
Contributions
Abstract: EP973
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Therapies for multiple myeloma (MM) combine multiple drug classes including IMiDs, proteasome inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, alkylators, histone deacetylase inhibitors, XPO1 inhibitors, and anti-B cell maturation antigen therapies (Legarda et al. Cancer. 2020;12:3576). Despite advances in therapy, outcomes remain poor for patients with relapsed/refractory MM (RRMM). Melphalan flufenamide (melflufen) is a first-in-class peptide-drug conjugate (PDC) that leverages aminopeptidases and thereby rapidly delivers and releases alkylating agents inside tumor cells. Melflufen has a mechanism of action (MOA) distinct from other alkylating agents (Slipicevic et al. AACR 2020. Abs. 1843). In the O-12-M1 (NCT01897714) and HORIZON (OP-106; NCT02963493) studies, melflufen plus dexamethasone showed meaningful efficacy and a clinically manageable safety profile in patients with RRMM (Richardson et al. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7:5; Richardson et al. J Clin Oncol. 2020;Dec 9 [Epub]).
Aims
To examine the clinical activity of melflufen in patients from the O-12-M1 (phase 2 only) and HORIZON studies who were exposed to alkylators in prior lines of therapy (LoTs).
Methods
Patients in the phase 2 portion of the O-12-M1 study and HORIZON had RRMM with ≥2 prior LoTs and received melflufen 40 mg plus dexamethasone 40 mg (20 mg if aged ≥75 years). Both studies had a primary endpoint of overall response rate (ORR); secondary endpoints included progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and safety. Data from the 2 studies were pooled and analyzed according to prior exposure and refractory status to alkylators before study entry. Refractory status to prior alkylator therapy was defined as failure to achieve a minimal response or progression while on therapy, or within 60 days of last dose of alkylator therapy.
Results
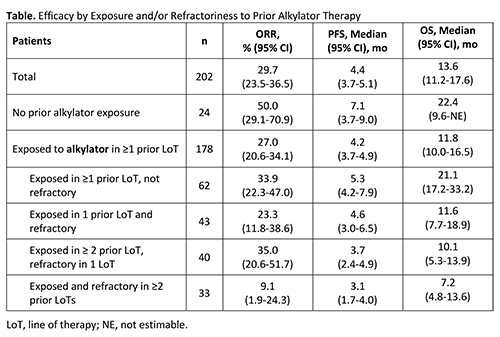
A total of 202 patients were included in the analysis (HORIZON: n=157; O-12-M1: n=45); of these, 24 (12%) had not been exposed to an alkylator and 178 (88%) had been exposed to alkylators in ≥1 prior LoT (see Table for prior alkylator exposure/refractory status). Patients without prior exposure to an alkylator had the best response to therapy (ORR, 50.0% [95% CI, 29.1-70.9]; PFS, 7.1 months [95% CI, 3.7-9.0]). However, meaningful responses were also seen among patients exposed and refractory to prior alkylators (Table). PFS and OS were better or similar to that in the overall population in patients exposed to an alkylator in ≥1 prior LoT but not refractory and in patients exposed to an alkylator in 1 prior LoT and refractory, respectively. PFS and OS were shortest when both exposed and refractory to an alkylator in ≥2 prior LoTs; this group had more patients refractory to an alkylator in their last LoT (61%) and 82% were refractory to an alkylator within 12 months of study entry. Results should be interpreted with caution due to limited patient numbers.
Grade 3/4 adverse events (AEs) were similar among patients exposed to prior alkylators (O-12-M1: 85%; HORIZON: 89%) and the overall population (O-12-M1: 84%; HORIZON: 89%). The most common AEs were hematologic but were mostly reversible and clinically manageable. Nonhematologic AEs were infrequent and primarily grade 1/2.
Conclusion
Melflufen in combination with dexamethasone showed meaningful efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with RRMM including those exposed and/or refractory to prior alkylators and is in line with pre-clinical studies showing that melflufen has an MOA distinct from that of other alkylating agents.
Keyword(s): Multiple myeloma
Abstract: EP973
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Therapies for multiple myeloma (MM) combine multiple drug classes including IMiDs, proteasome inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, alkylators, histone deacetylase inhibitors, XPO1 inhibitors, and anti-B cell maturation antigen therapies (Legarda et al. Cancer. 2020;12:3576). Despite advances in therapy, outcomes remain poor for patients with relapsed/refractory MM (RRMM). Melphalan flufenamide (melflufen) is a first-in-class peptide-drug conjugate (PDC) that leverages aminopeptidases and thereby rapidly delivers and releases alkylating agents inside tumor cells. Melflufen has a mechanism of action (MOA) distinct from other alkylating agents (Slipicevic et al. AACR 2020. Abs. 1843). In the O-12-M1 (NCT01897714) and HORIZON (OP-106; NCT02963493) studies, melflufen plus dexamethasone showed meaningful efficacy and a clinically manageable safety profile in patients with RRMM (Richardson et al. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7:5; Richardson et al. J Clin Oncol. 2020;Dec 9 [Epub]).
Aims
To examine the clinical activity of melflufen in patients from the O-12-M1 (phase 2 only) and HORIZON studies who were exposed to alkylators in prior lines of therapy (LoTs).
Methods
Patients in the phase 2 portion of the O-12-M1 study and HORIZON had RRMM with ≥2 prior LoTs and received melflufen 40 mg plus dexamethasone 40 mg (20 mg if aged ≥75 years). Both studies had a primary endpoint of overall response rate (ORR); secondary endpoints included progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and safety. Data from the 2 studies were pooled and analyzed according to prior exposure and refractory status to alkylators before study entry. Refractory status to prior alkylator therapy was defined as failure to achieve a minimal response or progression while on therapy, or within 60 days of last dose of alkylator therapy.
Results
A total of 202 patients were included in the analysis (HORIZON: n=157; O-12-M1: n=45); of these, 24 (12%) had not been exposed to an alkylator and 178 (88%) had been exposed to alkylators in ≥1 prior LoT (see Table for prior alkylator exposure/refractory status). Patients without prior exposure to an alkylator had the best response to therapy (ORR, 50.0% [95% CI, 29.1-70.9]; PFS, 7.1 months [95% CI, 3.7-9.0]). However, meaningful responses were also seen among patients exposed and refractory to prior alkylators (Table). PFS and OS were better or similar to that in the overall population in patients exposed to an alkylator in ≥1 prior LoT but not refractory and in patients exposed to an alkylator in 1 prior LoT and refractory, respectively. PFS and OS were shortest when both exposed and refractory to an alkylator in ≥2 prior LoTs; this group had more patients refractory to an alkylator in their last LoT (61%) and 82% were refractory to an alkylator within 12 months of study entry. Results should be interpreted with caution due to limited patient numbers.
Grade 3/4 adverse events (AEs) were similar among patients exposed to prior alkylators (O-12-M1: 85%; HORIZON: 89%) and the overall population (O-12-M1: 84%; HORIZON: 89%). The most common AEs were hematologic but were mostly reversible and clinically manageable. Nonhematologic AEs were infrequent and primarily grade 1/2.

Conclusion
Melflufen in combination with dexamethasone showed meaningful efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with RRMM including those exposed and/or refractory to prior alkylators and is in line with pre-clinical studies showing that melflufen has an MOA distinct from that of other alkylating agents.
Keyword(s): Multiple myeloma


