
Contributions
Abstract: EP620
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and related disorders - Biology & Translational Research
Background
GSK-3β is a serine/threonine kinase that plays a role in several disease processes, including cancer. Aberrant overexpression of GSK-3β promotes survival in B cell lymphoma cells. By contrast, little is known about the role GSK-3β in CLL and its potential as a new therapeutic target. 9-ING-41 is a selective GSK-3β inhibitor with significant pre-clinical and clinical activity in advanced malignancies. Its modes of action include direct induction of apoptosis, reversal of chemoresistance, immune-modulation, and reversal of fibrosis. 9-ING-41 induces apoptosis in B lymphoma cell lines. We hypothesized that targeting GSK-3β with 9-ING-41 may be a new CLL treatment strategy via interference with tumor survival through novel pathways.
Aims
To explore the effects of single agent 9-ING-41 on viability and apoptosis in a preclinical in vitro model of CLL.
Methods
Experiments were conducted in the PGA1 CLL cell line. 9-ING-41 was obtained from Actuate Therapeutics, Inc. Cell viability/apoptosis were assessed using Celltiter-Glo assay and flow cytometry after Annexin V-APC/propidium iodide (PI) staining. Real-time PCR and western blotting were used to measure apoptotic markers.
Results
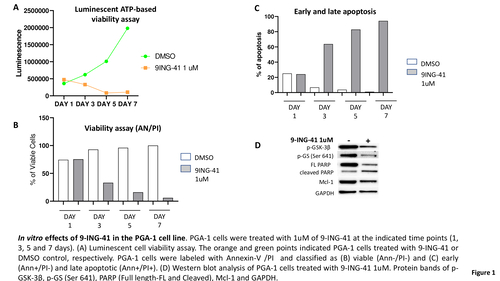
In PGA-1 cells, 1 μM 9-ING-41 concentration resulted in reduction of the phosphorylation levels of GSK-3β and its substrate glycogen synthase (GS) (Fig. 1D). Sensitivity to 9-ING-41 was evaluated using a luminescent ATP-based viability assay to measure the killing efficacy of the GSK3 inhibitor. Starting at day 3, 9-ING-41 caused a reduction in cell viability, with the highest impact on intracellular ATP concentration observed after 7 days of treatment (Fig. 1A). Annexin V/PI labeling further supports the anti-leukemic effects of 9-ING-41. The percentage of double negative viable PGA-1 cells decreased at day 3, 5 and 7 in the presence of 9-ING-41 compared to vehicle control (33.2% vs 92.3%, 16.1% vs 96% and 6.1% vs 99%, respectively; Fig. 1B). The cytotoxicity induced by 9-ING-41 was due to apoptosis, as indicated by a significantly increased percentage of Annexin V/PI apoptotic cells compared to vehicle. Early and late apoptosis increased at day 3, 5 and 7 treatment with 9-ING-41 compared to vehicle (63.9% vs 6.8%, 82.9% vs 3.8%, 94.2% vs 1%, respectively; Fig. 1C). 9-ING-41 treatment was associated with a 1.5-fold and 2.4-fold upregulation of the pro-apoptotic family members BAX and NOXA at the mRNA level (N=2; p<0.01). At day 3, BCL2 anti-apoptotic expression was 1.4-fold lower in 9-ING-41 treated cells compared with the vehicle control. In vitro studies are ongoing to investigate the potential association of 9-ING-41 with the BCL2 inhibitor Venetoclax. The apoptotic effects of 9-ING-41 were further supported by the detection of increased degradation of PARP protein to its inactive fragment (Fig. 1D). Cleavage of PARP suggests caspase activation contributed to 9-ING-41 induced apoptosis of CLL cells. Treatment with 9-ING-41 resulted in increased active cleaved products of caspase-3, concurrent with a decrease in its pro-form (Fig. 1D). Additionally, 9-ING-41 treatment was associated with reduction of MCL-1 protein expression.
Conclusion
Our study is the first to explore the relevance of 9-ING-41 as a therapeutic strategy in CLL. 9-ING-41 has significant single agent activity with the ability to induce apoptosis in a cell line-dependent manner. Targeting GSK-3β may expand therapeutic options for CLL patients. Ongoing work continues to assess combinations with approved targeted agents in order to overcome drug-induced resistance.
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Targeted therapy
Abstract: EP620
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and related disorders - Biology & Translational Research
Background
GSK-3β is a serine/threonine kinase that plays a role in several disease processes, including cancer. Aberrant overexpression of GSK-3β promotes survival in B cell lymphoma cells. By contrast, little is known about the role GSK-3β in CLL and its potential as a new therapeutic target. 9-ING-41 is a selective GSK-3β inhibitor with significant pre-clinical and clinical activity in advanced malignancies. Its modes of action include direct induction of apoptosis, reversal of chemoresistance, immune-modulation, and reversal of fibrosis. 9-ING-41 induces apoptosis in B lymphoma cell lines. We hypothesized that targeting GSK-3β with 9-ING-41 may be a new CLL treatment strategy via interference with tumor survival through novel pathways.
Aims
To explore the effects of single agent 9-ING-41 on viability and apoptosis in a preclinical in vitro model of CLL.
Methods
Experiments were conducted in the PGA1 CLL cell line. 9-ING-41 was obtained from Actuate Therapeutics, Inc. Cell viability/apoptosis were assessed using Celltiter-Glo assay and flow cytometry after Annexin V-APC/propidium iodide (PI) staining. Real-time PCR and western blotting were used to measure apoptotic markers.
Results
In PGA-1 cells, 1 μM 9-ING-41 concentration resulted in reduction of the phosphorylation levels of GSK-3β and its substrate glycogen synthase (GS) (Fig. 1D). Sensitivity to 9-ING-41 was evaluated using a luminescent ATP-based viability assay to measure the killing efficacy of the GSK3 inhibitor. Starting at day 3, 9-ING-41 caused a reduction in cell viability, with the highest impact on intracellular ATP concentration observed after 7 days of treatment (Fig. 1A). Annexin V/PI labeling further supports the anti-leukemic effects of 9-ING-41. The percentage of double negative viable PGA-1 cells decreased at day 3, 5 and 7 in the presence of 9-ING-41 compared to vehicle control (33.2% vs 92.3%, 16.1% vs 96% and 6.1% vs 99%, respectively; Fig. 1B). The cytotoxicity induced by 9-ING-41 was due to apoptosis, as indicated by a significantly increased percentage of Annexin V/PI apoptotic cells compared to vehicle. Early and late apoptosis increased at day 3, 5 and 7 treatment with 9-ING-41 compared to vehicle (63.9% vs 6.8%, 82.9% vs 3.8%, 94.2% vs 1%, respectively; Fig. 1C). 9-ING-41 treatment was associated with a 1.5-fold and 2.4-fold upregulation of the pro-apoptotic family members BAX and NOXA at the mRNA level (N=2; p<0.01). At day 3, BCL2 anti-apoptotic expression was 1.4-fold lower in 9-ING-41 treated cells compared with the vehicle control. In vitro studies are ongoing to investigate the potential association of 9-ING-41 with the BCL2 inhibitor Venetoclax. The apoptotic effects of 9-ING-41 were further supported by the detection of increased degradation of PARP protein to its inactive fragment (Fig. 1D). Cleavage of PARP suggests caspase activation contributed to 9-ING-41 induced apoptosis of CLL cells. Treatment with 9-ING-41 resulted in increased active cleaved products of caspase-3, concurrent with a decrease in its pro-form (Fig. 1D). Additionally, 9-ING-41 treatment was associated with reduction of MCL-1 protein expression.

Conclusion
Our study is the first to explore the relevance of 9-ING-41 as a therapeutic strategy in CLL. 9-ING-41 has significant single agent activity with the ability to induce apoptosis in a cell line-dependent manner. Targeting GSK-3β may expand therapeutic options for CLL patients. Ongoing work continues to assess combinations with approved targeted agents in order to overcome drug-induced resistance.
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Targeted therapy


