
Contributions
Abstract: EP502
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Aggressive Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
Ibrutinib is a first-in-class, potent, orally-administered covalently-binding small molecule, an inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK). It was found to be effective in Diffuse large B cell lymphoma Lymphoma (DLBCL) specifically of the Activated (ABC) type. Ibrutinib, bendamustine, and rituximab (IBR) combination was found to be effective for the treatment of B cell lymphomas, including DLBCL in phase I clinical trial.
Aims
To explore the efficacy of the IBR regimen in relapse & refractory (RR) DLBCL.
Methods
We performed a phase II single-center trial. Patients (pts) with RR DLBCL and transformed low-grade lymphoma were eligible. Patients with CNS lymphoma, inadequate bone marrow function or previous exposure to bendamustine or ibrutinib were excluded. FDG/PET-CT's were interpreted according to the Lugano criteria. Rituximab and bendamustine were given in a 28 days cycle in their standard dose. Ibrutinib 560 mg, was administered continuously from day 1. FDG/PET-CT was repeated afters cycles 3 and 6, and then every 16 weeks. Patients who achieved response after 3 cycles and were eligible were reffered to stem cell transplantation (SCT). For the time of this analysis, 62 pts were screened, and 56 were treated.
Results
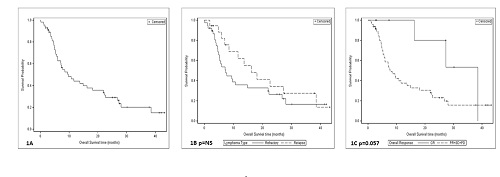
Thiry pts (54%) were male. Median age was 69.7 years ( 28-94). Lymphoma subtype which was defined by the Hans criteria was as follows : GCB in 7 (12.5%), non GCB in 21 (37.5%), double/triple hit in 9 (16.1%), follicular grade 3B in 2 (3.6%), mediastinal in 3 (5.4%) transformed low grade in 4 (7.1%) and NA in 10 (17.9%). Thirty eight pts had refractory disease (67.9%). Thirty patiens (53%) had stage IV disease at screening. Sixteen pts received the therapy as second line and 40 as third line. Nine pts (16.1%) had previous autologous stem cell transplantation. ORR was 27.2% for the entire cohort and 36.1% for the pts that completed 3 cycles of therapy (n=36). Only 19% of the non-GCB pts responded to treatment. Thiry nine pts died during follow-up, 36 of them due to disease progression, the others due to stroke, myocardial infarction and allogeneic stem cell transplantation complications. Median follow-up was 7.9 months. Median OS of the entire cohort was 9.7 months (figure 1A). Refractoy pts had median OS of 7.3 months, while relapsed pts had 16.2 (figure 1B p=NS).Patients who achieved CR had median OS of 38.5 months while those who did not had 7.7 (p=0.057 figure 1C).Median PFS of the enitre chorot was 5 months and for the pts that completed at least 3 cycles of therapy 7 months. Patients that achieved response had significantly longer PFS than others ( p<0.0001). Five pts underwent either autologous or allogeneic SCT after 3 cycles of treatment, all of them are alive and 4 in remission. Altogether 37 serious adverse event (SAE) were recorded in 20 pts (35.7%). Fifteen of them were related to ibrutinib, and the most common were infections.
Conclusion
The IBR protocol is a conveniently administered ambulatory regimen. The regimen was found to be safe and effective in this cohort of elderly pts whose disease was mostly refractory to previous lines of treatment. Patients that achieved response had significantly better PFS and OS than those who did not. Response rate in the non-GCB group was not better than all other subtypes. Although the median OS of the entire cohort is short, pts who achieved remission and underwent SCT survived so far. We conclude that the IBR regimen should be considered for the treatment of R/R DLBCL pts and can also serve as a bridge to transplant.
Keyword(s): Bendamustine, Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Ibrutinib, Phase II
Abstract: EP502
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Aggressive Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
Ibrutinib is a first-in-class, potent, orally-administered covalently-binding small molecule, an inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK). It was found to be effective in Diffuse large B cell lymphoma Lymphoma (DLBCL) specifically of the Activated (ABC) type. Ibrutinib, bendamustine, and rituximab (IBR) combination was found to be effective for the treatment of B cell lymphomas, including DLBCL in phase I clinical trial.
Aims
To explore the efficacy of the IBR regimen in relapse & refractory (RR) DLBCL.
Methods
We performed a phase II single-center trial. Patients (pts) with RR DLBCL and transformed low-grade lymphoma were eligible. Patients with CNS lymphoma, inadequate bone marrow function or previous exposure to bendamustine or ibrutinib were excluded. FDG/PET-CT's were interpreted according to the Lugano criteria. Rituximab and bendamustine were given in a 28 days cycle in their standard dose. Ibrutinib 560 mg, was administered continuously from day 1. FDG/PET-CT was repeated afters cycles 3 and 6, and then every 16 weeks. Patients who achieved response after 3 cycles and were eligible were reffered to stem cell transplantation (SCT). For the time of this analysis, 62 pts were screened, and 56 were treated.
Results
Thiry pts (54%) were male. Median age was 69.7 years ( 28-94). Lymphoma subtype which was defined by the Hans criteria was as follows : GCB in 7 (12.5%), non GCB in 21 (37.5%), double/triple hit in 9 (16.1%), follicular grade 3B in 2 (3.6%), mediastinal in 3 (5.4%) transformed low grade in 4 (7.1%) and NA in 10 (17.9%). Thirty eight pts had refractory disease (67.9%). Thirty patiens (53%) had stage IV disease at screening. Sixteen pts received the therapy as second line and 40 as third line. Nine pts (16.1%) had previous autologous stem cell transplantation. ORR was 27.2% for the entire cohort and 36.1% for the pts that completed 3 cycles of therapy (n=36). Only 19% of the non-GCB pts responded to treatment. Thiry nine pts died during follow-up, 36 of them due to disease progression, the others due to stroke, myocardial infarction and allogeneic stem cell transplantation complications. Median follow-up was 7.9 months. Median OS of the entire cohort was 9.7 months (figure 1A). Refractoy pts had median OS of 7.3 months, while relapsed pts had 16.2 (figure 1B p=NS).Patients who achieved CR had median OS of 38.5 months while those who did not had 7.7 (p=0.057 figure 1C).Median PFS of the enitre chorot was 5 months and for the pts that completed at least 3 cycles of therapy 7 months. Patients that achieved response had significantly longer PFS than others ( p<0.0001). Five pts underwent either autologous or allogeneic SCT after 3 cycles of treatment, all of them are alive and 4 in remission. Altogether 37 serious adverse event (SAE) were recorded in 20 pts (35.7%). Fifteen of them were related to ibrutinib, and the most common were infections.

Conclusion
The IBR protocol is a conveniently administered ambulatory regimen. The regimen was found to be safe and effective in this cohort of elderly pts whose disease was mostly refractory to previous lines of treatment. Patients that achieved response had significantly better PFS and OS than those who did not. Response rate in the non-GCB group was not better than all other subtypes. Although the median OS of the entire cohort is short, pts who achieved remission and underwent SCT survived so far. We conclude that the IBR regimen should be considered for the treatment of R/R DLBCL pts and can also serve as a bridge to transplant.
Keyword(s): Bendamustine, Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Ibrutinib, Phase II


