
Contributions
Abstract: EP901
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myelodysplastic syndromes - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are characterized by dysplastic bone marrow,ineffective hematopoiesis and high-risk transformation to acute myeloid leukemia (AML).It has been clearly addressed that the BM microenvironment plays an important role in malignant hematopoiesis, but the mechanism leading to MDS-associated immune is still unknown.
Aims
To analyzed the immune status of MDS patients, evaluated its impact on prognosis, and tried to study the specific mechanism of how mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) affecting immunity.
Methods
The study included 84 healthy controls and 84 inpatients with primary MDS, 22 patients with AML.We collected flow cytometry(FCM) reports and clinical data, including patient's sex, age, peripheral blood trilineage at initial diagnosis, number of bone marrow blast cells, karyotype analysis, etc. All MDS patients were stratified by IPSS-R for disease risk. 1. Statistical analysis of lymphocyte subset counts and cytokines in peripheral blood of different types of patients and healthy controls. 2. Correlation analysis between hemoglobin, platelets,neutrophil, blast cells, cytogenetics and lymphocyte counts was performed.3.We generated MSCs in BM samples from MDS patients and HCs.The expression of CD155 in MSCs and TIGIT/CD226 in lymphocytes were detected by FCM.
Results
1.Percentage counts of NK cells in the HC group(19.94,95%CI 17.86-22.02,P<0.001)were significantly higher than other groups.The higher-risk group of MDS(11.51,95%CI 9.34-13.68) was obviously lower than the lower-risk group(16.91,95%CI 13.85-19,97)(P=0.006),close to the AML group(9.77,95%CI 6.33-13.20).Meanwhile, the level of IFN-Ƴ in serum which is secreted mainly by NK cells was also the highest in the HC group(5.50,95%CI 3.74-7.26), followed by the MDS group and the lowest in the AML group(2.64,95%CI 1.91-3.37).Moerover,the higher-risk group(3.26,95%CI 2.45-4.07) was significantly lower than the lower-risk group(4.80,95%CI 3.66-5.95).In addition, CD8+ T cells and CD19+ cells had similar results as NK cells, but there was no significant difference with CD3+ cells and CD4+ T cells.2.Significantly higher level of NK cells percentage counts were found in patients with hemoglobin ≥ 100 ×1012/L compared to patients with lower hemoglobin(23.23,95%CI 17.26-29.21 and 15.77,95%CI 13.00-18.55,P=0.010). While the levels of NK cells were higher in patients with blast cells≤5% than in those with higher blast cells.(19.51,95%CI 16.09-22.93 and 14.65,95%CI 11.55-17.74,P=0.027). Patients with better karyotypes also had higher NK levels than those with poorer karyotypes(22.75,95%CI 19.47-22.03 and16.26,95%CI 11.36-21.15,P=0.060).No significant difference was found between NK cell levels with regard to platelet and neutrophil counts.CD8+ T cells behaved similarly to NK cells. 3.The expression of CD155 on the surface of BMSCs was significantly higher in the MDS group than that in the HC group(P=0.001,Figure1).Moreover,MDS patients had higher expression of TIGIT(P=0.012) and lower expression of CD226(P=0.001,Figure2B) on the surface of NK cells in bone marrow than that in HCs.And CD8+ T cells also have similar results as NK cells.We analyzed the correlation between TIGIT of NK cells and CD155 of BMSCs, and found that they were negatively correlated(P=0.0297), while CD226 was positively correlated with CD155(P=0.0706,Figure 2C).
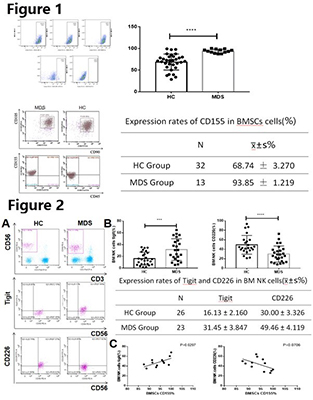
Conclusion
The decreased immune function in MDS patients is associated with prognosis.BMSCs are responsible for inducing an immune-suppressive microenvironment in MDS through CD155/TIGIT/CD226 pathway, the underlying mechanism remains to be further study.
Keyword(s): Bone marrow stroma, Immune deficiency, NK cell
Abstract: EP901
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myelodysplastic syndromes - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are characterized by dysplastic bone marrow,ineffective hematopoiesis and high-risk transformation to acute myeloid leukemia (AML).It has been clearly addressed that the BM microenvironment plays an important role in malignant hematopoiesis, but the mechanism leading to MDS-associated immune is still unknown.
Aims
To analyzed the immune status of MDS patients, evaluated its impact on prognosis, and tried to study the specific mechanism of how mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) affecting immunity.
Methods
The study included 84 healthy controls and 84 inpatients with primary MDS, 22 patients with AML.We collected flow cytometry(FCM) reports and clinical data, including patient's sex, age, peripheral blood trilineage at initial diagnosis, number of bone marrow blast cells, karyotype analysis, etc. All MDS patients were stratified by IPSS-R for disease risk. 1. Statistical analysis of lymphocyte subset counts and cytokines in peripheral blood of different types of patients and healthy controls. 2. Correlation analysis between hemoglobin, platelets,neutrophil, blast cells, cytogenetics and lymphocyte counts was performed.3.We generated MSCs in BM samples from MDS patients and HCs.The expression of CD155 in MSCs and TIGIT/CD226 in lymphocytes were detected by FCM.
Results
1.Percentage counts of NK cells in the HC group(19.94,95%CI 17.86-22.02,P<0.001)were significantly higher than other groups.The higher-risk group of MDS(11.51,95%CI 9.34-13.68) was obviously lower than the lower-risk group(16.91,95%CI 13.85-19,97)(P=0.006),close to the AML group(9.77,95%CI 6.33-13.20).Meanwhile, the level of IFN-Ƴ in serum which is secreted mainly by NK cells was also the highest in the HC group(5.50,95%CI 3.74-7.26), followed by the MDS group and the lowest in the AML group(2.64,95%CI 1.91-3.37).Moerover,the higher-risk group(3.26,95%CI 2.45-4.07) was significantly lower than the lower-risk group(4.80,95%CI 3.66-5.95).In addition, CD8+ T cells and CD19+ cells had similar results as NK cells, but there was no significant difference with CD3+ cells and CD4+ T cells.2.Significantly higher level of NK cells percentage counts were found in patients with hemoglobin ≥ 100 ×1012/L compared to patients with lower hemoglobin(23.23,95%CI 17.26-29.21 and 15.77,95%CI 13.00-18.55,P=0.010). While the levels of NK cells were higher in patients with blast cells≤5% than in those with higher blast cells.(19.51,95%CI 16.09-22.93 and 14.65,95%CI 11.55-17.74,P=0.027). Patients with better karyotypes also had higher NK levels than those with poorer karyotypes(22.75,95%CI 19.47-22.03 and16.26,95%CI 11.36-21.15,P=0.060).No significant difference was found between NK cell levels with regard to platelet and neutrophil counts.CD8+ T cells behaved similarly to NK cells. 3.The expression of CD155 on the surface of BMSCs was significantly higher in the MDS group than that in the HC group(P=0.001,Figure1).Moreover,MDS patients had higher expression of TIGIT(P=0.012) and lower expression of CD226(P=0.001,Figure2B) on the surface of NK cells in bone marrow than that in HCs.And CD8+ T cells also have similar results as NK cells.We analyzed the correlation between TIGIT of NK cells and CD155 of BMSCs, and found that they were negatively correlated(P=0.0297), while CD226 was positively correlated with CD155(P=0.0706,Figure 2C).

Conclusion
The decreased immune function in MDS patients is associated with prognosis.BMSCs are responsible for inducing an immune-suppressive microenvironment in MDS through CD155/TIGIT/CD226 pathway, the underlying mechanism remains to be further study.
Keyword(s): Bone marrow stroma, Immune deficiency, NK cell


