
Contributions
Abstract: EP481
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Background
The combination of venetoclax (Ven) with hypomethylating agents (VenHMA) has shown promising results both in newly diagnosed and relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) patients, ineligible for intensive chemotherapy. Due to our expertise acquired in at-home management of diverse complex haematological procedures, we initiated in February 2020 an at-home (AH) programme for the VenHMA regimen. This AH-VenHMA programme included the initial dose ramp-up to prevent tumour lysis syndrome (TLS), a phase usually recommended to be performed as an inpatient hospital admission.
Aims
Herein we present preliminary results of our AH experience during the first two cycles of VenHMA treatment for AML patients.
Methods
Before implementation of AH-VenH programme, ramp-up was performed during a hospital admission (n=29, reference cohort). In Feb 2020, we initiated the VenH programme; outcome of in this patient cohort are compared with the reference cohort.
In AH programme, prior to VenHMA initiation, medical evaluation is performed by a haematologist and a liaison nurse. Medical history, potential drug interactions and TLS risk are thoroughly evaluated. Laboratory tests (LT) including blood count and biochemistry are completed. Extensive health education is provided to patient and caregiver before the first cycle.
A peripheral insertion intravenous catheter (PICC) is placed to all patients before starting ramp-up. Intravenous (IV) fluids by a portable pump (PP) are started 24hrs before the beginning of VenHMA, as well as uricosurics agents; patients are advised to maintain oral hydration. Daily morning visits during ramp-up are performed by trained nurses who complete vital sign, obtain LT, review therapeutic compliance, replaced PP and administer hypomethylating agent. Patients are started on Ven in an escalation schedule of 100mg on day 1, 200mg on day 2, and 400mg on day 3 of the cycle, they are advised to take Ven after dinner, following an explicit indication of our team given after daily LT review. An appropriate dose reduction is performed in patients receiving concomitantly CYP3A4 inhibitors. After achieving planned Ven full dose, IV fluids are ceased (Image 1). Patients are followed throughout the whole cycle by the AH team. Platelet transfusions are administered at-home while red cell concentrates are administered at the hospital, due to our transfusion policy.
Results
Between February 2020 and January 2021, 22 AML patients (40 cycles) received VenHMA at-home. Fourteen patients were men (63.6%), with a median age of 73 years (23-83). Main characteristics were well balance in both patient cohorts.
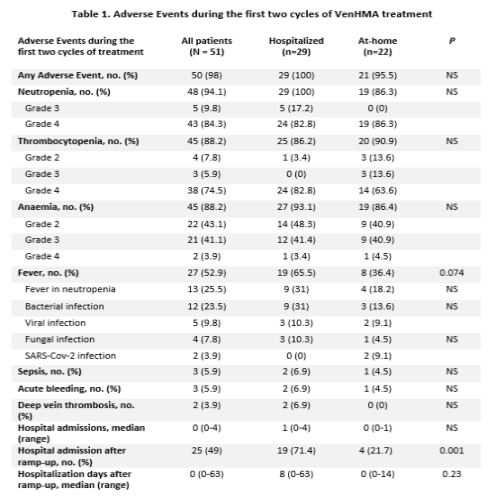
Neutropenia (86.3%), thrombocytopenia (90.9%) and anaemia (86.4%) were the most frequent adverse events (AEs). A trend to a lower proportion of febrile episodes was observed in the AH program (19/29 vs. 8/22, p=0.074). Hospital readmission rate after ramp-up was markedly low in the AH cohort, significantly lower than in the reference cohort (4/22 vs. 19/29, p = 0.001). TLS was not observed in any group. Main AEs are shown in table 1. Median days of at-home treatment were 49 (19-187). Discontinuation was due to refractoriness in 5 (22.7%) patients. Two patients presented SARS-CoV-2 infection in early March 2020, resulting in death in both cases.
Conclusion
Home care during the ramp-up and early phase of VenHEM regimen is a feasible and safe option. An AH programme was followed by a low readmission rate and offers diverse benefits such as optimization of health resources and increase of the comfort and well-being of patients and their caregivers.
Keyword(s): AML, Neutropenia, Treatment
Abstract: EP481
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Background
The combination of venetoclax (Ven) with hypomethylating agents (VenHMA) has shown promising results both in newly diagnosed and relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) patients, ineligible for intensive chemotherapy. Due to our expertise acquired in at-home management of diverse complex haematological procedures, we initiated in February 2020 an at-home (AH) programme for the VenHMA regimen. This AH-VenHMA programme included the initial dose ramp-up to prevent tumour lysis syndrome (TLS), a phase usually recommended to be performed as an inpatient hospital admission.
Aims
Herein we present preliminary results of our AH experience during the first two cycles of VenHMA treatment for AML patients.
Methods
Before implementation of AH-VenH programme, ramp-up was performed during a hospital admission (n=29, reference cohort). In Feb 2020, we initiated the VenH programme; outcome of in this patient cohort are compared with the reference cohort.
In AH programme, prior to VenHMA initiation, medical evaluation is performed by a haematologist and a liaison nurse. Medical history, potential drug interactions and TLS risk are thoroughly evaluated. Laboratory tests (LT) including blood count and biochemistry are completed. Extensive health education is provided to patient and caregiver before the first cycle.
A peripheral insertion intravenous catheter (PICC) is placed to all patients before starting ramp-up. Intravenous (IV) fluids by a portable pump (PP) are started 24hrs before the beginning of VenHMA, as well as uricosurics agents; patients are advised to maintain oral hydration. Daily morning visits during ramp-up are performed by trained nurses who complete vital sign, obtain LT, review therapeutic compliance, replaced PP and administer hypomethylating agent. Patients are started on Ven in an escalation schedule of 100mg on day 1, 200mg on day 2, and 400mg on day 3 of the cycle, they are advised to take Ven after dinner, following an explicit indication of our team given after daily LT review. An appropriate dose reduction is performed in patients receiving concomitantly CYP3A4 inhibitors. After achieving planned Ven full dose, IV fluids are ceased (Image 1). Patients are followed throughout the whole cycle by the AH team. Platelet transfusions are administered at-home while red cell concentrates are administered at the hospital, due to our transfusion policy.
Results
Between February 2020 and January 2021, 22 AML patients (40 cycles) received VenHMA at-home. Fourteen patients were men (63.6%), with a median age of 73 years (23-83). Main characteristics were well balance in both patient cohorts.
Neutropenia (86.3%), thrombocytopenia (90.9%) and anaemia (86.4%) were the most frequent adverse events (AEs). A trend to a lower proportion of febrile episodes was observed in the AH program (19/29 vs. 8/22, p=0.074). Hospital readmission rate after ramp-up was markedly low in the AH cohort, significantly lower than in the reference cohort (4/22 vs. 19/29, p = 0.001). TLS was not observed in any group. Main AEs are shown in table 1. Median days of at-home treatment were 49 (19-187). Discontinuation was due to refractoriness in 5 (22.7%) patients. Two patients presented SARS-CoV-2 infection in early March 2020, resulting in death in both cases.

Conclusion
Home care during the ramp-up and early phase of VenHEM regimen is a feasible and safe option. An AH programme was followed by a low readmission rate and offers diverse benefits such as optimization of health resources and increase of the comfort and well-being of patients and their caregivers.
Keyword(s): AML, Neutropenia, Treatment


