
Contributions
Abstract: EP888
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myelodysplastic syndromes - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Spliceosome mutations are common in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), but their role in cancer biogenesis and progression is not fully understood. U2AF1 mutation is associated with a poor prognosis. This splicing factor is responsible for recognition of the 3’ splice site, a process which is altered by the two commonly found hotspot mutations at residues S34 and Q157. Circular RNAs are produced when backsplicing events occur, in competition with linear mRNA splicing. CircRNAs have been implicated in numerous cancers and immune processes.
Aims
To explore the impact of U2AF1 mutation on circRNA expression in MDS.
Methods
We analyzed RNAseq data from a transgenic mouse model with doxycycline-inducible U2AF1S34F/U2AF1WT expression.1 In addition, we generated total RNAseq data from FACS sorted CD34+ bone marrow cells from patients with MDS with U2AF1 mutation (3 S34 mutations, 3 Q157 mutations), along with 5 matched MDS controls without spliceosome mutations and 4 healthy controls. CircRNAs were identified using the pipelines CIRI2 and find_circ, with detection by both pipelines required. CircRNA counts were normalized using DESeq2 including linear mRNA expression. DESeq2 was also used to generate adjusted p values.
Results
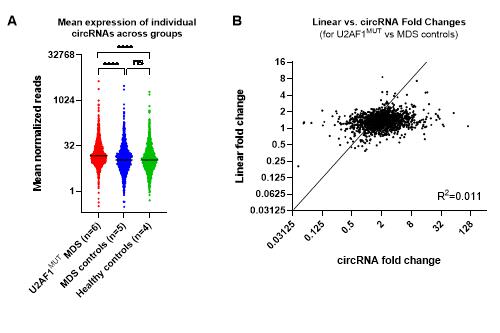
CircRNA expression was predominantly upregulated with the induction of U2AF1S34F mutation in mice (p<0.0001, Wilcoxon test). The correlation between fold changes in circular and linear RNA expression (from corresponding splice sites) was low (R2 =0.005) indicating that altered circRNA expression was independent to changes in linear expression. In MDS patients, circRNA expression was significantly higher in those with U2AF1 mutations than matched controls (Figure A, p<0.0001, Wilcoxon test), whilst there was no significant difference between the MDS controls and the healthy controls. Again, changes in circRNA expression were independent to changes in linear expression (Figure B, R2=0.011). Seven specific circRNAs were significantly upregulated (padj<0.05 and fold change >2) in patients with U2AF1 mutation vs MDS controls. Literature searching revealed that two of these circRNAs (circZNF609 and circCSNK1G3) have previously been linked to cancer (hepatic cell carcinoma and renal cell carcinoma, respectively).2,3 Global circRNA expression levels did not differ between patients with S34 and those with Q157 mutations (p=0.374, Wilcoxon test), but the patterns of expression were found to be distinct, indicated by separation of the two mutations on unsupervised cluster analysis.
Conclusion
We found both in a murine model and in MDS patients that U2AF1 mutations lead to an increase in circRNA expression. Furthermore, distinct circRNA expression profiles were seen for mutations at the S34 and Q157 loci. Further investigation of the biological mechanism by which U2AF1 mutation supports backsplicing, and profiling of a larger cohort of MDS patients, is merited.
References
1. Shirai, C. L. et al. Mutant U2AF1-expressing cells are sensitive to pharmacological modulation of the spliceosome. Nat. Commun. 8, (2017).
2. He, Y. et al. CircZNF609 enhances hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, metastasis, and stemness by activating the Hedgehog pathway through the regulation of miR-15a-5p/15b-5p and GLI2 expressions. Cell Death Dis. 11, (2020).
3. Li, W. et al. CircCSNK1G3 up‐regulates miR‐181b to promote growth and metastasis via TIMP3‐mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transitions in renal cell carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. (2021).
Keyword(s): MDS
Abstract: EP888
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myelodysplastic syndromes - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Spliceosome mutations are common in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), but their role in cancer biogenesis and progression is not fully understood. U2AF1 mutation is associated with a poor prognosis. This splicing factor is responsible for recognition of the 3’ splice site, a process which is altered by the two commonly found hotspot mutations at residues S34 and Q157. Circular RNAs are produced when backsplicing events occur, in competition with linear mRNA splicing. CircRNAs have been implicated in numerous cancers and immune processes.
Aims
To explore the impact of U2AF1 mutation on circRNA expression in MDS.
Methods
We analyzed RNAseq data from a transgenic mouse model with doxycycline-inducible U2AF1S34F/U2AF1WT expression.1 In addition, we generated total RNAseq data from FACS sorted CD34+ bone marrow cells from patients with MDS with U2AF1 mutation (3 S34 mutations, 3 Q157 mutations), along with 5 matched MDS controls without spliceosome mutations and 4 healthy controls. CircRNAs were identified using the pipelines CIRI2 and find_circ, with detection by both pipelines required. CircRNA counts were normalized using DESeq2 including linear mRNA expression. DESeq2 was also used to generate adjusted p values.
Results
CircRNA expression was predominantly upregulated with the induction of U2AF1S34F mutation in mice (p<0.0001, Wilcoxon test). The correlation between fold changes in circular and linear RNA expression (from corresponding splice sites) was low (R2 =0.005) indicating that altered circRNA expression was independent to changes in linear expression. In MDS patients, circRNA expression was significantly higher in those with U2AF1 mutations than matched controls (Figure A, p<0.0001, Wilcoxon test), whilst there was no significant difference between the MDS controls and the healthy controls. Again, changes in circRNA expression were independent to changes in linear expression (Figure B, R2=0.011). Seven specific circRNAs were significantly upregulated (padj<0.05 and fold change >2) in patients with U2AF1 mutation vs MDS controls. Literature searching revealed that two of these circRNAs (circZNF609 and circCSNK1G3) have previously been linked to cancer (hepatic cell carcinoma and renal cell carcinoma, respectively).2,3 Global circRNA expression levels did not differ between patients with S34 and those with Q157 mutations (p=0.374, Wilcoxon test), but the patterns of expression were found to be distinct, indicated by separation of the two mutations on unsupervised cluster analysis.

Conclusion
We found both in a murine model and in MDS patients that U2AF1 mutations lead to an increase in circRNA expression. Furthermore, distinct circRNA expression profiles were seen for mutations at the S34 and Q157 loci. Further investigation of the biological mechanism by which U2AF1 mutation supports backsplicing, and profiling of a larger cohort of MDS patients, is merited.
References
1. Shirai, C. L. et al. Mutant U2AF1-expressing cells are sensitive to pharmacological modulation of the spliceosome. Nat. Commun. 8, (2017).
2. He, Y. et al. CircZNF609 enhances hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, metastasis, and stemness by activating the Hedgehog pathway through the regulation of miR-15a-5p/15b-5p and GLI2 expressions. Cell Death Dis. 11, (2020).
3. Li, W. et al. CircCSNK1G3 up‐regulates miR‐181b to promote growth and metastasis via TIMP3‐mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transitions in renal cell carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. (2021).
Keyword(s): MDS


