
Contributions
Abstract: EP577
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Bleeding disorders (congenital and acquired)
Background
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an autoimmune disease characterized by a low platelet count which is caused by increased destruction of thrombocytes due to platelet autoantibodies and impaired platelet production.The antibodies that aim at proteins within the nucleus of a cell are called antinuclear antibodies (ANA). ANA positivity was reported between 25-39 % in studies conducted with ITP patients. Thereafter; testing for ANA was suggested as a test of potential utility according to the International consensus report on the investigation and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia. The first-line treatment of ITP consists of corticosteroids and IVIG. In patients who are corticosteroids dependent or do not have a response to corticosteroids; recommended treatment options are thrombopoietin receptor agonists (TPO-RAs), splenectomy, and rituximab. Eltrombopag and romiplostim are the currently licensed TPO-RAs for ITP. Eltrombopag is an orally available non-peptide TPO-RA and accessible in Turkey.
Aims
Despite being widely used, markers to show the response for eltrombopag are lacking and needed. In the present study, we tried to show the association between ANA positivity and eltrombopag response in ITP patients.
Methods
Patients who were diagnosed with ITP at Trakya University Faculty of Medicine Hematology Department between 01.01.2016 and 31.12.2020 and who received eltrombopag treatment due to their resistance to steroids and other treatments were included in our study. ANA measurement was made with indirect fluorescent antibody and titers of 1:160 and above were considered positive. Response criteria are listed as follows:complete response (CR): platelet count ≥100 × 109 / L and no bleeding, response (R): platelet count ≥30 × 109 / L and no bleeding, no response: defined as platelet count <30 × 109 / L or bleeding. For statistical analysis, SPSS 22.0 was used and a two-sided p-value below or equal to 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Chi-square and Fisher's exact test was used in the analysis of variables. Chi-square contingency analysis was also performed due to lack of sample size.
Results
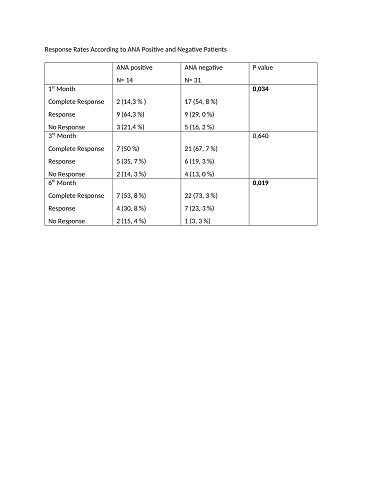
A total of 45 patients were included in our study. 33 were female and 12 were male. The mean age of the patients was 45, 73. There were 14 patients with ANA positivity and 31 patients found to be ANA negative. Response rates of the patients were evaluated according to their thrombocyte count during the treatment 1st month, 3rd month, and 6th month. One patient developed pulmonary emboli and grade 3 hyperbilirubinemia occurred in another patient while eltrombopag treatment and eltrombopag discontinued in both cases.Response rates were higher in ANA positive patients compared to ANA negative patients in the first and sixth months of the eltrombopag treatment (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Various autoimmune antibodies have been shown to be more positive in ITP patients than in people in the healthy normal population. Positive ANA test in ITP patients was associated with poor response to steroids and a more chronic disease outcome in retrospective studies. Our study population includes steroid resistant or dependent patients which could be a factor for low response rates seen in ANA positive patients. To conclude, ANA positivity in ITP may indicate unresponsiveness to eltrombopag treatment, and this should be supported by prospective studies involving more patients
Keyword(s): ITP, TPO
Abstract: EP577
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Bleeding disorders (congenital and acquired)
Background
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an autoimmune disease characterized by a low platelet count which is caused by increased destruction of thrombocytes due to platelet autoantibodies and impaired platelet production.The antibodies that aim at proteins within the nucleus of a cell are called antinuclear antibodies (ANA). ANA positivity was reported between 25-39 % in studies conducted with ITP patients. Thereafter; testing for ANA was suggested as a test of potential utility according to the International consensus report on the investigation and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia. The first-line treatment of ITP consists of corticosteroids and IVIG. In patients who are corticosteroids dependent or do not have a response to corticosteroids; recommended treatment options are thrombopoietin receptor agonists (TPO-RAs), splenectomy, and rituximab. Eltrombopag and romiplostim are the currently licensed TPO-RAs for ITP. Eltrombopag is an orally available non-peptide TPO-RA and accessible in Turkey.
Aims
Despite being widely used, markers to show the response for eltrombopag are lacking and needed. In the present study, we tried to show the association between ANA positivity and eltrombopag response in ITP patients.
Methods
Patients who were diagnosed with ITP at Trakya University Faculty of Medicine Hematology Department between 01.01.2016 and 31.12.2020 and who received eltrombopag treatment due to their resistance to steroids and other treatments were included in our study. ANA measurement was made with indirect fluorescent antibody and titers of 1:160 and above were considered positive. Response criteria are listed as follows:complete response (CR): platelet count ≥100 × 109 / L and no bleeding, response (R): platelet count ≥30 × 109 / L and no bleeding, no response: defined as platelet count <30 × 109 / L or bleeding. For statistical analysis, SPSS 22.0 was used and a two-sided p-value below or equal to 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Chi-square and Fisher's exact test was used in the analysis of variables. Chi-square contingency analysis was also performed due to lack of sample size.
Results
A total of 45 patients were included in our study. 33 were female and 12 were male. The mean age of the patients was 45, 73. There were 14 patients with ANA positivity and 31 patients found to be ANA negative. Response rates of the patients were evaluated according to their thrombocyte count during the treatment 1st month, 3rd month, and 6th month. One patient developed pulmonary emboli and grade 3 hyperbilirubinemia occurred in another patient while eltrombopag treatment and eltrombopag discontinued in both cases.Response rates were higher in ANA positive patients compared to ANA negative patients in the first and sixth months of the eltrombopag treatment (p < 0.05).

Conclusion
Various autoimmune antibodies have been shown to be more positive in ITP patients than in people in the healthy normal population. Positive ANA test in ITP patients was associated with poor response to steroids and a more chronic disease outcome in retrospective studies. Our study population includes steroid resistant or dependent patients which could be a factor for low response rates seen in ANA positive patients. To conclude, ANA positivity in ITP may indicate unresponsiveness to eltrombopag treatment, and this should be supported by prospective studies involving more patients
Keyword(s): ITP, TPO


