
Contributions
Abstract: EP736
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Gene therapy, cellular immunotherapy and vaccination - Clinical
Background
Elevated levels of fetal hemoglobin (HbF) are associated with improved clinical outcomes in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD). CTX001™ is a novel cell therapy that uses non-viral, ex vivo CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing in autologous hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells at the erythroid enhancer region of the BCL11A gene to reduce expression of BCL11A, a repressor of γ-globin, and reactivate HbF production. Early data from patients with SCD infused with CTX001 showed increased levels of total hemoglobin (Hb), HbF, and F-cell pancellularity over time. No vaso-occlusive crises (VOCs) were reported for any patient after CTX001 infusion. The safety profile was generally consistent with myeloablative conditioning.
Aims
Here, we present additional patient data and follow-up from an interim data cut on 28 January 2021. Included in the data set are all patients with SCD enrolled in the CLIMB SCD-121 trial (NCT03745287) infused with CTX001 who had at least 3 months of follow-up available at the time of analysis (N=4).
Methods
Patients (aged 12 to 35 years) with severe SCD, defined as ≥2 VOCs/year requiring medical care over the previous 2 years, were eligible. After mobilization with plerixafor, peripheral CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells were collected by apheresis and edited using a specific single-guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease. Prior to CTX001 infusion on Day 1, patients received myeloablation with busulfan. Patients were monitored for stem cell engraftment and hematopoietic recovery, adverse events, total Hb and HbF production, hemolysis, percentage of F-cells, and VOCs during follow-up.
Results
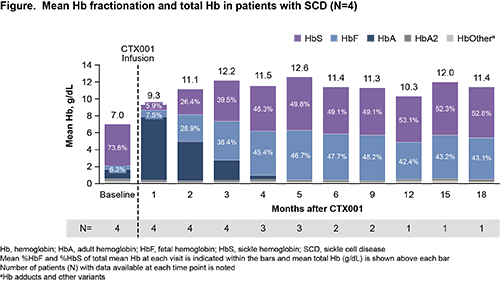
Mean duration of follow-up was 10.1 months (range: 4.3 to 19.2). At baseline, patients had mean (SD) total Hb of 7.0 (1.6) g/dL and mean (SD) HbF of 6.3% (2.2%) of total Hb. Patients had a mean of 5.3 severe VOCs annually in the previous 2 years. Following CTX001 infusion, median neutrophil engraftment occurred on Day 25.5 (range: 17 to 30) and median platelet engraftment occurred on Day 31.5 (range: 30 to 40).
All 4 patients reported adverse events; most were mild or moderate in severity and the post-CTX001 safety profile was generally consistent with busulfan myeloablation. No serious adverse events considered by the principal investigator to be related or possibly related to CTX001 were reported.
All patients demonstrated increases in total Hb and HbF (Figure), as well as F-cell pancellularity over time. Mean %HbF rose to >30% by month 3 and all patients had %HbF >30% as of the last visit before data cut. No patients experienced VOCs during the time of this analysis (up to 19.2 months). Markers of hemolysis, including haptoglobin, lactate dehydrogenase, and total bilirubin, improved in all patients and normalized by month 6.
Conclusion
The updated data presented here confirm previous reports showing CTX001 infusion increases total Hb and %HbF with F-cell pancellularity in patients with SCD, and demonstrate the durability of efficacy up to 19.2 months of follow-up. All 4 patients were free of VOCs from CTX001 infusion through the time of this analysis. The safety profile of CTX001 remained generally consistent with myeloablative conditioning and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. These results strongly support continued investigation of CTX001 as a potential functional cure for patients with SCD.
Submitted on behalf of the CLIMB SCD-121 Investigators.
Keyword(s): Hemoglobin, Sickle cell disease, Stem cell gene therapy
Abstract: EP736
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Gene therapy, cellular immunotherapy and vaccination - Clinical
Background
Elevated levels of fetal hemoglobin (HbF) are associated with improved clinical outcomes in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD). CTX001™ is a novel cell therapy that uses non-viral, ex vivo CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing in autologous hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells at the erythroid enhancer region of the BCL11A gene to reduce expression of BCL11A, a repressor of γ-globin, and reactivate HbF production. Early data from patients with SCD infused with CTX001 showed increased levels of total hemoglobin (Hb), HbF, and F-cell pancellularity over time. No vaso-occlusive crises (VOCs) were reported for any patient after CTX001 infusion. The safety profile was generally consistent with myeloablative conditioning.
Aims
Here, we present additional patient data and follow-up from an interim data cut on 28 January 2021. Included in the data set are all patients with SCD enrolled in the CLIMB SCD-121 trial (NCT03745287) infused with CTX001 who had at least 3 months of follow-up available at the time of analysis (N=4).
Methods
Patients (aged 12 to 35 years) with severe SCD, defined as ≥2 VOCs/year requiring medical care over the previous 2 years, were eligible. After mobilization with plerixafor, peripheral CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells were collected by apheresis and edited using a specific single-guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease. Prior to CTX001 infusion on Day 1, patients received myeloablation with busulfan. Patients were monitored for stem cell engraftment and hematopoietic recovery, adverse events, total Hb and HbF production, hemolysis, percentage of F-cells, and VOCs during follow-up.
Results
Mean duration of follow-up was 10.1 months (range: 4.3 to 19.2). At baseline, patients had mean (SD) total Hb of 7.0 (1.6) g/dL and mean (SD) HbF of 6.3% (2.2%) of total Hb. Patients had a mean of 5.3 severe VOCs annually in the previous 2 years. Following CTX001 infusion, median neutrophil engraftment occurred on Day 25.5 (range: 17 to 30) and median platelet engraftment occurred on Day 31.5 (range: 30 to 40).
All 4 patients reported adverse events; most were mild or moderate in severity and the post-CTX001 safety profile was generally consistent with busulfan myeloablation. No serious adverse events considered by the principal investigator to be related or possibly related to CTX001 were reported.
All patients demonstrated increases in total Hb and HbF (Figure), as well as F-cell pancellularity over time. Mean %HbF rose to >30% by month 3 and all patients had %HbF >30% as of the last visit before data cut. No patients experienced VOCs during the time of this analysis (up to 19.2 months). Markers of hemolysis, including haptoglobin, lactate dehydrogenase, and total bilirubin, improved in all patients and normalized by month 6.

Conclusion
The updated data presented here confirm previous reports showing CTX001 infusion increases total Hb and %HbF with F-cell pancellularity in patients with SCD, and demonstrate the durability of efficacy up to 19.2 months of follow-up. All 4 patients were free of VOCs from CTX001 infusion through the time of this analysis. The safety profile of CTX001 remained generally consistent with myeloablative conditioning and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. These results strongly support continued investigation of CTX001 as a potential functional cure for patients with SCD.
Submitted on behalf of the CLIMB SCD-121 Investigators.
Keyword(s): Hemoglobin, Sickle cell disease, Stem cell gene therapy


