
Contributions
Abstract: EP900
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myelodysplastic syndromes - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Ferroptosis, a form of regulated cell death (RCD) that involves iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation, is remarkably distinguishable from other forms of RCD, including necroptosis, apoptosis, and unregulated necrosis, in terms of its biochemistry, morphology, and genetics. Ferroptosis has been declared to be involved in many diseases, especially kinds of cancers. These studies provide useful evidence for the treatment of cancers. The Proviral Integration site for Moloney murine leukemia virus (PIM) kinases were reported to increased in several cancers, such as AML (acute myeloid leukemia) and MM (multiple myeloma). Nowadays the pim inhibitors are undergoing clinical trials. However, the mechanism of the pim inhibitors on tumor cells is still unclear.
Aims
The study aims to investigate whether the pim inhibitors can induce the ferroptosis in hematological malignant cells and what the mechanism is.
Methods
The cell lines SKM-1, MUTZ-3, THP-1, U266 and LP-1 treated with pim inhibitors (SMI-16a and Pim-447). CCK-8 assay was used to examine the cell proliferation following treated with drugs. The MDA (malondialdehyde) and GPXs were detected with biochemical method. FCM(flow cytometry method)was used to detected the ROS(reactive oxygen species). RT-qPCR was used to detected the relative expression level of mRNA involved. The related proteins were detected by western blot.
Results
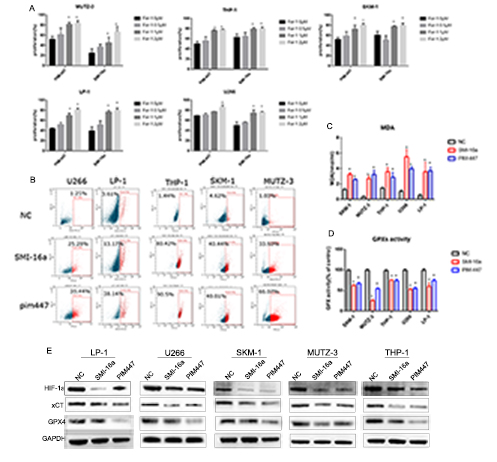
The two pim inhibitors could decrease the proliferation of these cell lines significantly (Fig.1). And the inhibition effect treated for 48h was more obvious than 24h.The growth-inhibitory effect of pim inhibitors could be partially reversed by ferrostatin-1(ferroptosis inhibitors) (Fig.2). Then we analyzed the intracellular ROS level of the cells treated with SMI-16a and Pim-447 (Fig.2). SMI -16a and Pim-447 could increase the ROS level. The MDA level increased and the GPXs activity decreased following the treatment of SMI-16a and Pim-447(Fig.2). These results revealed that SMI-16a and Pim-447 induce ferroptosis in these cell lines. In order to investigate what the mechanism is, we preformed the western blot to examine the related proteins. The results showed that HIF-1αand xCT declined, which induced the GPX4 decreased(Fig.3).
Conclusion
Our study provides significant evidence to confirm the occurrence of ferroptosis in hematological malignant cells treated with pim inhibitors, and demonstrates that inhibition of ferroptosis was through HIF-1α/GPX4 pathway. These findings reveal a new form of cell death in the treatment of pim inhibitors.
Keyword(s): Hematological malignancy
Abstract: EP900
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myelodysplastic syndromes - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Ferroptosis, a form of regulated cell death (RCD) that involves iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation, is remarkably distinguishable from other forms of RCD, including necroptosis, apoptosis, and unregulated necrosis, in terms of its biochemistry, morphology, and genetics. Ferroptosis has been declared to be involved in many diseases, especially kinds of cancers. These studies provide useful evidence for the treatment of cancers. The Proviral Integration site for Moloney murine leukemia virus (PIM) kinases were reported to increased in several cancers, such as AML (acute myeloid leukemia) and MM (multiple myeloma). Nowadays the pim inhibitors are undergoing clinical trials. However, the mechanism of the pim inhibitors on tumor cells is still unclear.
Aims
The study aims to investigate whether the pim inhibitors can induce the ferroptosis in hematological malignant cells and what the mechanism is.
Methods
The cell lines SKM-1, MUTZ-3, THP-1, U266 and LP-1 treated with pim inhibitors (SMI-16a and Pim-447). CCK-8 assay was used to examine the cell proliferation following treated with drugs. The MDA (malondialdehyde) and GPXs were detected with biochemical method. FCM(flow cytometry method)was used to detected the ROS(reactive oxygen species). RT-qPCR was used to detected the relative expression level of mRNA involved. The related proteins were detected by western blot.
Results
The two pim inhibitors could decrease the proliferation of these cell lines significantly (Fig.1). And the inhibition effect treated for 48h was more obvious than 24h.The growth-inhibitory effect of pim inhibitors could be partially reversed by ferrostatin-1(ferroptosis inhibitors) (Fig.2). Then we analyzed the intracellular ROS level of the cells treated with SMI-16a and Pim-447 (Fig.2). SMI -16a and Pim-447 could increase the ROS level. The MDA level increased and the GPXs activity decreased following the treatment of SMI-16a and Pim-447(Fig.2). These results revealed that SMI-16a and Pim-447 induce ferroptosis in these cell lines. In order to investigate what the mechanism is, we preformed the western blot to examine the related proteins. The results showed that HIF-1αand xCT declined, which induced the GPX4 decreased(Fig.3).

Conclusion
Our study provides significant evidence to confirm the occurrence of ferroptosis in hematological malignant cells treated with pim inhibitors, and demonstrates that inhibition of ferroptosis was through HIF-1α/GPX4 pathway. These findings reveal a new form of cell death in the treatment of pim inhibitors.
Keyword(s): Hematological malignancy


