
Contributions
Abstract: EP870
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Lymphoma Biology & Translational Research
Background
EZH2 encodes the catalytic subunit of Polycomb repressor complex (PCR2) and mediates methylation of Lys27 residue of histone H3 (H3K27). Missense mutations in EZH2 lead to decreased transcriptional function of genes involved in cell cycle regulation and plasma cell differentiation, which contributes to oncogenic transformation. EZH2 have been detected to be mutated in near 20% of follicular lymphomas (FL) and this gene is included in the risk model m7-FL International Prognostic Index (m7-FLIPI). Furthermore, EZH2 inhibitors appear as a new treatment option in FL.
Aims
We aimed to analyse retrospectively the frequency of mutations in EZH2 at diagnosis in tissue and circulating cell free DNA (cfDNA) in patients with FL and assess the patient's response to therapy, depending on the EZH2 mutation status.
Methods
We included 179 consecutive patients diagnosed with FL from 2002 to 2019. Thirty-seven patients were excluded due to insufficient DNA quantity or quality. Of the 142 analysed patients, 49 had cfDNA sample at diagnosis. DNA was extracted from solid biopsies using Maxwell(R) 16 FFPE Plus LEV DNA Purification Kit (Promega). We obtained cfDNA from plasma samples, using QIAamp® Circulating Nucleic Acid (Qiagen). RT-qPCR reactions were performed in ctDNA using PrimeTime Mini LNA probe for EZH2 Y646. Sanger sequencing were used in tumor DNA for detection of mutations in exon 16 (Y646) and 18 (A682 and A692). Clinical characteristics, therapy and outcome were collected. Data analysis including descriptive statistics and Fisher’s exact test was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 26 (IBM, USA).
Results
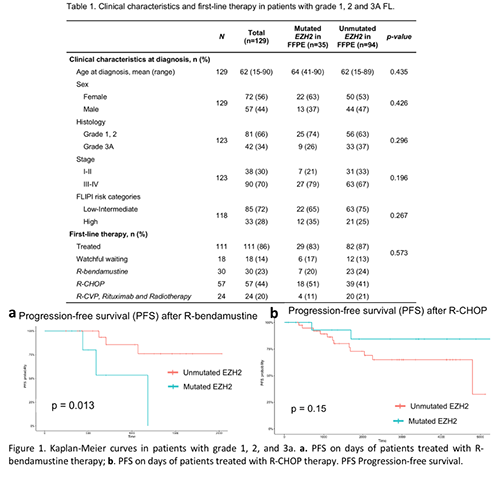
Of the 142 patients analysed in tissue, 41 (29%) presented mutations in EZH2. These mutations were found in 46% of grade 3B FL and 27% of grades 1, 2 and 3A FL (Table 1). Y646 mutations in cfDNA were detected in 5/49 (10%) with EZH2 mutated in tumor and stage III-IV FL. Clinical and biological characteristics according to EZH2 mutation status in tumor were compared in patients with lower-grade FL (Table 1) and high grade 3B (data not shown). No statistical differences were found in lower grade-FL. Instead, patients with grade 3B and mutated EZH2 had statistically higher FLIPI risk (80% vs 0%; p=0.048). Overall survival (OS) of total cohort and according to therapy received and EZH2 mutation status were compared and there were no statistically significant differences. In terms of progression free survival (PFS), our results shown that mutated EZH2 patients treated with R-bendamustine were significantly associated with inferior PFS (p=0.013) (Figure 1a), unlike R-CHOP treated patients (p=0.15) (Figure 1b).
Conclusion
The frequency of EZH2 mutations in our total cohort is similar to previously reported. Mutations were more frequent in high grade FL patients. Low grade FL patients mutated at diagnosis, receiving R-bendamustine were associated with inferior PFS. The mutational status of these patients at diagnosis could be useful to guide treatment. In patients with stage III-IV, liquid biopsy may be used at diagnosis to guide on the selection of therapy, as EZH2 mutations are detectable in advanced stage FL.
Keyword(s): EZH2, Follicular lymphoma, Lymphoma therapy, Plasma
Abstract: EP870
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Lymphoma Biology & Translational Research
Background
EZH2 encodes the catalytic subunit of Polycomb repressor complex (PCR2) and mediates methylation of Lys27 residue of histone H3 (H3K27). Missense mutations in EZH2 lead to decreased transcriptional function of genes involved in cell cycle regulation and plasma cell differentiation, which contributes to oncogenic transformation. EZH2 have been detected to be mutated in near 20% of follicular lymphomas (FL) and this gene is included in the risk model m7-FL International Prognostic Index (m7-FLIPI). Furthermore, EZH2 inhibitors appear as a new treatment option in FL.
Aims
We aimed to analyse retrospectively the frequency of mutations in EZH2 at diagnosis in tissue and circulating cell free DNA (cfDNA) in patients with FL and assess the patient's response to therapy, depending on the EZH2 mutation status.
Methods
We included 179 consecutive patients diagnosed with FL from 2002 to 2019. Thirty-seven patients were excluded due to insufficient DNA quantity or quality. Of the 142 analysed patients, 49 had cfDNA sample at diagnosis. DNA was extracted from solid biopsies using Maxwell(R) 16 FFPE Plus LEV DNA Purification Kit (Promega). We obtained cfDNA from plasma samples, using QIAamp® Circulating Nucleic Acid (Qiagen). RT-qPCR reactions were performed in ctDNA using PrimeTime Mini LNA probe for EZH2 Y646. Sanger sequencing were used in tumor DNA for detection of mutations in exon 16 (Y646) and 18 (A682 and A692). Clinical characteristics, therapy and outcome were collected. Data analysis including descriptive statistics and Fisher’s exact test was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 26 (IBM, USA).
Results
Of the 142 patients analysed in tissue, 41 (29%) presented mutations in EZH2. These mutations were found in 46% of grade 3B FL and 27% of grades 1, 2 and 3A FL (Table 1). Y646 mutations in cfDNA were detected in 5/49 (10%) with EZH2 mutated in tumor and stage III-IV FL. Clinical and biological characteristics according to EZH2 mutation status in tumor were compared in patients with lower-grade FL (Table 1) and high grade 3B (data not shown). No statistical differences were found in lower grade-FL. Instead, patients with grade 3B and mutated EZH2 had statistically higher FLIPI risk (80% vs 0%; p=0.048). Overall survival (OS) of total cohort and according to therapy received and EZH2 mutation status were compared and there were no statistically significant differences. In terms of progression free survival (PFS), our results shown that mutated EZH2 patients treated with R-bendamustine were significantly associated with inferior PFS (p=0.013) (Figure 1a), unlike R-CHOP treated patients (p=0.15) (Figure 1b).

Conclusion
The frequency of EZH2 mutations in our total cohort is similar to previously reported. Mutations were more frequent in high grade FL patients. Low grade FL patients mutated at diagnosis, receiving R-bendamustine were associated with inferior PFS. The mutational status of these patients at diagnosis could be useful to guide treatment. In patients with stage III-IV, liquid biopsy may be used at diagnosis to guide on the selection of therapy, as EZH2 mutations are detectable in advanced stage FL.
Keyword(s): EZH2, Follicular lymphoma, Lymphoma therapy, Plasma


