
Contributions
Abstract: EP966
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Activating mutations of the RAS genes NRAS, KRAS, and HRAS (RASmut) occur in up to 50% of MM and portend poor survival and high recurrence rates. MM cells with RASmut are susceptible to inhibition of germinal center kinase (GCK), resulting in IKAROS degradation independent of cereblon (CRBN). Selinexor is a selective inhibitor of nuclear export (SINE) compound that can induce IKAROS degradation through CRBN-independent pathways to overcome immunomodulatory drug resistance. We explored the benefit of selinexor treatment for pts with RASmut MM.
Aims
To evaluate the effect of NRAS, KRAS or HRAS mutations on outcomes in MM pts treated with a selinexor regimen.
Methods
In the randomized BOSTON study, pts with MM after 1-3 therapies received weekly XVd or twice weekly Vd. In the single-arm STORM study, pts with penta-treated, triple class refractory MM were treated with twice weekly Xd. Both treatment regimens are now FDA approved. Mutations were assessed post-hoc by exome sequencing of 119 and 52 pts from BOSTON and STORM, respectively. Pts were considered RASmut if their MM had NRAS, KRAS or HRAS mutations in codons 12, 13 or 61.
Results
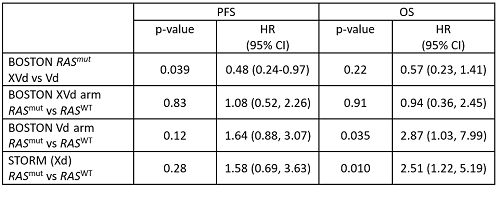
There were 54 pts (45%) with RASmut in BOSTON (XVd=26, Vd=28), and 17 (33%) in STORM (all receiving Xd). In BOSTON, pts with RASmut MM treated with XVd had significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) than those treated with Vd (median [med]=12.9 vs 6.7 months [mo], hazard ratio [HR]=0.48 [95% CI 0.24-0.97], p=0.039). For pts treated with Vd, those with RASmut had significantly shorter overall survival (OS) compared to RASwild-type (WT) (med=16.8 mo vs not reached [NR], HR=2.87 [95% CI 1.03-7.99], p=0.035). PFS trended shorter in RASmut (med=6.74 vs 9.82 mo, HR=1.64 [95% CI 0.88-3.07], p=0.122). In contrast, amongst pts on XVd, there was no difference in survival between RASmut and RASWT pts (PFS: med=12.8 vs 12.9 mo, HR=1.08 [95% CI 0.52-2.26], p=0.83; OS: med=NR vs NR, HR=0.94 [95% CI 0.36-2.45], p=0.91). In STORM, pts with RASmut had shorter OS compared to RASwt pts (med=6.1 vs NR, HR=2.51 [95% CI 1.22-5.19], p=0.010). Preliminary studies to explore the mechanisms of action related to RASmut MM sensitivity to XVd demonstrated that selinexor treatment in vitro leads to downregulation of GCK.
Conclusion
Despite typically having the worst outcomes, pts with RASmut MM had a similar benefit from XVd as RASWT MM, showing that the XVd combination can overcome traditionally poor prognostic RASmut. Mechanistically, selinexor induced down regulation of GCK and enhanced killing of RASmut MM cells. With a manageable safety profile, the XVd regimen could provide a viable treatment option to improve PFS and OS in pts with MM with RAS mutations.
Keyword(s): Multiple myeloma, Mutation analysis, Ras
Abstract: EP966
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Activating mutations of the RAS genes NRAS, KRAS, and HRAS (RASmut) occur in up to 50% of MM and portend poor survival and high recurrence rates. MM cells with RASmut are susceptible to inhibition of germinal center kinase (GCK), resulting in IKAROS degradation independent of cereblon (CRBN). Selinexor is a selective inhibitor of nuclear export (SINE) compound that can induce IKAROS degradation through CRBN-independent pathways to overcome immunomodulatory drug resistance. We explored the benefit of selinexor treatment for pts with RASmut MM.
Aims
To evaluate the effect of NRAS, KRAS or HRAS mutations on outcomes in MM pts treated with a selinexor regimen.
Methods
In the randomized BOSTON study, pts with MM after 1-3 therapies received weekly XVd or twice weekly Vd. In the single-arm STORM study, pts with penta-treated, triple class refractory MM were treated with twice weekly Xd. Both treatment regimens are now FDA approved. Mutations were assessed post-hoc by exome sequencing of 119 and 52 pts from BOSTON and STORM, respectively. Pts were considered RASmut if their MM had NRAS, KRAS or HRAS mutations in codons 12, 13 or 61.
Results
There were 54 pts (45%) with RASmut in BOSTON (XVd=26, Vd=28), and 17 (33%) in STORM (all receiving Xd). In BOSTON, pts with RASmut MM treated with XVd had significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) than those treated with Vd (median [med]=12.9 vs 6.7 months [mo], hazard ratio [HR]=0.48 [95% CI 0.24-0.97], p=0.039). For pts treated with Vd, those with RASmut had significantly shorter overall survival (OS) compared to RASwild-type (WT) (med=16.8 mo vs not reached [NR], HR=2.87 [95% CI 1.03-7.99], p=0.035). PFS trended shorter in RASmut (med=6.74 vs 9.82 mo, HR=1.64 [95% CI 0.88-3.07], p=0.122). In contrast, amongst pts on XVd, there was no difference in survival between RASmut and RASWT pts (PFS: med=12.8 vs 12.9 mo, HR=1.08 [95% CI 0.52-2.26], p=0.83; OS: med=NR vs NR, HR=0.94 [95% CI 0.36-2.45], p=0.91). In STORM, pts with RASmut had shorter OS compared to RASwt pts (med=6.1 vs NR, HR=2.51 [95% CI 1.22-5.19], p=0.010). Preliminary studies to explore the mechanisms of action related to RASmut MM sensitivity to XVd demonstrated that selinexor treatment in vitro leads to downregulation of GCK.

Conclusion
Despite typically having the worst outcomes, pts with RASmut MM had a similar benefit from XVd as RASWT MM, showing that the XVd combination can overcome traditionally poor prognostic RASmut. Mechanistically, selinexor induced down regulation of GCK and enhanced killing of RASmut MM cells. With a manageable safety profile, the XVd regimen could provide a viable treatment option to improve PFS and OS in pts with MM with RAS mutations.
Keyword(s): Multiple myeloma, Mutation analysis, Ras


