a manageable safety profile in heavily pretreated triple-class exposed (to immunomodulatory drugs [IMiDs], proteasome inhibitors [PIs], and anti-CD38 antibodies) RRMM patients. In the absence of head-to-head trials, matched adjusted comparison methods may be helpful to compare the relative efficacy of different treatment regimens. A systematic literature review using PRISMA guidelines identified belantamab mafodotin as a potential BCMA-targeting non-CAR T-cell comparator in the triple-class exposed RRMM patient population.
Aims
To compare efficacy outcomes for cilta-cel from the CARTITUDE-1 study to the approved 2.5 mg/kg (every 3 weeks) dose of belantamab mafodotin from the DREAMM-2 trial (NCT03525678).
Methods
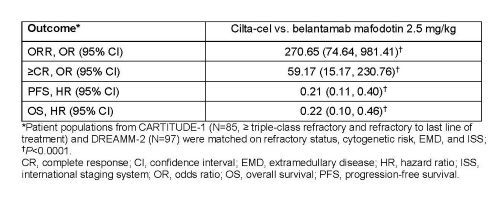
CARTITUDE-1 included triple class exposed patients who received ≥3 prior lines of therapy or were double refractory to an IMiD and PI, had ECOG score of ≤1, and disease progression ≤12 months after the last line of therapy. Unanchored matching-adjusted indirect treatment comparisons (MAIC) were performed based on individual patient-level data from 97 infused patients in CARTITUDE-1 and published aggregate-level data from DREAMM-2 (N=97). Patients from CARTITUDE-1 (N=85) who matched the eligibility criteria for DREAMM-2 (≥ triple-class refractory and refractory to last line of treatment) were included in the analysis. Individual patient data for time-to-event outcomes from DREAMM-2 were simulated based on the published Kaplan-Meier curves. Matching of CARTITUDE-1 patients to the DREAMM-2 population was based on propensity score weighting methods, using available prognostic factors identified from the literature and based on clinical expertise. Outcomes included overall response rate (ORR), complete response or better (≥CR), progression free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS). For ORR and ≥CR, the relative effects of cilta-cel versus belantamab mafodotin were quantified using an odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) derived from a weighted logistic regression analysis, while time to event endpoints were analyzed using a weighted Cox proportional hazards model. A similar comparative analysis was performed including all enrolled patients from CARTITUDE-1.
Results
Cilta-cel was associated with significantly higher ORR and ≥CR, and improved PFS and OS compared with belantamab mafodotin in a population matched to DREAMM-2 (Table). Similarly, higher efficacy was associated with cilta-cel in the comparative analysis which included all patients enrolled in CARTITUDE-1.
Conclusion
These analyses demonstrated improved efficacy with cilta-cel versus belantamab mafodotin for ORR, ≥CR, PFS, and OS, highlighting its potential in patients with triple-class exposed RRMM.
Keyword(s): B-cell maturation antigen, CAR-T, Multiple myeloma
Abstract: EP978
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Ciltacabtagene autoleucel (cilta-cel; JNJ-68284528) is a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy with two BCMA–targeting, single-domain antibodies designed to confer avidity. In the phase 1b/2 CARTITUDE-1 single arm study (NCT03548207), a single infusion of cilta-cel yielded early, deep, and durable responses with a manageable safety profile in heavily pretreated triple-class exposed (to immunomodulatory drugs [IMiDs], proteasome inhibitors [PIs], and anti-CD38 antibodies) RRMM patients. In the absence of head-to-head trials, matched adjusted comparison methods may be helpful to compare the relative efficacy of different treatment regimens. A systematic literature review using PRISMA guidelines identified belantamab mafodotin as a potential BCMA-targeting non-CAR T-cell comparator in the triple-class exposed RRMM patient population.
Aims
To compare efficacy outcomes for cilta-cel from the CARTITUDE-1 study to the approved 2.5 mg/kg (every 3 weeks) dose of belantamab mafodotin from the DREAMM-2 trial (NCT03525678).
Methods
CARTITUDE-1 included triple class exposed patients who received ≥3 prior lines of therapy or were double refractory to an IMiD and PI, had ECOG score of ≤1, and disease progression ≤12 months after the last line of therapy. Unanchored matching-adjusted indirect treatment comparisons (MAIC) were performed based on individual patient-level data from 97 infused patients in CARTITUDE-1 and published aggregate-level data from DREAMM-2 (N=97). Patients from CARTITUDE-1 (N=85) who matched the eligibility criteria for DREAMM-2 (≥ triple-class refractory and refractory to last line of treatment) were included in the analysis. Individual patient data for time-to-event outcomes from DREAMM-2 were simulated based on the published Kaplan-Meier curves. Matching of CARTITUDE-1 patients to the DREAMM-2 population was based on propensity score weighting methods, using available prognostic factors identified from the literature and based on clinical expertise. Outcomes included overall response rate (ORR), complete response or better (≥CR), progression free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS). For ORR and ≥CR, the relative effects of cilta-cel versus belantamab mafodotin were quantified using an odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) derived from a weighted logistic regression analysis, while time to event endpoints were analyzed using a weighted Cox proportional hazards model. A similar comparative analysis was performed including all enrolled patients from CARTITUDE-1.
Results
Cilta-cel was associated with significantly higher ORR and ≥CR, and improved PFS and OS compared with belantamab mafodotin in a population matched to DREAMM-2 (Table). Similarly, higher efficacy was associated with cilta-cel in the comparative analysis which included all patients enrolled in CARTITUDE-1.

Conclusion
These analyses demonstrated improved efficacy with cilta-cel versus belantamab mafodotin for ORR, ≥CR, PFS, and OS, highlighting its potential in patients with triple-class exposed RRMM.
Keyword(s): B-cell maturation antigen, CAR-T, Multiple myeloma


