
Contributions
Abstract: EP633
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and related disorders - Clinical
Background
Despite the marked efficacy of covalent BTK inhibitors (BTKi) in CLL/SLL, the development of resistance and discontinuation for adverse events can lead to treatment failure. Moreover, pharmacological liabilities of these agents such as low oral bioavailability or short half-life can lead to suboptimal BTK target coverage and ultimately result in acquired resistance in some patients (pts). To address these limitations, pirtobrutinib (LOXO-305), a highly selective, non-covalent BTKi that inhibits both WT and C481-mutated BTK with equal low nM potency was developed.
Aims
To evaluate safety and efficacy of pirtobrutinib in previously treated CLL/SLL.
Methods
BRUIN is a multicenter phase 1/2 trial (NCT03740529) enrolling pts with advanced B-cell malignancies who have received >2 prior therapies. Oral pirtobrutinib was dose escalated in a standard 3+3 design in 28-day cycles. The primary endpoint was MTD/RP2D identification. Efficacy evaluable pts included all dosed pts who underwent their first response evaluation or discontinued therapy. Safety was assessed in all pts (n=323). Response was assessed according to the iwCLL 2018 criteria, including PR with lymphocytosis (PR-L).
Results
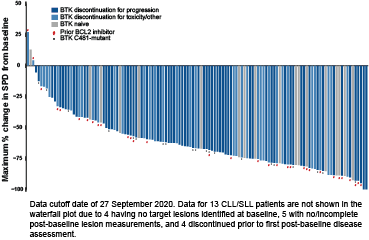
As of 27 September 2020, 323 pts with B-cell malignancies (170 CLL/SLL, 61 MCL, 26 WM, and 66 other B-cell lymphomas) were treated on 7 dose levels (25-300mg QD). Among the 170 CLL/SLL pts, the median age was 69 (range 36-84) years. Median number of prior lines of therapies was 3 (range 1-11), 86% of CLL/SLL pts had received a prior BTKi, and 67% an anti-CD20 antibody, chemotherapy, and BTKi; 21% had received a PI3K inhibitor and 34% venetoclax. At enrollment, high risk features such as 17p deletion were present in 25% (20/81), TP53 mutation in 30% (27/91), and unmutated IGHV in 88% (71/81). Pirtobrutinib demonstrated high oral exposures, with doses ≥100mg QD exceeding the BTK IC90 for the entirety of the dosing interval. No DLTs occurred. Consistent with pirtobrutinib’s selectivity, the only treatment-emergent adverse events regardless of attribution or grade seen in >10% of pts (n=323) were fatigue (20%), diarrhea (17%) and contusion (13%). Responses were observed at the first dose level of 25mg QD. A RP2D of 200mg QD was selected for future studies. At the efficacy cutoff date, 150 CLL/SLL pts remained on therapy and 139 were efficacy evaluable (121 BTKi-treated). Median follow-up was 6 months (range 0.6-17.8+) for efficacy evaluable pts. The ORR was 63% with 69 PRs, 19 PR-Ls, 45 SDs, 1 PD, and 5 discontinued prior to first response assessment (Figure). An additional 37 pts were ongoing and awaiting initial radiologic assessment. Responses deepened over time; among pts with at least 10 months of follow-up (n=29), the ORR was 86%. ORR was not influenced by the reason for prior BTKi discontinuation (i.e. progression vs intolerance), or other classes of prior therapy received (including a covalent BTK and a BCL2 inhibitor). Of the 88 responding pts, all except 5 remain on therapy (4 progressed, and 1 achieved a PR and electively discontinued). The longest followed responding pt continues on treatment for 17.8+ months.
Conclusion
Pirtobrutinib demonstrated promising efficacy in CLL/SLL pts following multiple prior lines of therapy including a covalent BTKi and a BCL2 inhibitor. Importantly, the activity of pirtobrutinib was not restricted to pts with BTK C481 mutations. Pirtobrutinib was well tolerated and exhibited a wide therapeutic index.
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Clinical trial, Phase I/II, Targeted therapy
Abstract: EP633
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and related disorders - Clinical
Background
Despite the marked efficacy of covalent BTK inhibitors (BTKi) in CLL/SLL, the development of resistance and discontinuation for adverse events can lead to treatment failure. Moreover, pharmacological liabilities of these agents such as low oral bioavailability or short half-life can lead to suboptimal BTK target coverage and ultimately result in acquired resistance in some patients (pts). To address these limitations, pirtobrutinib (LOXO-305), a highly selective, non-covalent BTKi that inhibits both WT and C481-mutated BTK with equal low nM potency was developed.
Aims
To evaluate safety and efficacy of pirtobrutinib in previously treated CLL/SLL.
Methods
BRUIN is a multicenter phase 1/2 trial (NCT03740529) enrolling pts with advanced B-cell malignancies who have received >2 prior therapies. Oral pirtobrutinib was dose escalated in a standard 3+3 design in 28-day cycles. The primary endpoint was MTD/RP2D identification. Efficacy evaluable pts included all dosed pts who underwent their first response evaluation or discontinued therapy. Safety was assessed in all pts (n=323). Response was assessed according to the iwCLL 2018 criteria, including PR with lymphocytosis (PR-L).
Results
As of 27 September 2020, 323 pts with B-cell malignancies (170 CLL/SLL, 61 MCL, 26 WM, and 66 other B-cell lymphomas) were treated on 7 dose levels (25-300mg QD). Among the 170 CLL/SLL pts, the median age was 69 (range 36-84) years. Median number of prior lines of therapies was 3 (range 1-11), 86% of CLL/SLL pts had received a prior BTKi, and 67% an anti-CD20 antibody, chemotherapy, and BTKi; 21% had received a PI3K inhibitor and 34% venetoclax. At enrollment, high risk features such as 17p deletion were present in 25% (20/81), TP53 mutation in 30% (27/91), and unmutated IGHV in 88% (71/81). Pirtobrutinib demonstrated high oral exposures, with doses ≥100mg QD exceeding the BTK IC90 for the entirety of the dosing interval. No DLTs occurred. Consistent with pirtobrutinib’s selectivity, the only treatment-emergent adverse events regardless of attribution or grade seen in >10% of pts (n=323) were fatigue (20%), diarrhea (17%) and contusion (13%). Responses were observed at the first dose level of 25mg QD. A RP2D of 200mg QD was selected for future studies. At the efficacy cutoff date, 150 CLL/SLL pts remained on therapy and 139 were efficacy evaluable (121 BTKi-treated). Median follow-up was 6 months (range 0.6-17.8+) for efficacy evaluable pts. The ORR was 63% with 69 PRs, 19 PR-Ls, 45 SDs, 1 PD, and 5 discontinued prior to first response assessment (Figure). An additional 37 pts were ongoing and awaiting initial radiologic assessment. Responses deepened over time; among pts with at least 10 months of follow-up (n=29), the ORR was 86%. ORR was not influenced by the reason for prior BTKi discontinuation (i.e. progression vs intolerance), or other classes of prior therapy received (including a covalent BTK and a BCL2 inhibitor). Of the 88 responding pts, all except 5 remain on therapy (4 progressed, and 1 achieved a PR and electively discontinued). The longest followed responding pt continues on treatment for 17.8+ months.

Conclusion
Pirtobrutinib demonstrated promising efficacy in CLL/SLL pts following multiple prior lines of therapy including a covalent BTKi and a BCL2 inhibitor. Importantly, the activity of pirtobrutinib was not restricted to pts with BTK C481 mutations. Pirtobrutinib was well tolerated and exhibited a wide therapeutic index.
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Clinical trial, Phase I/II, Targeted therapy


