
Contributions
Abstract: EP454
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Background
MLL-PTD is a special MLL rearrangement gene that occurs in about 5-10% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with a normal karyotype and in 5-6% of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) is currently one of the curative therapies available for AML and MDS with excess blasts (MDS-EB). However, how the prognosis of patients with high levels of MLL-PTD after allo-HSCT, including AML and MDS, and whether MLL-PTD could be used as a reliable indicator for minimal residual disease (MRD) monitoring in transplant patients remains unknown.
Aims
Our study purposed to analyze the dynamic changes of MLL-PTD peri-transplantation and the best threshold for predicting relapse after transplantation.
Methods
We retrospectively collected the clinical data of 48 patients with MLL-PTD AML or MDS-EB who underwent allo-HSCT in Peking University People’s Hospital. The MLL-PTD was examined by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR) at the diagnosis, before transplantation and the fixed time points after transplantation. Detectable MLL-PTD/ABL>0.08% was defined as MLL-PTD positive in this study.
Results
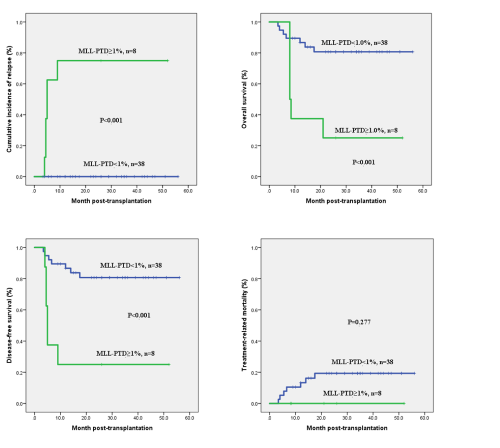
The 48 patients included 33 AML patients and 15 MDS-EB patients. The median follow-up time was 26(0.7-56) months after HSCT. In AML patients, 7 patients (21.2%) died of TRM, 6 patients (18.2%) underwent hematological relapse and died ultimately. Of the 15 patients with MDS-EB, 2 patients (13.3%) died of infection. The 3-year cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR), overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS) and treatment-related mortality (TRM) were 13.7%±5.2%, 67.8%±6.9%, 68.1%±6.8% and 20.3%±6.1%, respectively. ROC curve showed that post-transplant MLL-PTD≥1.0% was the optimal cut-off value for predicting hematological relapse after allo-HSCT. There was statistical difference between post-transplant MLL-PTD≥1.0% and MLL-PTD<1.0% groups (3-year CIR: 75%±15.3% vs. 0%, P<0.001; 3-year OS: 25.0±15.3% vs. 80.7%±6.6%, P<0.001; 3-year DFS: 25.0±15.3% vs. 80.7%±6.6%, P<0.001; 3-year TRM: 0 vs. 19.3±6.6%, P=0.277). However, whether MLL-PTD≥1% or MLL-PTD<1% before transplantation has no significant difference on the prognosis.
Conclusion
Our study indicated that MLL-PTD had a certain stability and could effectively reflect the change of tumor burden. The expression level of MLL-PTD after transplantation can serve as an effective indicator for predicting relapse.
Keyword(s): Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, Gene expression, Minimal residual disease (MRD), Relapse
Abstract: EP454
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Background
MLL-PTD is a special MLL rearrangement gene that occurs in about 5-10% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with a normal karyotype and in 5-6% of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) is currently one of the curative therapies available for AML and MDS with excess blasts (MDS-EB). However, how the prognosis of patients with high levels of MLL-PTD after allo-HSCT, including AML and MDS, and whether MLL-PTD could be used as a reliable indicator for minimal residual disease (MRD) monitoring in transplant patients remains unknown.
Aims
Our study purposed to analyze the dynamic changes of MLL-PTD peri-transplantation and the best threshold for predicting relapse after transplantation.
Methods
We retrospectively collected the clinical data of 48 patients with MLL-PTD AML or MDS-EB who underwent allo-HSCT in Peking University People’s Hospital. The MLL-PTD was examined by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR) at the diagnosis, before transplantation and the fixed time points after transplantation. Detectable MLL-PTD/ABL>0.08% was defined as MLL-PTD positive in this study.
Results
The 48 patients included 33 AML patients and 15 MDS-EB patients. The median follow-up time was 26(0.7-56) months after HSCT. In AML patients, 7 patients (21.2%) died of TRM, 6 patients (18.2%) underwent hematological relapse and died ultimately. Of the 15 patients with MDS-EB, 2 patients (13.3%) died of infection. The 3-year cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR), overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS) and treatment-related mortality (TRM) were 13.7%±5.2%, 67.8%±6.9%, 68.1%±6.8% and 20.3%±6.1%, respectively. ROC curve showed that post-transplant MLL-PTD≥1.0% was the optimal cut-off value for predicting hematological relapse after allo-HSCT. There was statistical difference between post-transplant MLL-PTD≥1.0% and MLL-PTD<1.0% groups (3-year CIR: 75%±15.3% vs. 0%, P<0.001; 3-year OS: 25.0±15.3% vs. 80.7%±6.6%, P<0.001; 3-year DFS: 25.0±15.3% vs. 80.7%±6.6%, P<0.001; 3-year TRM: 0 vs. 19.3±6.6%, P=0.277). However, whether MLL-PTD≥1% or MLL-PTD<1% before transplantation has no significant difference on the prognosis.

Conclusion
Our study indicated that MLL-PTD had a certain stability and could effectively reflect the change of tumor burden. The expression level of MLL-PTD after transplantation can serve as an effective indicator for predicting relapse.
Keyword(s): Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, Gene expression, Minimal residual disease (MRD), Relapse


