
Contributions
Abstract: EP777
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
ABVD or escBEACOPP chemotherapy +/- radiation is the treatment approach for patients with Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). As a result of treatment improvement, there are many long-term survivors, in whom treatment-related complications are recognized. Among these, gonadal insufficiency plays a fundamental role, with major psychological/social consequences. This is more prevalent in female patients, in whom collection and cryopreservation of oocytes or ovarian tissue are usually not applied in everyday clinical practice. Evidence-based data are scarce on this subject. Moreover, little is known about the kinetics of gonadal function and sex hormones during chemotherapy to safely guide contraceptive measures.
Aims
The aim of this study is the prospective evaluation of gonadal function in young men and women with hematological malignancies receiving chemotherapy. We here present the preliminary results on 45 patients with Hodgkin lymphoma.
Methods
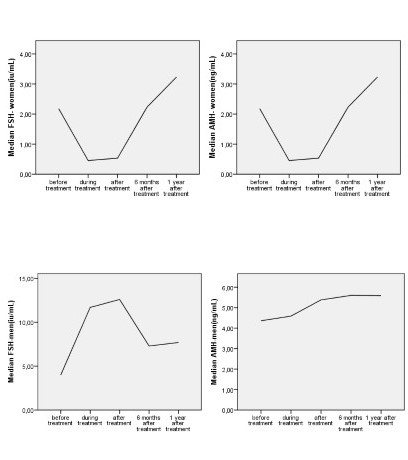
This is a prospective study of gonadal function in HL patients, with an age limit of ≤40 years in women and ≤45 years in men. Hormonal measurements were performed at pre-specified time points: before treatment, during chemotherapy, at the end of chemotherapy and every six months for the following three years. The following hormones were measured: follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), lutenizing hormone (LH), progesterone (PG), estradiol (Ε2), anti-Mullerian hormone (ΑΜΗ) in women and FSH, LH, testosterone, AMH and inhibin–β in men. The study included: 19 women [median age: 27 years, 19 ABVD] and 26 men [median age: 30 years, 26 ABVD]. FSH reflects gonadal function in both men (Sertoli cells) and women (increased levels indicate gonadal dysfunction). AMH is considered as the most sensitive biomarker for gonadal reserve in women (decreasing values correlate with ovarian insufficiency), but its exact role in men is not clarified. E2 and testosterone are the major sex hormones.
Results
Women: FSH values increased between the beginning and the end of treatment (median value: 4.35IU/mL, 7.7IU/mL, p=0.001). FSH increased from the beginning, peaking in the middle and remaining high until the end, without reaching normal levels six months after the end. Consistently with FSH, AMH showed a decrease during treatment: [median values: 1,92IU/mL (start), 0,18IU/mL (middle), p=0.000], maintained low levels through the rest of the treatment and slowly reached normal values six months later. Estradiol was not affected.
Men: Spermatogenesis, reflected by the increase of FSH, was affected: [median values: 3,7IU/mL (start), 11IU/mL (middle), 15IU/mL (end), fsh0-1 p=0.000, fsh0-2 p=0,000]. FSH increased during treatment, reaching a peak towards the end. FSH did not reach normal values after six months (p=0,017), but only after one year. Contrary to women, AMH values gradually increased during treatment: [median values: 4,13IU/mL (start), 4,28IU/mL (middle), 5,61IU/mL (end), p=0.001] and remained high until six months after the end of treatment. Most surprisingly, testosterone increased (start, middle, end: 430ng.dl, 534ng/dl, 596ng/dl, 0-1 p=0,003, 0-2 p=0,002 respectively).
Conclusion
Gonadal function in patients with HL is affected during chemotherapy in both sexes. In women, both FSH and AMH indicate gonadal dysfunction for at least 6 months after chemotherapy; AMH proved as a more sensitive marker compared to FSH. In men, gonadal function returned to baseline levels at one year after chemotherapy. However, in men, unexpectedly, AMH and testosterone significantly increased during treatment, possibly reflecting destruction of Leydig cells.
Keyword(s): Comorbidities, Hodgkin's disease, Lymphoid malignancy
Abstract: EP777
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
ABVD or escBEACOPP chemotherapy +/- radiation is the treatment approach for patients with Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). As a result of treatment improvement, there are many long-term survivors, in whom treatment-related complications are recognized. Among these, gonadal insufficiency plays a fundamental role, with major psychological/social consequences. This is more prevalent in female patients, in whom collection and cryopreservation of oocytes or ovarian tissue are usually not applied in everyday clinical practice. Evidence-based data are scarce on this subject. Moreover, little is known about the kinetics of gonadal function and sex hormones during chemotherapy to safely guide contraceptive measures.
Aims
The aim of this study is the prospective evaluation of gonadal function in young men and women with hematological malignancies receiving chemotherapy. We here present the preliminary results on 45 patients with Hodgkin lymphoma.
Methods
This is a prospective study of gonadal function in HL patients, with an age limit of ≤40 years in women and ≤45 years in men. Hormonal measurements were performed at pre-specified time points: before treatment, during chemotherapy, at the end of chemotherapy and every six months for the following three years. The following hormones were measured: follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), lutenizing hormone (LH), progesterone (PG), estradiol (Ε2), anti-Mullerian hormone (ΑΜΗ) in women and FSH, LH, testosterone, AMH and inhibin–β in men. The study included: 19 women [median age: 27 years, 19 ABVD] and 26 men [median age: 30 years, 26 ABVD]. FSH reflects gonadal function in both men (Sertoli cells) and women (increased levels indicate gonadal dysfunction). AMH is considered as the most sensitive biomarker for gonadal reserve in women (decreasing values correlate with ovarian insufficiency), but its exact role in men is not clarified. E2 and testosterone are the major sex hormones.
Results
Women: FSH values increased between the beginning and the end of treatment (median value: 4.35IU/mL, 7.7IU/mL, p=0.001). FSH increased from the beginning, peaking in the middle and remaining high until the end, without reaching normal levels six months after the end. Consistently with FSH, AMH showed a decrease during treatment: [median values: 1,92IU/mL (start), 0,18IU/mL (middle), p=0.000], maintained low levels through the rest of the treatment and slowly reached normal values six months later. Estradiol was not affected.
Men: Spermatogenesis, reflected by the increase of FSH, was affected: [median values: 3,7IU/mL (start), 11IU/mL (middle), 15IU/mL (end), fsh0-1 p=0.000, fsh0-2 p=0,000]. FSH increased during treatment, reaching a peak towards the end. FSH did not reach normal values after six months (p=0,017), but only after one year. Contrary to women, AMH values gradually increased during treatment: [median values: 4,13IU/mL (start), 4,28IU/mL (middle), 5,61IU/mL (end), p=0.001] and remained high until six months after the end of treatment. Most surprisingly, testosterone increased (start, middle, end: 430ng.dl, 534ng/dl, 596ng/dl, 0-1 p=0,003, 0-2 p=0,002 respectively).

Conclusion
Gonadal function in patients with HL is affected during chemotherapy in both sexes. In women, both FSH and AMH indicate gonadal dysfunction for at least 6 months after chemotherapy; AMH proved as a more sensitive marker compared to FSH. In men, gonadal function returned to baseline levels at one year after chemotherapy. However, in men, unexpectedly, AMH and testosterone significantly increased during treatment, possibly reflecting destruction of Leydig cells.
Keyword(s): Comorbidities, Hodgkin's disease, Lymphoid malignancy


