
Contributions
Abstract: EP569
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Bleeding disorders (congenital and acquired)
Background
The accuracy of pharmacokinetic (PK)-guided dosing of factor concentrates in hemophilia A and B patients is dependent on the clinical and laboratory data used to construct the applied population PK model, next to the individual PK profile of the patient.
Aims
This review aims to supply a detailed overview of the data used for these models as reported in literature and to evaluate best practice, in order to enable physicians to establish which models best suit the individual patient.
Methods
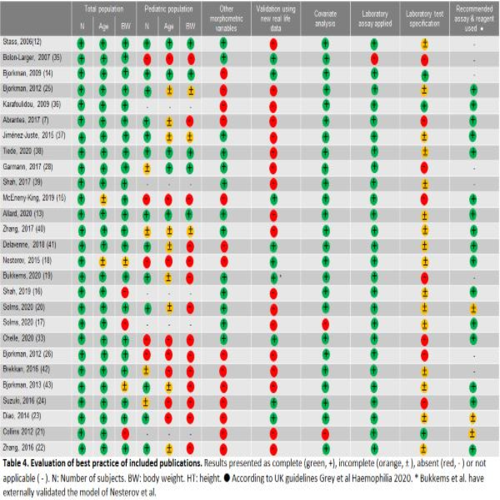
A literature search was performed on PubMed; publications describing prophylactic population PK models for factor VIII (FVIII) or factor IX (FIX) concentrates based on original patient data and constructed using non-linear mixed-effect modeling (NLMEM) were included. The following data was collected: detailed demographics of study populations, severity of hemophilia, type of product, assessed and included covariates, laboratory specifications and validation of models. According to our recommendations of best practice, included models were scored on 10 criteria as complete (+), incomplete (±) or absent (-) to evaluate their quality. Figure 1 depicts the evaluation of our best practice.
Results
This review comprehended twenty and seven models for FVIII and FIX concentrates respectively. Although most models (22/27) included pediatric patient, only four models reported complete pediatric demographics. The wide range of body weight suggested that overweight and obese adults were represented in the models. However, other morphometric variables (mostly BMI) were described in only 13/27 publications. Almost all models (26/27) reported the applied assay to measure the factor level, whereas only 15 models specified the reagent. Eight models were validated using a second dataset.
Conclusion
This evaluation of available prophylactic population PK models for FVIII and FIX shows a wide variation in detail of included clinical and laboratory data used to construct these models. We provide an overview and give recommendations with regard to best practice to increase the reliability of PK-guided dosing of factor concentrates for prophylaxis in hemophilia A and B.
Keyword(s): Factor IX, Factor VIII, Hemophilia, Pharmacokinetic
Abstract: EP569
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Bleeding disorders (congenital and acquired)
Background
The accuracy of pharmacokinetic (PK)-guided dosing of factor concentrates in hemophilia A and B patients is dependent on the clinical and laboratory data used to construct the applied population PK model, next to the individual PK profile of the patient.
Aims
This review aims to supply a detailed overview of the data used for these models as reported in literature and to evaluate best practice, in order to enable physicians to establish which models best suit the individual patient.
Methods
A literature search was performed on PubMed; publications describing prophylactic population PK models for factor VIII (FVIII) or factor IX (FIX) concentrates based on original patient data and constructed using non-linear mixed-effect modeling (NLMEM) were included. The following data was collected: detailed demographics of study populations, severity of hemophilia, type of product, assessed and included covariates, laboratory specifications and validation of models. According to our recommendations of best practice, included models were scored on 10 criteria as complete (+), incomplete (±) or absent (-) to evaluate their quality. Figure 1 depicts the evaluation of our best practice.
Results
This review comprehended twenty and seven models for FVIII and FIX concentrates respectively. Although most models (22/27) included pediatric patient, only four models reported complete pediatric demographics. The wide range of body weight suggested that overweight and obese adults were represented in the models. However, other morphometric variables (mostly BMI) were described in only 13/27 publications. Almost all models (26/27) reported the applied assay to measure the factor level, whereas only 15 models specified the reagent. Eight models were validated using a second dataset.

Conclusion
This evaluation of available prophylactic population PK models for FVIII and FIX shows a wide variation in detail of included clinical and laboratory data used to construct these models. We provide an overview and give recommendations with regard to best practice to increase the reliability of PK-guided dosing of factor concentrates for prophylaxis in hemophilia A and B.
Keyword(s): Factor IX, Factor VIII, Hemophilia, Pharmacokinetic


