
Contributions
Abstract: EP801
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Indolent and mantle-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
Information on the outcomes and treatments of early-stage (I/II) primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma (PCMZL) is limited.
Aims
This study aims to identify the prognostic factors in early-stage PCMZL and compare long-term population-based survival outcomes of conventional approaches.
Methods
We extracted data on stage I/II PCMZL patients from the Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) database and used the Kaplan-Meier plot, log-rank test, Cox regression, propensity score matching (PSM) analyses to explore the association of characteristics and therapeutic methods with survival.
Results
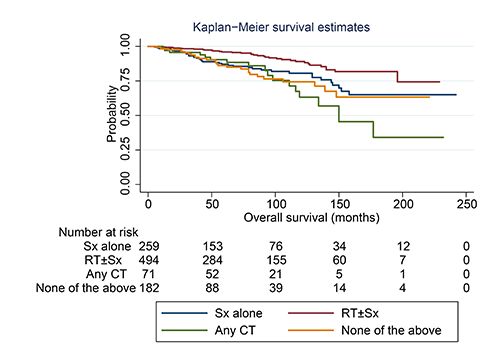
We identified 1,006 early-stage PCMZL cases between 1993 and 2016 in the SEER registry. Multivariate analysis indicated that age over 60 years at diagnosis, specific primary sites (i.e., face, scalp, neck, lower limb, and hip), diagnosis before 2005, and coexisting malignancy were unfavorable predictors for overall survival (OS), while radiotherapy (RT) with or without surgery (Sx) improved OS independently. Besides, we also noted that age over 60 years, diagnosis before 2005, and chemotherapy (CT) were adverse predictors for disease-specific survival (DSS). According to Cox regression and PSM analyses, RT improved the OS and DSS rates while CT reduced the OS and DSS rates. No data demonstrated a survival benefit with Sx in this study.
Conclusion
For early-stage PCMZL patients, RT can probably be an essential component for the initial therapy, and a combination with new treatment options, such as rituximab, could be considered in future studies. Sx has no survival benefit throughout this study but it is an available diagnostic workup. Systemic CT had inferior efficacy and is not recommended as an initial regimen for such an indolent tumor in an early stage.
Keyword(s): Cutaneous lymphoma, Marginal zone, Survival prediction, Treatment
Abstract: EP801
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Indolent and mantle-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
Information on the outcomes and treatments of early-stage (I/II) primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma (PCMZL) is limited.
Aims
This study aims to identify the prognostic factors in early-stage PCMZL and compare long-term population-based survival outcomes of conventional approaches.
Methods
We extracted data on stage I/II PCMZL patients from the Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) database and used the Kaplan-Meier plot, log-rank test, Cox regression, propensity score matching (PSM) analyses to explore the association of characteristics and therapeutic methods with survival.
Results
We identified 1,006 early-stage PCMZL cases between 1993 and 2016 in the SEER registry. Multivariate analysis indicated that age over 60 years at diagnosis, specific primary sites (i.e., face, scalp, neck, lower limb, and hip), diagnosis before 2005, and coexisting malignancy were unfavorable predictors for overall survival (OS), while radiotherapy (RT) with or without surgery (Sx) improved OS independently. Besides, we also noted that age over 60 years, diagnosis before 2005, and chemotherapy (CT) were adverse predictors for disease-specific survival (DSS). According to Cox regression and PSM analyses, RT improved the OS and DSS rates while CT reduced the OS and DSS rates. No data demonstrated a survival benefit with Sx in this study.

Conclusion
For early-stage PCMZL patients, RT can probably be an essential component for the initial therapy, and a combination with new treatment options, such as rituximab, could be considered in future studies. Sx has no survival benefit throughout this study but it is an available diagnostic workup. Systemic CT had inferior efficacy and is not recommended as an initial regimen for such an indolent tumor in an early stage.
Keyword(s): Cutaneous lymphoma, Marginal zone, Survival prediction, Treatment


