
Contributions
Abstract: EP946
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Bone marrow microenvironment plays a significant supporting role in the proliferation, differentiation, migration, survival and drug resistance of myeloma cells.
Aims
To detect the expression of the co-inhibitory receptor TIGIT and the co-stimulatory receptor CD226 on the surface of natural killer cells (NK cells) in multiple myeloma (MM) patients, and changes in the immune phenotypes and killing function of NK cells. Furthermore, to explore the underlying mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) regulating NK cells function through TIGIT/CD226 in patients with MM.
Methods
1. The expressions of TIGIT, CD226, activated molecules NKG2D and CD107a and functional molecules IFN-γ and Perforin on the NK cells in bone marrow or peripheral blood were detedted by FCM. 2. BMSCs and NK cells were co-cultured at a ratio of 1:4 in vitro, which was grouped according to different monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) added. After co-cultured, the changes in the expression of NKG2D, NKp30, NKp44 and CD69 of NK cells and IFN-γ concentration were examined by FCM. 3. NK cells and U266 were co-cultured with different E:T ratio and the apoptosis of U266 was detected to evaluate the killing function of NK cells by FCM. 4. The expressions of CD155 on BMSCs and CD138+CD38+cells in the bone marrow were detected by FCM. The correlations between CD155 expression on BMSCs and the production of IFN-γ and Perforin in bone marrow NK cells, as well as clinical characteristics were analyzed.
Results
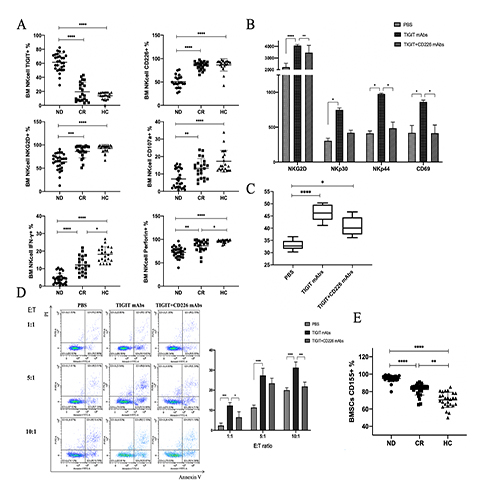
1. In bone marrow, expression of TIGIT was significantly higher in patients with NDMM than those in patients with CR and HC (both P values <0.01). CD226 was significantly lower in NDMM patients than those in patients with CR and HC (both P values <0.01). NK cell surface activated molecules NKG2D and CD107a, and functional molecules IFN-γ and Perforin were significantly decreased in NDMM (Fig. A). In peripheral blood, TIGIT, CD226 and above immune phenotype expression levels were basically consistent with the trend in bone marrow. 2. In co-culture experiments of BMSCs and NK cells, only added anti-TIGIT mAbs, compared to both added anti-TIGIT and CD226 mAbs, the immune phenotypes of NK cells significantly increased (Fig. B). And the concentration of IFN-γ in the co-culture supernatants also increased (Fig. C). 3. After co-cultured with BMSCs, NK cells were co-cultured again with U266 in vitro, the apoptosis level of U266 in TIGIT mAbs group increased than those in TIGIT+ CD226 mAbs group at different E: T ratio (Fig. D). 4. The expression of CD155, the ligand of TIGIT and CD226, increased notably on the surface of BMSCs in MM patients(P<0.01) (Fig. E). 5. The expression of CD155 on BMSCs was negatively correlated with the production of IFN-γ and perforin in bone marrow NK cells with NDMM patients. And it has correlation with clinical characteristics including β2-MG, LDH, ALB, Hb, ISS stage and R-ISS stage in patients with MM.
Conclusion
1. BMSCs may regulate NK cells through TIGIT/CD226. High expression of TIGIT on NK cells may mediate the inhibitory effect of BMSCs in MM patients. Blocking TIGIT could restore NK cells activation and killing function. 2. CD155, a common ligand of TIGIT and CD226, was overexpressed on BMSCs in NDMM patients. And it has correlation with NK cells function and clinical characteristics, indicating that CD155 maybe involved in the regulation of NK cells function by BMSCs.
Keyword(s): Mesenchymal stem cell, Multiple myeloma, NK cell
Abstract: EP946
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Bone marrow microenvironment plays a significant supporting role in the proliferation, differentiation, migration, survival and drug resistance of myeloma cells.
Aims
To detect the expression of the co-inhibitory receptor TIGIT and the co-stimulatory receptor CD226 on the surface of natural killer cells (NK cells) in multiple myeloma (MM) patients, and changes in the immune phenotypes and killing function of NK cells. Furthermore, to explore the underlying mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) regulating NK cells function through TIGIT/CD226 in patients with MM.
Methods
1. The expressions of TIGIT, CD226, activated molecules NKG2D and CD107a and functional molecules IFN-γ and Perforin on the NK cells in bone marrow or peripheral blood were detedted by FCM. 2. BMSCs and NK cells were co-cultured at a ratio of 1:4 in vitro, which was grouped according to different monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) added. After co-cultured, the changes in the expression of NKG2D, NKp30, NKp44 and CD69 of NK cells and IFN-γ concentration were examined by FCM. 3. NK cells and U266 were co-cultured with different E:T ratio and the apoptosis of U266 was detected to evaluate the killing function of NK cells by FCM. 4. The expressions of CD155 on BMSCs and CD138+CD38+cells in the bone marrow were detected by FCM. The correlations between CD155 expression on BMSCs and the production of IFN-γ and Perforin in bone marrow NK cells, as well as clinical characteristics were analyzed.
Results
1. In bone marrow, expression of TIGIT was significantly higher in patients with NDMM than those in patients with CR and HC (both P values <0.01). CD226 was significantly lower in NDMM patients than those in patients with CR and HC (both P values <0.01). NK cell surface activated molecules NKG2D and CD107a, and functional molecules IFN-γ and Perforin were significantly decreased in NDMM (Fig. A). In peripheral blood, TIGIT, CD226 and above immune phenotype expression levels were basically consistent with the trend in bone marrow. 2. In co-culture experiments of BMSCs and NK cells, only added anti-TIGIT mAbs, compared to both added anti-TIGIT and CD226 mAbs, the immune phenotypes of NK cells significantly increased (Fig. B). And the concentration of IFN-γ in the co-culture supernatants also increased (Fig. C). 3. After co-cultured with BMSCs, NK cells were co-cultured again with U266 in vitro, the apoptosis level of U266 in TIGIT mAbs group increased than those in TIGIT+ CD226 mAbs group at different E: T ratio (Fig. D). 4. The expression of CD155, the ligand of TIGIT and CD226, increased notably on the surface of BMSCs in MM patients(P<0.01) (Fig. E). 5. The expression of CD155 on BMSCs was negatively correlated with the production of IFN-γ and perforin in bone marrow NK cells with NDMM patients. And it has correlation with clinical characteristics including β2-MG, LDH, ALB, Hb, ISS stage and R-ISS stage in patients with MM.

Conclusion
1. BMSCs may regulate NK cells through TIGIT/CD226. High expression of TIGIT on NK cells may mediate the inhibitory effect of BMSCs in MM patients. Blocking TIGIT could restore NK cells activation and killing function. 2. CD155, a common ligand of TIGIT and CD226, was overexpressed on BMSCs in NDMM patients. And it has correlation with NK cells function and clinical characteristics, indicating that CD155 maybe involved in the regulation of NK cells function by BMSCs.
Keyword(s): Mesenchymal stem cell, Multiple myeloma, NK cell


