
Contributions
Abstract: EP595
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Bone marrow failure syndromes incl. PNH - Clinical
Background
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare, acquired, life-threatening hematologic disease characterized by chronic complement-mediated red blood cell hemolysis. Current standard treatments for PNH are the C5 inhibitors eculizumab (ECU) or ravulizumab. Despite their proven efficacy in the control of intravascular hemolysis (IVH), up to 72% of patients experience persistent hemolysis leading to suboptimal hemoglobin (Hb) levels and 36% require transfusions despite ECU treatment which results in significant impact on quality of life (QoL), including persistent fatigue. Pegcetacoplan (PEG) is a C3 inhibitor that provides broad hemolysis control (including IVH and extravascular hemolysis) in patients with PNH.
Aims
This analysis evaluates QoL measures in the PEGASUS study (NCT03500549), a phase 3, open-label, randomized, active-comparator trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of PEG compared with ECU.
Methods
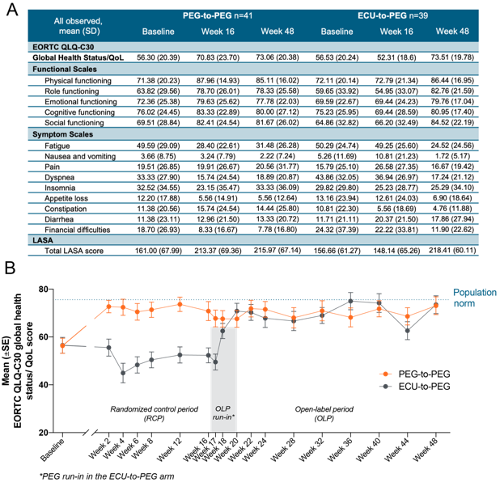
This study is an extension of the PEGASUS trial. PEGASUS enrolled patients ≥18 years of age with PNH and Hb levels <10.5 g/dL despite receiving treatment with ECU for ≥3 months. Patients entered a 4-week run-in period in which they received ECU plus twice-weekly PEG (1080 mg, administered subcutaneously) and were then randomized 1:1 to monotherapy with PEG or ECU for 16 weeks. Patients receiving ECU during the randomized controlled period entered another 4-week run-in period (ECU+PEG), before PEG monotherapy (groups: PEG-to-PEG and ECU-to-PEG). This was followed by an Open Label Period (OLP), in which all patients received pegcetacoplan monotherapy. The primary endpoint was change from baseline in Hb levels at Week 16, where PEG demonstrated superiority to ECU (Hillmen P et al, EHA 2020). Secondary endpoints included the QoL measures by the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire-Core 30 Scale (EORTC QLQ-C30) and Linear Analog Scale Assessment (LASA). The EORTC QLQ-C30 contains 30 questions comprising 5 functional, 9 individual symptom, and one global health status/QoL item(s). The LASA consists of 3 sections asking to rate the perceived level of functioning (scale 0-100) and contains specific domains for activity level, ability to carry out daily activities, and overall QoL.
Results
PEGASUS enrolled 80 patients (Peg, n=41; ECU, n=39). Overall, mean baseline scores of the EORTC QLQ-C30 functional and symptom scales were similar between groups. At Week 16, patients in the PEG group typically scored better than ECU (ECU only to Week 16) patients on various scales of the EORTC QLQ-C30 (Figure A). After receiving PEG monotherapy for 28 weeks (OLP), both groups showed improvements in all functional scales (Figure A) and the global health status/QoL at Week 48 (Figure B) and as indicated by an increase in the score from baseline. Improvements in the fatigue (Figure B) and dyspnea scales were also observed in both groups at Week 48 as indicated by a reduction in the symptom score close to the population norms (fatigue general population norm: 24.1 [22.7], dyspnea general population norm: 10.9 [20.6]). Mean total LASA scores increased in the PEG-to-PEG group as compared to the ECU-to-PEG group to Week 16 and after 28 Weeks of open-label PEG monotherapy the mean score was comparable between both groups at Week 48 (Figure A).
Conclusion
Although no statistical tests were performed on these QoL endpoints based on the trial protocol, substantial and clinically relevant improvements in QoL were consistently observed with PEG across both LASA and EORTC QLQ-C30 scores.
Keyword(s): Clinical trial, Fatigue, Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), Quality of life
Abstract: EP595
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Bone marrow failure syndromes incl. PNH - Clinical
Background
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare, acquired, life-threatening hematologic disease characterized by chronic complement-mediated red blood cell hemolysis. Current standard treatments for PNH are the C5 inhibitors eculizumab (ECU) or ravulizumab. Despite their proven efficacy in the control of intravascular hemolysis (IVH), up to 72% of patients experience persistent hemolysis leading to suboptimal hemoglobin (Hb) levels and 36% require transfusions despite ECU treatment which results in significant impact on quality of life (QoL), including persistent fatigue. Pegcetacoplan (PEG) is a C3 inhibitor that provides broad hemolysis control (including IVH and extravascular hemolysis) in patients with PNH.
Aims
This analysis evaluates QoL measures in the PEGASUS study (NCT03500549), a phase 3, open-label, randomized, active-comparator trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of PEG compared with ECU.
Methods
This study is an extension of the PEGASUS trial. PEGASUS enrolled patients ≥18 years of age with PNH and Hb levels <10.5 g/dL despite receiving treatment with ECU for ≥3 months. Patients entered a 4-week run-in period in which they received ECU plus twice-weekly PEG (1080 mg, administered subcutaneously) and were then randomized 1:1 to monotherapy with PEG or ECU for 16 weeks. Patients receiving ECU during the randomized controlled period entered another 4-week run-in period (ECU+PEG), before PEG monotherapy (groups: PEG-to-PEG and ECU-to-PEG). This was followed by an Open Label Period (OLP), in which all patients received pegcetacoplan monotherapy. The primary endpoint was change from baseline in Hb levels at Week 16, where PEG demonstrated superiority to ECU (Hillmen P et al, EHA 2020). Secondary endpoints included the QoL measures by the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire-Core 30 Scale (EORTC QLQ-C30) and Linear Analog Scale Assessment (LASA). The EORTC QLQ-C30 contains 30 questions comprising 5 functional, 9 individual symptom, and one global health status/QoL item(s). The LASA consists of 3 sections asking to rate the perceived level of functioning (scale 0-100) and contains specific domains for activity level, ability to carry out daily activities, and overall QoL.
Results
PEGASUS enrolled 80 patients (Peg, n=41; ECU, n=39). Overall, mean baseline scores of the EORTC QLQ-C30 functional and symptom scales were similar between groups. At Week 16, patients in the PEG group typically scored better than ECU (ECU only to Week 16) patients on various scales of the EORTC QLQ-C30 (Figure A). After receiving PEG monotherapy for 28 weeks (OLP), both groups showed improvements in all functional scales (Figure A) and the global health status/QoL at Week 48 (Figure B) and as indicated by an increase in the score from baseline. Improvements in the fatigue (Figure B) and dyspnea scales were also observed in both groups at Week 48 as indicated by a reduction in the symptom score close to the population norms (fatigue general population norm: 24.1 [22.7], dyspnea general population norm: 10.9 [20.6]). Mean total LASA scores increased in the PEG-to-PEG group as compared to the ECU-to-PEG group to Week 16 and after 28 Weeks of open-label PEG monotherapy the mean score was comparable between both groups at Week 48 (Figure A).

Conclusion
Although no statistical tests were performed on these QoL endpoints based on the trial protocol, substantial and clinically relevant improvements in QoL were consistently observed with PEG across both LASA and EORTC QLQ-C30 scores.
Keyword(s): Clinical trial, Fatigue, Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), Quality of life


