
Contributions
Abstract: EP863
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Lymphoma Biology & Translational Research
Background
The outcome for patients with Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL) has markedly improved after introduction of cytarabine-containing chemoimmunotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT). Despite the improved survival, a continuous relapse pattern, even beyond ten years, is observed and consequently a strong need for prognostic biomarkers to support clinical decision making, persists.
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are endogenous non-coding RNA molecules with tissue and disease specific expression patterns, that serve gene-regulatory functions in cells, and might be implicated in carcinogenesis. Because circRNAs are highly stable with much longer half-lives than mRNAs they are promising for use as biomarkers in cancer. We have previously shown that circRNAs can be accurately quantified in samples from patients with B cell malignancies using the nanostring nCounter technology (Dahl et al., Lab. Invest. 2018). Thus, a potential for a seamless implementation of a circRNA based biomarker into clinical practice, exists.
Aims
We aimed to perform a genome-wide profiling of circRNA expression patterns in MCL and to examine the prognostic potential of selected circRNAs in MCL using diagnostic samples from patients enrolled in the MCL2 and MCL3 clinical trials, amounting to a total of 163 younger patients, all treated with chemoimmunotherapy and ASCT.
Methods
We performed RNA-sequencing and bioinformatic identification of circRNAs in an exploratory cohort of 14 newly diagnosed patients with MCL and six healthy controls. 40 circRNAs were selected for quantification with nanostring using RNA samples from diagnostic tumor tissues of patients from the MCL2/MCL3 trials. We then assessed the prognostic potential of these circRNAs with the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) selecting the most predictive circRNAs for time to progression (TTP) in MCL2 (n=74), which served as the training cohort. Nine circRNAs were identified, the expression levels and regression coefficients of which were used to calculate a risk score (circSCORE) for each patient, stratifying them into two groups, separated by a cut-off value. CircSCORE was also calculated for each patient in the independent validation cohort MCL3 (n=89), thereby stratifying these patients into a circSCORE high risk and a circSCORE low risk group, as well.
Results
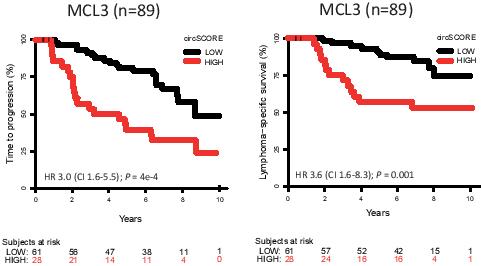
We detected 2 962 unique circRNAs in MCL and found that expression levels were, in general, inversely correlated with the proliferation marker Ki67. In MCL2, circSCORE separated patients into a high risk group (n=29, 39%) and a low risk group (n=45, 61%) with remarkable difference in TTP. Interestingly, we confirmed the predictive impact of circSCORE for both TTP (HR 3.0;P < 0.001;Figure) and lymphoma-specific survival (LSS) (HR 3.6;P < 0.01;Figure) in the similarly treated, independent cohort MCL3. As patients in the circSCORE high risk group more frequently displayed other high risk features compared to patients in the circSCORE low risk group, we assessed whether circSCORE was an independent prognostic factor in MCL3. Even when adjusting for Ki67, blastoid morphology, MIPI and presence of TP53 mutations, circSCORE maintained prognostic impact for both TTP (HR 3.2; P = 0.01), and LSS (HR 4.6; P = 0.02), and only MIPI high risk and presence of TP53 mutations also had prognostic effect in these models.
Conclusion
With this study, we are the first to perform a genome-wide profiling of circRNA expression in MCL, and we show that circSCORE is a novel prognostic biomarker highly predictive of outcome in younger patients treated with chemoimmunotherapy and ASCT.
Keyword(s): Mantle cell lymphoma, Prognostic factor
Abstract: EP863
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Lymphoma Biology & Translational Research
Background
The outcome for patients with Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL) has markedly improved after introduction of cytarabine-containing chemoimmunotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT). Despite the improved survival, a continuous relapse pattern, even beyond ten years, is observed and consequently a strong need for prognostic biomarkers to support clinical decision making, persists.
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are endogenous non-coding RNA molecules with tissue and disease specific expression patterns, that serve gene-regulatory functions in cells, and might be implicated in carcinogenesis. Because circRNAs are highly stable with much longer half-lives than mRNAs they are promising for use as biomarkers in cancer. We have previously shown that circRNAs can be accurately quantified in samples from patients with B cell malignancies using the nanostring nCounter technology (Dahl et al., Lab. Invest. 2018). Thus, a potential for a seamless implementation of a circRNA based biomarker into clinical practice, exists.
Aims
We aimed to perform a genome-wide profiling of circRNA expression patterns in MCL and to examine the prognostic potential of selected circRNAs in MCL using diagnostic samples from patients enrolled in the MCL2 and MCL3 clinical trials, amounting to a total of 163 younger patients, all treated with chemoimmunotherapy and ASCT.
Methods
We performed RNA-sequencing and bioinformatic identification of circRNAs in an exploratory cohort of 14 newly diagnosed patients with MCL and six healthy controls. 40 circRNAs were selected for quantification with nanostring using RNA samples from diagnostic tumor tissues of patients from the MCL2/MCL3 trials. We then assessed the prognostic potential of these circRNAs with the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) selecting the most predictive circRNAs for time to progression (TTP) in MCL2 (n=74), which served as the training cohort. Nine circRNAs were identified, the expression levels and regression coefficients of which were used to calculate a risk score (circSCORE) for each patient, stratifying them into two groups, separated by a cut-off value. CircSCORE was also calculated for each patient in the independent validation cohort MCL3 (n=89), thereby stratifying these patients into a circSCORE high risk and a circSCORE low risk group, as well.
Results
We detected 2 962 unique circRNAs in MCL and found that expression levels were, in general, inversely correlated with the proliferation marker Ki67. In MCL2, circSCORE separated patients into a high risk group (n=29, 39%) and a low risk group (n=45, 61%) with remarkable difference in TTP. Interestingly, we confirmed the predictive impact of circSCORE for both TTP (HR 3.0;P < 0.001;Figure) and lymphoma-specific survival (LSS) (HR 3.6;P < 0.01;Figure) in the similarly treated, independent cohort MCL3. As patients in the circSCORE high risk group more frequently displayed other high risk features compared to patients in the circSCORE low risk group, we assessed whether circSCORE was an independent prognostic factor in MCL3. Even when adjusting for Ki67, blastoid morphology, MIPI and presence of TP53 mutations, circSCORE maintained prognostic impact for both TTP (HR 3.2; P = 0.01), and LSS (HR 4.6; P = 0.02), and only MIPI high risk and presence of TP53 mutations also had prognostic effect in these models.

Conclusion
With this study, we are the first to perform a genome-wide profiling of circRNA expression in MCL, and we show that circSCORE is a novel prognostic biomarker highly predictive of outcome in younger patients treated with chemoimmunotherapy and ASCT.
Keyword(s): Mantle cell lymphoma, Prognostic factor


