
Contributions
Abstract: EP786
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Indolent and mantle-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
Patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who progress after receiving a Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi) have generally poor prognosis. KTE-X19, an autologous anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy, is being evaluated in patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) MCL who received 1–5 prior therapies including a BTKi (phase II multicenter, single arm ZUMA-2 trial). Results for 60 efficacy-evaluable patients with ≥12 months of follow-up have been previously reported (Wang et al., ASH 2020, Abstract 1120). After a median follow-up of 17.5 months, the estimated overall survival (OS) rate at 15 months was 76%; median OS was not reached.
Aims
To estimate and compare effectiveness of treatment of R/R MCL post-BTKi with KTE-X19 versus active standard of care (SOC) in a real-world patient cohort in Europe, based on individual patient data.
Methods
The estimated clinical efficacy of KTE-X19 came from ZUMA-2, and real-world data on the effectiveness of SOC across Europe was collected in a retrospective, observational, multicenter chart review (SCHOLAR-2). An SOC cohort was constructed to closely match the patients enrolled in ZUMA-2 (patients with ECOG 0–1 and a minimum of 12-month potential follow-up from initiation of active therapy post-BTKi). A naïve (unadjusted) comparison was performed as a benchmark, followed by three separate comparisons using inverse probability weighting (IPW), multivariable regression (MVR), and doubly robust methods designed to adjust for imbalances in prognostic factors across the two non-randomized populations. Survival times were summarized using Kaplan-Meier curves. Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate the effect of KTE-X19 relative to SOC with outcomes presented as hazard ratios (HRs) along with the 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
Clinical data from 288 R/R MCL patients treated with a BTKi between July 2012–July 2018 were collected in SCHOLAR-2 across 24 centres in Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Sweden, and the United Kingdom. The SOC cohort included 59 patients who received their first subsequent active treatment(s), referred to as SOC, prior to July 2019. Baseline characteristics were median age of 63 years, 73% male, 46%/54% ECOG 0/1, 82% stage III–IV disease, 36% with a prior autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT), and 95% with ≥2 prior lines of therapy. The median number of prior lines of therapy including BTKi was 3 (range: 1–6). Median duration on prior BTKi was 7.3 months, and the ORR to prior BTKi was 40%. In ZUMA-2, baseline characteristics were median age of 65 years, 85% male, 97% Stage III-IV, median of 3 prior lines of therapy, 43% prior ASCT, and median duration of 7 months on prior BTKi with ORR of 37%.
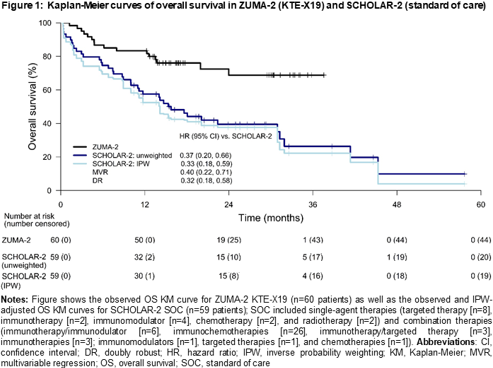
At a median follow-up of 27.6 months from initiation of SOC in SCHOLAR-2, the median OS was 15.7 (95% CI: 10.0–30.9) months; 15-month OS rate was 52%. Results of the naïve, unweighted, comparison showed that KTE-X19 was superior to SOC with an OS HR of 0.37 (95% CI: 0.20–0.66; p<0.001). The IPW-adjusted median OS in SCHOLAR-2 was 14.2 (95% CI: 8.8–30.9) months. With the IPW approach (base-case), the HR was 0.33 (95% CI: 0.18–0.59; p<0.001), consistent with the naïve analysis. The HR estimates were also consistent across sensitivity analyses using the MVR and doubly robust models (Figure 1).
Conclusion
This analysis suggests that KTE-X19 can improve survival over current active SOC in Europe for the treatment of R/R MCL in patients who have previously received BTKi therapy.
Keyword(s): CAR-T, Mantle cell lymphoma, Salvage therapy, Survival
Abstract: EP786
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Indolent and mantle-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
Patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who progress after receiving a Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi) have generally poor prognosis. KTE-X19, an autologous anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy, is being evaluated in patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) MCL who received 1–5 prior therapies including a BTKi (phase II multicenter, single arm ZUMA-2 trial). Results for 60 efficacy-evaluable patients with ≥12 months of follow-up have been previously reported (Wang et al., ASH 2020, Abstract 1120). After a median follow-up of 17.5 months, the estimated overall survival (OS) rate at 15 months was 76%; median OS was not reached.
Aims
To estimate and compare effectiveness of treatment of R/R MCL post-BTKi with KTE-X19 versus active standard of care (SOC) in a real-world patient cohort in Europe, based on individual patient data.
Methods
The estimated clinical efficacy of KTE-X19 came from ZUMA-2, and real-world data on the effectiveness of SOC across Europe was collected in a retrospective, observational, multicenter chart review (SCHOLAR-2). An SOC cohort was constructed to closely match the patients enrolled in ZUMA-2 (patients with ECOG 0–1 and a minimum of 12-month potential follow-up from initiation of active therapy post-BTKi). A naïve (unadjusted) comparison was performed as a benchmark, followed by three separate comparisons using inverse probability weighting (IPW), multivariable regression (MVR), and doubly robust methods designed to adjust for imbalances in prognostic factors across the two non-randomized populations. Survival times were summarized using Kaplan-Meier curves. Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate the effect of KTE-X19 relative to SOC with outcomes presented as hazard ratios (HRs) along with the 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
Clinical data from 288 R/R MCL patients treated with a BTKi between July 2012–July 2018 were collected in SCHOLAR-2 across 24 centres in Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Sweden, and the United Kingdom. The SOC cohort included 59 patients who received their first subsequent active treatment(s), referred to as SOC, prior to July 2019. Baseline characteristics were median age of 63 years, 73% male, 46%/54% ECOG 0/1, 82% stage III–IV disease, 36% with a prior autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT), and 95% with ≥2 prior lines of therapy. The median number of prior lines of therapy including BTKi was 3 (range: 1–6). Median duration on prior BTKi was 7.3 months, and the ORR to prior BTKi was 40%. In ZUMA-2, baseline characteristics were median age of 65 years, 85% male, 97% Stage III-IV, median of 3 prior lines of therapy, 43% prior ASCT, and median duration of 7 months on prior BTKi with ORR of 37%.
At a median follow-up of 27.6 months from initiation of SOC in SCHOLAR-2, the median OS was 15.7 (95% CI: 10.0–30.9) months; 15-month OS rate was 52%. Results of the naïve, unweighted, comparison showed that KTE-X19 was superior to SOC with an OS HR of 0.37 (95% CI: 0.20–0.66; p<0.001). The IPW-adjusted median OS in SCHOLAR-2 was 14.2 (95% CI: 8.8–30.9) months. With the IPW approach (base-case), the HR was 0.33 (95% CI: 0.18–0.59; p<0.001), consistent with the naïve analysis. The HR estimates were also consistent across sensitivity analyses using the MVR and doubly robust models (Figure 1).

Conclusion
This analysis suggests that KTE-X19 can improve survival over current active SOC in Europe for the treatment of R/R MCL in patients who have previously received BTKi therapy.
Keyword(s): CAR-T, Mantle cell lymphoma, Salvage therapy, Survival


