
Contributions
Abstract: EP672
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Chronic myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Background
Bosutinib is approved for patients with Philadelphia chromosome–positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) resistant/intolerant to prior therapy and newly diagnosed Ph+ chronic phase (CP) CML. In a phase 1/2 study, second-line bosutinib showed durable efficacy and manageable toxicity in patients with imatinib-resistant (IM-R) or imatinib-intolerant (IM-I) Ph+ CP CML.
Aims
The final efficacy and safety analysis of this phase 1/2 study and its extension study (NCT00261846 and NCT01903733) is presented.
Methods
Patients with Ph+ CP CML who received bosutinib starting at 500 mg/day after prior treatment with imatinib only were included. This analysis was based on ≥10 years of follow-up.
Results
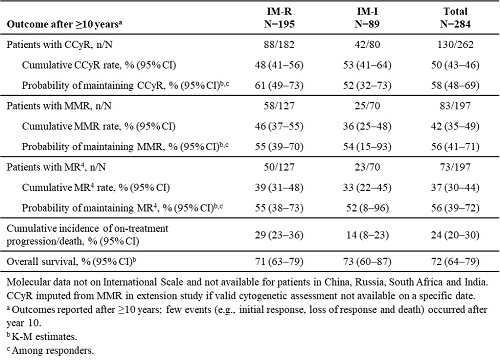
19% of patients were on treatment with bosutinib at year 10, and 13% were still receiving bosutinib at study completion after ≥10 years; 19% completed ≥10 years of follow-up. Median duration of treatment and follow-up were 26 and 54 months, respectively. Median (range) dose intensity was 436 (87–599) mg/day. The most common primary reasons for permanent treatment discontinuation were lack of efficacy (unsatisfactory response or disease progression; 27%) and adverse events (AEs; 26%). In patients with a valid baseline assessment, cumulative complete cytogenetic response (CCyR), major molecular response (MMR) and MR4 rates were 50%, 42% and 37%, respectively (Table). Responses were durable, with estimated probabilities of maintaining CCyR, MMR and MR4 >50% after ≥10 years (Table). At 10 years, cumulative incidence of on-treatment progression/death was 24% and Kaplan-Meier (K-M) overall survival 72% (Table). 55 deaths (IM-R: n=41; IM-I: n=14) occurred on study; causes of death were disease progression (n=30), AEs (n=16; none bosutinib-related), other (n=5) and unknown (n=4). Any grade treatment-emergent AEs (TEAEs) occurring in ≥40% of patients were diarrhea (86%), nausea (46%) and thrombocytopenia (42%). Pleural effusion, cardiac and vascular TEAEs occurred in 13%, 12% and 11% of patients, respectively. 28% of patients had AEs leading to permanent treatment discontinuation; the most common (≥2% of patients) were thrombocytopenia (6%), neutropenia (2%) and alanine aminotransferase increased (2%).
Conclusion
These 10-year data are consistent with prior results of durable efficacy and manageable toxicity with second-line bosutinib and support long-term bosutinib use in patients with CP CML after imatinib failure.
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Clinical trial, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Abstract: EP672
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Chronic myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Background
Bosutinib is approved for patients with Philadelphia chromosome–positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) resistant/intolerant to prior therapy and newly diagnosed Ph+ chronic phase (CP) CML. In a phase 1/2 study, second-line bosutinib showed durable efficacy and manageable toxicity in patients with imatinib-resistant (IM-R) or imatinib-intolerant (IM-I) Ph+ CP CML.
Aims
The final efficacy and safety analysis of this phase 1/2 study and its extension study (NCT00261846 and NCT01903733) is presented.
Methods
Patients with Ph+ CP CML who received bosutinib starting at 500 mg/day after prior treatment with imatinib only were included. This analysis was based on ≥10 years of follow-up.
Results
19% of patients were on treatment with bosutinib at year 10, and 13% were still receiving bosutinib at study completion after ≥10 years; 19% completed ≥10 years of follow-up. Median duration of treatment and follow-up were 26 and 54 months, respectively. Median (range) dose intensity was 436 (87–599) mg/day. The most common primary reasons for permanent treatment discontinuation were lack of efficacy (unsatisfactory response or disease progression; 27%) and adverse events (AEs; 26%). In patients with a valid baseline assessment, cumulative complete cytogenetic response (CCyR), major molecular response (MMR) and MR4 rates were 50%, 42% and 37%, respectively (Table). Responses were durable, with estimated probabilities of maintaining CCyR, MMR and MR4 >50% after ≥10 years (Table). At 10 years, cumulative incidence of on-treatment progression/death was 24% and Kaplan-Meier (K-M) overall survival 72% (Table). 55 deaths (IM-R: n=41; IM-I: n=14) occurred on study; causes of death were disease progression (n=30), AEs (n=16; none bosutinib-related), other (n=5) and unknown (n=4). Any grade treatment-emergent AEs (TEAEs) occurring in ≥40% of patients were diarrhea (86%), nausea (46%) and thrombocytopenia (42%). Pleural effusion, cardiac and vascular TEAEs occurred in 13%, 12% and 11% of patients, respectively. 28% of patients had AEs leading to permanent treatment discontinuation; the most common (≥2% of patients) were thrombocytopenia (6%), neutropenia (2%) and alanine aminotransferase increased (2%).

Conclusion
These 10-year data are consistent with prior results of durable efficacy and manageable toxicity with second-line bosutinib and support long-term bosutinib use in patients with CP CML after imatinib failure.
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Clinical trial, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor


