
Contributions
Abstract: EP895
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myelodysplastic syndromes - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are characterized by malignant clonal hematopoietic stem cells with high-risk of progression to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Pim-2 is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is elevated in various types of cancer and plays essential roles in the regulation of signal transduction cascades, which promote cell survival and cell proliferation. Our previous study revealed that pim-2 was highly expressed in CD34+ cells derived from the bone marrow of patients with MDS/AML. The expression of Pim-2 induces elevated expression of HIF1-α by decreasing the expression of IDH1, resulting in acceleration of CD34+ cell proliferation.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) represent the majority of cellular transcripts and play pivotal roles in hematopoiesis. However, the functions of lncRNA on hematopoietic stem cells malignant clone remains largely unknown.
Aims
Here we investigate the profile of lncRNA derived from the bone marrow CD34+cells in MDS patients and AML secondary to MDS (sAML) patients. And we focused on the lncRNA which could regulate pim2
Methods
The profile of lncRNAs in bone marrow CD34+ cells from MDS patients and sAML patients was detected by high throughput RNA-seq technology. The biological function and signal pathway of the target genes of differentially lncRNAs were analyzed by GO and KEGG cluster analysis. RT-PCR were used to detected the lncRNA and pim2. The SKM-1cell line was used in the study. The lentiviral vector(sh-RNA) were transfected into SKM-1 to interfere the lncRNA. CCK8 was performed to measure the proliferation rate of SKM-1 transfected with the lentiviral vector. 7-AAD/PI was used to analyze the apoptosis of SKM-1.
Results
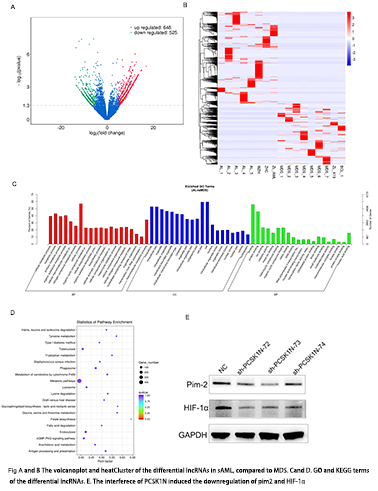
In sAML, we found 1173 lncRNAs (648 upregulated/525 downregulated) and 326 mRNAs (125 upregulated/201 downregulated) significantly deregulated compared to those in MDS patients (|logFC| > 1, p value < 0.05). Overall, the KEGG enriched processes were mainly related to four mechanisms: metabolic pathways, phagosome, metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - lacto and neolacto series, fatty acid degradation, cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. GO term analysis showed the mainly related lncRNAs function on cellular metabolic process, organic cyclic compound metabolic process, nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process and etc. Of these, lncRNA PCSK1N-202 may targeted-regulate the pim2 mRNA. RT-PCR showed that PCSK1N-202 was upregulated in AML and MDA patients. And PCSK1N-202 was positive related with pim2. The SKM-1 transfected with LV-sh- PCSK1N-202 induced the decline of pim2 followed with decreased cell proliferation rate, and increased cell apoptosis.
Conclusion
We reported novel information on specific lncRNAs contributing to AML transformation of MDS, and proposed cellular processes associated with these lncRNAs. Of the lncRNAs, the upregulation of PCSK1N-202 transcript might promotes CD34+cell proliferation via pim2/HIF-1α in myelodysplastic syndromes.
Keyword(s): CD34+ cells, MDS
Abstract: EP895
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myelodysplastic syndromes - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are characterized by malignant clonal hematopoietic stem cells with high-risk of progression to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Pim-2 is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is elevated in various types of cancer and plays essential roles in the regulation of signal transduction cascades, which promote cell survival and cell proliferation. Our previous study revealed that pim-2 was highly expressed in CD34+ cells derived from the bone marrow of patients with MDS/AML. The expression of Pim-2 induces elevated expression of HIF1-α by decreasing the expression of IDH1, resulting in acceleration of CD34+ cell proliferation.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) represent the majority of cellular transcripts and play pivotal roles in hematopoiesis. However, the functions of lncRNA on hematopoietic stem cells malignant clone remains largely unknown.
Aims
Here we investigate the profile of lncRNA derived from the bone marrow CD34+cells in MDS patients and AML secondary to MDS (sAML) patients. And we focused on the lncRNA which could regulate pim2
Methods
The profile of lncRNAs in bone marrow CD34+ cells from MDS patients and sAML patients was detected by high throughput RNA-seq technology. The biological function and signal pathway of the target genes of differentially lncRNAs were analyzed by GO and KEGG cluster analysis. RT-PCR were used to detected the lncRNA and pim2. The SKM-1cell line was used in the study. The lentiviral vector(sh-RNA) were transfected into SKM-1 to interfere the lncRNA. CCK8 was performed to measure the proliferation rate of SKM-1 transfected with the lentiviral vector. 7-AAD/PI was used to analyze the apoptosis of SKM-1.
Results
In sAML, we found 1173 lncRNAs (648 upregulated/525 downregulated) and 326 mRNAs (125 upregulated/201 downregulated) significantly deregulated compared to those in MDS patients (|logFC| > 1, p value < 0.05). Overall, the KEGG enriched processes were mainly related to four mechanisms: metabolic pathways, phagosome, metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - lacto and neolacto series, fatty acid degradation, cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. GO term analysis showed the mainly related lncRNAs function on cellular metabolic process, organic cyclic compound metabolic process, nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process and etc. Of these, lncRNA PCSK1N-202 may targeted-regulate the pim2 mRNA. RT-PCR showed that PCSK1N-202 was upregulated in AML and MDA patients. And PCSK1N-202 was positive related with pim2. The SKM-1 transfected with LV-sh- PCSK1N-202 induced the decline of pim2 followed with decreased cell proliferation rate, and increased cell apoptosis.

Conclusion
We reported novel information on specific lncRNAs contributing to AML transformation of MDS, and proposed cellular processes associated with these lncRNAs. Of the lncRNAs, the upregulation of PCSK1N-202 transcript might promotes CD34+cell proliferation via pim2/HIF-1α in myelodysplastic syndromes.
Keyword(s): CD34+ cells, MDS


