
Contributions
Abstract: EP947
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Tumor-associated macrophages(TAMs)arise from in situ maturation of recruited circulating monocytes and constitue a significant part of myeloma tumor microenvironment. TAMs maybe contribute to the immune escape of multiple myeloma (MM).
Aims
Our study detected the expression of TAMs, CSF1R on macrophages and CSF1 on myeloma cells in bone marrow, and PD-1 on CD8 + T cells and PD-L1 on TAMs.
Methods
March 2020 to January 2021, 53 newly diagnosed MM patients, 33 remission MM (VGPR and above) patients and 28 healthy controls were selected as observation objects. The expression of TAMs, CSF1R on macrophages and CSF1 on myeloma cells,PD-1 on CD8 + T cells and PD-L1 on TAMswere detected by flow cytometry. Bone marrow mononuclear cells from newly diagnosed MM patients were extracted and cultured into TAMs, and then cocultured with CD8 + T cells to detect the expression of perforin and granzyme B.
Results
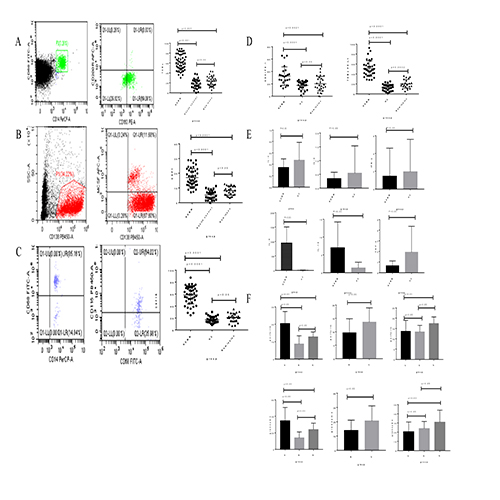
1. The expression of TAMs in NDMM group was significantly higher than remission group (P<0.001) and healthy control group (P<0.05)(Figure A). 2. The expression of CSF1 on CD138+ cells in the NDMM group was higher than the remission group (P<0.0001) and the healthy control group (P<0.05), the difference was statistically significant (Figure B). 3. The expression of CSF1R on macrophages in NDMM group was higher than the remission group (P<0.0001)and healthy control group,and there was no statistical significance between remission group and healthy control group(Figure C). 4. The expression of PD-1 on CD8+ T cells in the NDMM group was significantly higher than that in the remission group (P<0.05) and the healthy control group, but there was no significant difference between the remission group and the healthy control group (P>0.05).The expression of PDL-1 on TAMs in the NDMM group was higher than that in remission group(P<0.01)and healthy control group (P<0.05) (Figure D). 5. The expression of cytokines in the supernatants of TAMs cultured with mononuclear cells extracted from bone marrow. IL-6 and IL-10 in the NDMM group was significantly higher than that in the healthy control group ( both P<0.05). TNF-α、 in the NDMM group was significantly lower than that in the healthy control group (P<0.05)(Figure E). 6. The expression of functional molecules was detected after coculture of TAMs and CD8+ T cells. CD8+ T cells cultured alone were defined as group A (perforin: 17.82 ±1.887%, granzyme B: 29.82±3.882%). TAMs+CD8+ T cells cocultured alone as group B (perforin: 9.622±056%, granzyme B: 14.91±1.711%). TAMs+CD8+ T cells and PD-1 inhibitor cocultured as group C (perforin: 13.61±1.258%, granzyme B: 20.97±2.5%). TAMs, CSF1R inhibitor and CD8+ T cells were cocultured as group D (perforin: 13.37±0.789%, granzyme B: 25.37±2.297%). TAMs, CSF1R inhibitor, CD8+ T cells and PD-1 inhibitor were cocultured as group E (perforin: 17.42±0.806%, granzyme B: 34.47±3.486%). There were significant differences among three groups of A, B and D (P < 0.05), and between two groups of B and C (both P<0.05), and the difference among the three groups of C, D and E was statistically significant (P<0.05)(Figure F).
Conclusion
CSF1 combined with CSF1R on the surface of macrophages, recruits macrophages to tumor areas, and promotes the formation of TAMs. TAMs can express PDL-1, bind to PD-1 on the surface of CD8 + T cells, inhibit the function of CTL, and participate in MM immune escape.
Keyword(s): CD8 T cells, Multiple myeloma
Abstract: EP947
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Tumor-associated macrophages(TAMs)arise from in situ maturation of recruited circulating monocytes and constitue a significant part of myeloma tumor microenvironment. TAMs maybe contribute to the immune escape of multiple myeloma (MM).
Aims
Our study detected the expression of TAMs, CSF1R on macrophages and CSF1 on myeloma cells in bone marrow, and PD-1 on CD8 + T cells and PD-L1 on TAMs.
Methods
March 2020 to January 2021, 53 newly diagnosed MM patients, 33 remission MM (VGPR and above) patients and 28 healthy controls were selected as observation objects. The expression of TAMs, CSF1R on macrophages and CSF1 on myeloma cells,PD-1 on CD8 + T cells and PD-L1 on TAMswere detected by flow cytometry. Bone marrow mononuclear cells from newly diagnosed MM patients were extracted and cultured into TAMs, and then cocultured with CD8 + T cells to detect the expression of perforin and granzyme B.
Results
1. The expression of TAMs in NDMM group was significantly higher than remission group (P<0.001) and healthy control group (P<0.05)(Figure A). 2. The expression of CSF1 on CD138+ cells in the NDMM group was higher than the remission group (P<0.0001) and the healthy control group (P<0.05), the difference was statistically significant (Figure B). 3. The expression of CSF1R on macrophages in NDMM group was higher than the remission group (P<0.0001)and healthy control group,and there was no statistical significance between remission group and healthy control group(Figure C). 4. The expression of PD-1 on CD8+ T cells in the NDMM group was significantly higher than that in the remission group (P<0.05) and the healthy control group, but there was no significant difference between the remission group and the healthy control group (P>0.05).The expression of PDL-1 on TAMs in the NDMM group was higher than that in remission group(P<0.01)and healthy control group (P<0.05) (Figure D). 5. The expression of cytokines in the supernatants of TAMs cultured with mononuclear cells extracted from bone marrow. IL-6 and IL-10 in the NDMM group was significantly higher than that in the healthy control group ( both P<0.05). TNF-α、 in the NDMM group was significantly lower than that in the healthy control group (P<0.05)(Figure E). 6. The expression of functional molecules was detected after coculture of TAMs and CD8+ T cells. CD8+ T cells cultured alone were defined as group A (perforin: 17.82 ±1.887%, granzyme B: 29.82±3.882%). TAMs+CD8+ T cells cocultured alone as group B (perforin: 9.622±056%, granzyme B: 14.91±1.711%). TAMs+CD8+ T cells and PD-1 inhibitor cocultured as group C (perforin: 13.61±1.258%, granzyme B: 20.97±2.5%). TAMs, CSF1R inhibitor and CD8+ T cells were cocultured as group D (perforin: 13.37±0.789%, granzyme B: 25.37±2.297%). TAMs, CSF1R inhibitor, CD8+ T cells and PD-1 inhibitor were cocultured as group E (perforin: 17.42±0.806%, granzyme B: 34.47±3.486%). There were significant differences among three groups of A, B and D (P < 0.05), and between two groups of B and C (both P<0.05), and the difference among the three groups of C, D and E was statistically significant (P<0.05)(Figure F).

Conclusion
CSF1 combined with CSF1R on the surface of macrophages, recruits macrophages to tumor areas, and promotes the formation of TAMs. TAMs can express PDL-1, bind to PD-1 on the surface of CD8 + T cells, inhibit the function of CTL, and participate in MM immune escape.
Keyword(s): CD8 T cells, Multiple myeloma


