
Contributions
Abstract: EP795
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Indolent and mantle-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
Both rituximab plus bendamustine (BR), and rituximab, bendamustine, and cytarabine (R-BAC) are considered suitable induction therapies in elderly patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to most recent ESMO and NCCN clinical practice guidelines. However, a direct comparison between the two regimens, either prospective or retrospective, has never been performed.
Aims
To compare the outcome and the safety features of patients with newly diagnosed MCL treated with BR or R-BAC between 2009 and 2020 in 7 Departments from north-east of Italy.
Methods
This is a multicenter retrospective observational study. The two regimens (BR and R-BAC) represented routinary induction regimens in the selected centers for patients with MCL not candidate to autologous transplant. Primary endpoint was 2-years progression-free survival (PFS). All patients treated with at least one cycle of either BR or R-BAC were included, provided they had a minimum follow-up of 12 months since start of treatment. Response was based on Lugano criteria. Due to the retrospective nature of the study, treatment assignement to one therapy instead of the other was based on local doctor decision. Inclusion bias were estimated by a propensity score stratified by gender, age, MCL morphology, and MIPI score.
Results
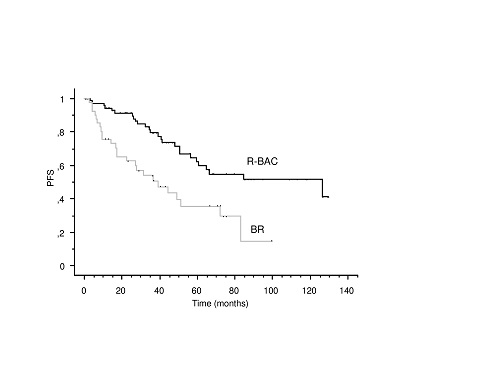
137 patients with MCL with a median age of 72 years (range 53-90) were retrospectively analyzed. According to our propensity score calculation, the probability of receiving R-BAC was higher in younger patients (P<0.0001), but no other significant difference in the distribution of above mentioned prognostic variables was observed between the two groups. Therefore, we limited our survival analysis to patients with 80 years or less, which allowed us a fair comparison between the two groups (P=NS). This cohort included 115 patients (42 BR, 73 R-BAC) that represented the subjects for the present analysis. Of them, 76 (66%) were males, MIPI was elevated in 61%, 15% had blastoid or pleomorphic morphology, and median follow-up was 48 months (range 12-133). Patients treated with R-BAC achieved CR in 93% of cases, as compared with 55% for BR (P<0.0001). The 2-years PFS was 91%±3% and 63%±7% for R-BAC and BR, respectively (P=0.0007, Figure 1). Median overall survival (OS) was 125 months for R-BAC and 78 months for BR (P=0.07). MIPI score was the only predictive significant variable both in terms of PFS and OS. In terms of toxicity, R-BAC was associated with significantly more pronounced grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia than BR (32% versus 15%), although R-BAC doses were frequently reduced as compared to the original scheme.
Conclusion
The BE-ve-BAC study indicates that R-BAC, even when administered in the 2-days schedule or with attenuated dose, is associated with significantly prolonged PFS than BR in elderly patients with previously untreated MCL. As hypotesized hematological toxicity was significantly higher for the latter regimen as compared to BR. Further patients from more centers of our area are expected to be included, and long-term follow up of the R-BAC500 study is awaited to confirm our findings in an independent prospective setting.
Keyword(s): Mantle cell lymphoma, Therapy
Abstract: EP795
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Indolent and mantle-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
Both rituximab plus bendamustine (BR), and rituximab, bendamustine, and cytarabine (R-BAC) are considered suitable induction therapies in elderly patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to most recent ESMO and NCCN clinical practice guidelines. However, a direct comparison between the two regimens, either prospective or retrospective, has never been performed.
Aims
To compare the outcome and the safety features of patients with newly diagnosed MCL treated with BR or R-BAC between 2009 and 2020 in 7 Departments from north-east of Italy.
Methods
This is a multicenter retrospective observational study. The two regimens (BR and R-BAC) represented routinary induction regimens in the selected centers for patients with MCL not candidate to autologous transplant. Primary endpoint was 2-years progression-free survival (PFS). All patients treated with at least one cycle of either BR or R-BAC were included, provided they had a minimum follow-up of 12 months since start of treatment. Response was based on Lugano criteria. Due to the retrospective nature of the study, treatment assignement to one therapy instead of the other was based on local doctor decision. Inclusion bias were estimated by a propensity score stratified by gender, age, MCL morphology, and MIPI score.
Results
137 patients with MCL with a median age of 72 years (range 53-90) were retrospectively analyzed. According to our propensity score calculation, the probability of receiving R-BAC was higher in younger patients (P<0.0001), but no other significant difference in the distribution of above mentioned prognostic variables was observed between the two groups. Therefore, we limited our survival analysis to patients with 80 years or less, which allowed us a fair comparison between the two groups (P=NS). This cohort included 115 patients (42 BR, 73 R-BAC) that represented the subjects for the present analysis. Of them, 76 (66%) were males, MIPI was elevated in 61%, 15% had blastoid or pleomorphic morphology, and median follow-up was 48 months (range 12-133). Patients treated with R-BAC achieved CR in 93% of cases, as compared with 55% for BR (P<0.0001). The 2-years PFS was 91%±3% and 63%±7% for R-BAC and BR, respectively (P=0.0007, Figure 1). Median overall survival (OS) was 125 months for R-BAC and 78 months for BR (P=0.07). MIPI score was the only predictive significant variable both in terms of PFS and OS. In terms of toxicity, R-BAC was associated with significantly more pronounced grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia than BR (32% versus 15%), although R-BAC doses were frequently reduced as compared to the original scheme.

Conclusion
The BE-ve-BAC study indicates that R-BAC, even when administered in the 2-days schedule or with attenuated dose, is associated with significantly prolonged PFS than BR in elderly patients with previously untreated MCL. As hypotesized hematological toxicity was significantly higher for the latter regimen as compared to BR. Further patients from more centers of our area are expected to be included, and long-term follow up of the R-BAC500 study is awaited to confirm our findings in an independent prospective setting.
Keyword(s): Mantle cell lymphoma, Therapy


