
Contributions
Abstract: EP638
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and related disorders - Clinical
Background
TG-1701 is a selective, covalent BTK inhibitor administered once daily (QD). Both the “U2” combination (anti-CD20 mAb ublituximab + the PI3Kδ-CK1ε inhibitor umbralisib) and BTK inhibition are highly active in treatment-naïve (TN) and relapsed/refractory (R/R) CLL, each having previously demonstrated superiority over standard chemoimmunotherapy. Herein we report the results of the dose escalation of TG-1701 monotherapy and TG-1701+U2.
Aims
The primary objectives of the study are to characterize the safety profile and define the recommended Ph 2 doses for the drugs alone and in combination.
Methods
Patients with R/R CLL, MCL and Waldenström's (WM) were enrolled in an ongoing Ph 1 study initially evaluating dose escalation (DE) of oral TG-1701 QD continuously administered in 28-day cycles (100, 200, 300, and 400 mg). After characterizing the safety profile of TG-1701 monotherapy, we implemented a parallel DE arm of TG-1701+U2. Select dose levels of TG-1701 monotherapy were expanded. All patients were treated until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or investigator/patient decision to withdraw.
Results
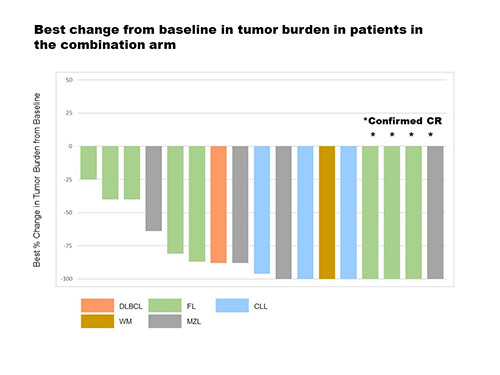
As of 03 February 2021, 123 patients were treated with TG-1701 as follows: 25 in the monotherapy DE arm, 61 in the 200 mg disease-specific cohorts (20 CLL [5 TN], 21 MCL [4 TN], 20 WM [8 TN]), 20 in the 300 mg CLL cohort (4 TN), and 17 in the 1701+U2 DE arm. The median # of prior therapies was 1 (range, 1 - 10). All patients were BTKi-naïve. All 123 patients were evaluable for safety. TG-1701 was well tolerated and the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) for monotherapy was not reached at 400 mg (demonstrating near 100% saturation of the BTK at all dose levels studied). Treatment emergent adverse events (TEAE) of clinical interest included atrial fibrillation (AF 4.0% of patients, G ≥3 in 1 case), G ≥3 hypertension (2.4%), and bleeding events (18.7%, all G1-2). No cases of ventricular tachyarrhythmia were reported. TEAEs leading to TG-1701 dose reduction occurred in 6.5% of patients. TEAEs leading to treatment discontinuation occurred in 1.6% of patients (AF, COVID-19). At the data cut-off, 119 patients were evaluable for response, including 40 in DE (Table). The median duration of response has not been reached among responders overall. The median follow-up (mFU range) was 15.9 mos (1.3 - 28.6+) in DE and 8.5 mos (1.4 -15.6+) in disease-specific cohorts. No complete responses (CR) were confirmed on TG-1701 monotherapy. The objective response rate (ORR) for 1701+U2 was 82.3% with a 23.5% CR rate. Best change from baseline in tumor burden in patients in the 1701+U2 combination arm is presented in the figure below.
Table. Response per investigator review by treatment group
| DE arm (N = 23) | 200 mg CLL (N = 20) | 200 mg MCL (N = 20) | 200 mg WM (N = 20) | 300 mg CLL (N = 19) | 1701+U2 DE arm (N = 17) |
ORR, % | 56.5 | 95.0 | 60.0 | 95.0 | 100 | 82.3 |
CR, % | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 23.5 |
Very good PR, % | 4.3 |
|
| 0 |
| 5.9 |
PR, % | 47.8 | 95.0 | 60.0 | 70.0 | 100 | 52.9 |
Minor response, % | 4.3 |
|
| 25.0 |
| 0 |
mFU mos | 17.5 | 11.6 | 8.2 | 9.7 | 5.8 | 14.3 |
Conclusion
TG-1701 exhibits an encouraging safety and efficacy profile. The combination of 1701+U2 has been well tolerated and dose escalation continues. The combination shows enhanced depth of response over TG-1701 monotherapy. Recruitment to this study (NCT03671590) continues.
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Abstract: EP638
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and related disorders - Clinical
Background
TG-1701 is a selective, covalent BTK inhibitor administered once daily (QD). Both the “U2” combination (anti-CD20 mAb ublituximab + the PI3Kδ-CK1ε inhibitor umbralisib) and BTK inhibition are highly active in treatment-naïve (TN) and relapsed/refractory (R/R) CLL, each having previously demonstrated superiority over standard chemoimmunotherapy. Herein we report the results of the dose escalation of TG-1701 monotherapy and TG-1701+U2.
Aims
The primary objectives of the study are to characterize the safety profile and define the recommended Ph 2 doses for the drugs alone and in combination.
Methods
Patients with R/R CLL, MCL and Waldenström's (WM) were enrolled in an ongoing Ph 1 study initially evaluating dose escalation (DE) of oral TG-1701 QD continuously administered in 28-day cycles (100, 200, 300, and 400 mg). After characterizing the safety profile of TG-1701 monotherapy, we implemented a parallel DE arm of TG-1701+U2. Select dose levels of TG-1701 monotherapy were expanded. All patients were treated until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or investigator/patient decision to withdraw.
Results
As of 03 February 2021, 123 patients were treated with TG-1701 as follows: 25 in the monotherapy DE arm, 61 in the 200 mg disease-specific cohorts (20 CLL [5 TN], 21 MCL [4 TN], 20 WM [8 TN]), 20 in the 300 mg CLL cohort (4 TN), and 17 in the 1701+U2 DE arm. The median # of prior therapies was 1 (range, 1 - 10). All patients were BTKi-naïve. All 123 patients were evaluable for safety. TG-1701 was well tolerated and the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) for monotherapy was not reached at 400 mg (demonstrating near 100% saturation of the BTK at all dose levels studied). Treatment emergent adverse events (TEAE) of clinical interest included atrial fibrillation (AF 4.0% of patients, G ≥3 in 1 case), G ≥3 hypertension (2.4%), and bleeding events (18.7%, all G1-2). No cases of ventricular tachyarrhythmia were reported. TEAEs leading to TG-1701 dose reduction occurred in 6.5% of patients. TEAEs leading to treatment discontinuation occurred in 1.6% of patients (AF, COVID-19). At the data cut-off, 119 patients were evaluable for response, including 40 in DE (Table). The median duration of response has not been reached among responders overall. The median follow-up (mFU range) was 15.9 mos (1.3 - 28.6+) in DE and 8.5 mos (1.4 -15.6+) in disease-specific cohorts. No complete responses (CR) were confirmed on TG-1701 monotherapy. The objective response rate (ORR) for 1701+U2 was 82.3% with a 23.5% CR rate. Best change from baseline in tumor burden in patients in the 1701+U2 combination arm is presented in the figure below.
Table. Response per investigator review by treatment group
| DE arm (N = 23) | 200 mg CLL (N = 20) | 200 mg MCL (N = 20) | 200 mg WM (N = 20) | 300 mg CLL (N = 19) | 1701+U2 DE arm (N = 17) |
ORR, % | 56.5 | 95.0 | 60.0 | 95.0 | 100 | 82.3 |
CR, % | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 23.5 |
Very good PR, % | 4.3 |
|
| 0 |
| 5.9 |
PR, % | 47.8 | 95.0 | 60.0 | 70.0 | 100 | 52.9 |
Minor response, % | 4.3 |
|
| 25.0 |
| 0 |
mFU mos | 17.5 | 11.6 | 8.2 | 9.7 | 5.8 | 14.3 |

Conclusion
TG-1701 exhibits an encouraging safety and efficacy profile. The combination of 1701+U2 has been well tolerated and dose escalation continues. The combination shows enhanced depth of response over TG-1701 monotherapy. Recruitment to this study (NCT03671590) continues.
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor


