
Contributions
Abstract: EP440
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Background
Cytogenetic risk (CGR) is an important prognostic factor in AML, but its role is less established for VEN based lower intensity therapy.
Aims
To determine the prognostic impact of CGR in pts treated with DEC10-VEN (NCT03404193)
Methods
Older pts with newly diagnosed (ND) (>60 years) and adult pts >18 years with secondary AML (sAML) with or without prior therapy, and relapsed/refractory (R/R) AML, with ECOG performance status <3 without prior BCL-2 inhibitor exposure were enrolled. Patients received 10-day decitabine at 20 mg/m2/day for induction followed by 5-days for consolidation. VEN dose was 400 mg PO daily or equivalent. Cytogenetic subgroups, response and outcomes were per ELN2017 criteria. Written informed consent was obtained from all pts.
Results
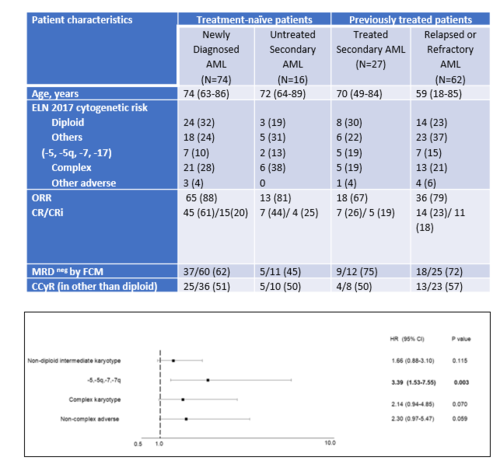
We included 179 pts including ND (N=74), untreated sAML (N=16), treated sAML (N=27), and R/R AML (N=62). The median age was 71 yrs (range 59-74 yrs). Overall response rate was 74% in the entire cohort, and negative MRD by flow cytometry was attained in 69 (64%) of 108 responding pts. In the treatment naïve cohort: the CR/CRi was 88% in diploid, 92% in non-diploid intermediate, 67% with abnormalities of chr 5,7,17, 66% in complex, and 66% in non-complex karyotype abnormalities and 63%,73%,11%,22%,26% CR in the pretreated cohort. On multivariable analysis: compared to diploid CG, pts with complex (OR 0.17; 95% CI 0.06,0.48; P <.001) and non-complex adverse (OR 0.07; 95% CI 0.01, 0.76; P=.028) groups are significantly less likely to achieve CR, and patients harboring Chr 5,7,17 abnormalities were significantly less likely to achieve CR/CRi (OR 0.17; 95% CI 0.05,0.65; P=.009), and at increased chance of death (HR 3.39; 95% CI 1.53, 7.55; P=.003). In the treatment naïve cohort, the median OS was 29.6 months (95% CI 0.6 to 3.7 mo) in diploid, 19.4 mo (95% CI 0.3 to 1.6 mo) in non-diploid intermediate;9.3 mo in in Chr 5,7,17 subgroup,6.9 mo in complex and 17.1 mo in the non-complex adverse subgroup. In the previously treated cohort, the median OS was 13.7 mo (95% CI 0.6 to 2.7 mo) with diploid,11.1 mo (95% CI 0.4 to 1.8 mo) in non-diploid intermediate (95% CI 0.4 to 1.8 mo),7.1 mo in Chr 5,7,17 subgroup, 4.9 mo in complex, and 6.8 mo in non-complex adverse group. Achievement of complete cytogenetic response (CCyR) was an independent predictor of improved OS compared to those who did not achieve CCyR (mOS 16.2 vs. 8.0 mo, HR 0.4, 95% CI 0.2, 0.9, p=.01).
Conclusion
CGR remain highly prognostic for response and survival, with CCyR conferring significant survival benefit in pts with AML receiving DEC10-VEN.
Keyword(s): AML, Cytogenetics, Prognosis, Treatment
Abstract: EP440
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Background
Cytogenetic risk (CGR) is an important prognostic factor in AML, but its role is less established for VEN based lower intensity therapy.
Aims
To determine the prognostic impact of CGR in pts treated with DEC10-VEN (NCT03404193)
Methods
Older pts with newly diagnosed (ND) (>60 years) and adult pts >18 years with secondary AML (sAML) with or without prior therapy, and relapsed/refractory (R/R) AML, with ECOG performance status <3 without prior BCL-2 inhibitor exposure were enrolled. Patients received 10-day decitabine at 20 mg/m2/day for induction followed by 5-days for consolidation. VEN dose was 400 mg PO daily or equivalent. Cytogenetic subgroups, response and outcomes were per ELN2017 criteria. Written informed consent was obtained from all pts.
Results
We included 179 pts including ND (N=74), untreated sAML (N=16), treated sAML (N=27), and R/R AML (N=62). The median age was 71 yrs (range 59-74 yrs). Overall response rate was 74% in the entire cohort, and negative MRD by flow cytometry was attained in 69 (64%) of 108 responding pts. In the treatment naïve cohort: the CR/CRi was 88% in diploid, 92% in non-diploid intermediate, 67% with abnormalities of chr 5,7,17, 66% in complex, and 66% in non-complex karyotype abnormalities and 63%,73%,11%,22%,26% CR in the pretreated cohort. On multivariable analysis: compared to diploid CG, pts with complex (OR 0.17; 95% CI 0.06,0.48; P <.001) and non-complex adverse (OR 0.07; 95% CI 0.01, 0.76; P=.028) groups are significantly less likely to achieve CR, and patients harboring Chr 5,7,17 abnormalities were significantly less likely to achieve CR/CRi (OR 0.17; 95% CI 0.05,0.65; P=.009), and at increased chance of death (HR 3.39; 95% CI 1.53, 7.55; P=.003). In the treatment naïve cohort, the median OS was 29.6 months (95% CI 0.6 to 3.7 mo) in diploid, 19.4 mo (95% CI 0.3 to 1.6 mo) in non-diploid intermediate;9.3 mo in in Chr 5,7,17 subgroup,6.9 mo in complex and 17.1 mo in the non-complex adverse subgroup. In the previously treated cohort, the median OS was 13.7 mo (95% CI 0.6 to 2.7 mo) with diploid,11.1 mo (95% CI 0.4 to 1.8 mo) in non-diploid intermediate (95% CI 0.4 to 1.8 mo),7.1 mo in Chr 5,7,17 subgroup, 4.9 mo in complex, and 6.8 mo in non-complex adverse group. Achievement of complete cytogenetic response (CCyR) was an independent predictor of improved OS compared to those who did not achieve CCyR (mOS 16.2 vs. 8.0 mo, HR 0.4, 95% CI 0.2, 0.9, p=.01).

Conclusion
CGR remain highly prognostic for response and survival, with CCyR conferring significant survival benefit in pts with AML receiving DEC10-VEN.
Keyword(s): AML, Cytogenetics, Prognosis, Treatment


