
Contributions
Abstract: EP923
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myelodysplastic syndromes - Clinical
Background
The treatment of patients with refractory and/or relapsed (R/R) high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (HR-MDS) or acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains a daunting clinical challenge. Venetoclax is a selective BCL-2 inhibitor, which combined with hypomethylating agents (HMA), has shown high response rates in unfit and previously untreated AML.
Aims
We performed a retrospective study of patients with R/R HR-MDS and AML receiving combination azacytidine (AZA) plus venetoclax (VEN) in order to determine their efficacy and toxicity in this context.
Methods
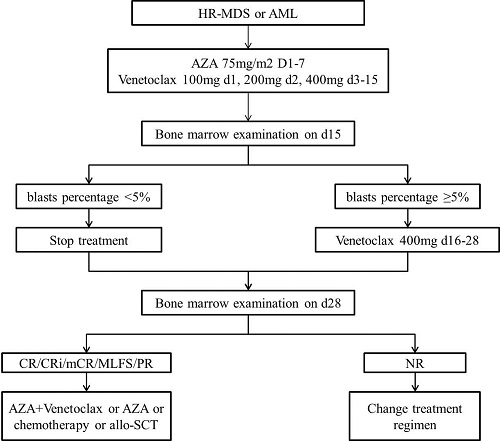
Venetoclax was recommended at a daily dose of 100 mg with a 3-day ramp to target dose of 400 mg for 28 days (VEN-28d) but was stopped on day 15 if bone marrow examination on day 15 showed residual blasts percentage was below 5% (VEN-15d). Azacitidine was administered 75 mg/m2 subcutaneously daily on days 1 to 7 of each 28-day cycle. The treatment decision tree was depicted in Figure 1.
Results
We have included a total of 35 patients with R/R MDS, R/R AML, or denovo AML. Among them 17 patients were R/R MDS, 10 patients were R/R AML, and 8 patients were denovo AML. The overall response rate (ORR) and was 58.8 % in R/R MDS and 50% in R/R AML respectively, the complete remission (CR) rate was 29.4% in R/R MDS and 10% in R/R AML respectively. And the ORR was 71.4% in 14 R/R MDS and 10 R/R AML who stopped VEN on day 15,among them the CR rate was 35.7% in R/R MDS and 14.3% in R/R AML. The median OS was significantly different among the three groups (not reached in R/R MDS and denove AML vs. 5 months with 95% CI of 3.4-6.5 months in the R/R AML, p = 0.002) . The most common treatment-emergent adverse events were peripheral blood cytopenias and infectious complications.
Conclusion
Our study showed that the real-world experience of treating patients with R/R MDS and AML with AZA plus VEN, which have high response rates but with a high frequency of myelosuppression. Of note, the dose reductions of venetoclax did not affect response and survival in our analysis. These data of combination AZA plus VEN in R/R AML and MDS warrant further prospective evaluation in clinical trials.
Keyword(s): Myeloid malignancies, Treatment
Abstract: EP923
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myelodysplastic syndromes - Clinical
Background
The treatment of patients with refractory and/or relapsed (R/R) high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (HR-MDS) or acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains a daunting clinical challenge. Venetoclax is a selective BCL-2 inhibitor, which combined with hypomethylating agents (HMA), has shown high response rates in unfit and previously untreated AML.
Aims
We performed a retrospective study of patients with R/R HR-MDS and AML receiving combination azacytidine (AZA) plus venetoclax (VEN) in order to determine their efficacy and toxicity in this context.
Methods
Venetoclax was recommended at a daily dose of 100 mg with a 3-day ramp to target dose of 400 mg for 28 days (VEN-28d) but was stopped on day 15 if bone marrow examination on day 15 showed residual blasts percentage was below 5% (VEN-15d). Azacitidine was administered 75 mg/m2 subcutaneously daily on days 1 to 7 of each 28-day cycle. The treatment decision tree was depicted in Figure 1.
Results
We have included a total of 35 patients with R/R MDS, R/R AML, or denovo AML. Among them 17 patients were R/R MDS, 10 patients were R/R AML, and 8 patients were denovo AML. The overall response rate (ORR) and was 58.8 % in R/R MDS and 50% in R/R AML respectively, the complete remission (CR) rate was 29.4% in R/R MDS and 10% in R/R AML respectively. And the ORR was 71.4% in 14 R/R MDS and 10 R/R AML who stopped VEN on day 15,among them the CR rate was 35.7% in R/R MDS and 14.3% in R/R AML. The median OS was significantly different among the three groups (not reached in R/R MDS and denove AML vs. 5 months with 95% CI of 3.4-6.5 months in the R/R AML, p = 0.002) . The most common treatment-emergent adverse events were peripheral blood cytopenias and infectious complications.

Conclusion
Our study showed that the real-world experience of treating patients with R/R MDS and AML with AZA plus VEN, which have high response rates but with a high frequency of myelosuppression. Of note, the dose reductions of venetoclax did not affect response and survival in our analysis. These data of combination AZA plus VEN in R/R AML and MDS warrant further prospective evaluation in clinical trials.
Keyword(s): Myeloid malignancies, Treatment


