
Contributions
Abstract: EP401
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute myeloid leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Background
In a phase 2 clinical trial in patients with relapsed/refractory AML, combining azacitidine with nivolumab demonstrated encouraging response rates (33%), median event-free and overall survival, compared with a historical cohort of contemporary patients treated with azacitidine-based therapies. Biomarkers of response are yet to be determined.
Aims
In this sudy, we aimed to identify biomarkers of response to nivolumab-based therapy using single cell polyfunctional proteomic assays.
Methods
Eleven non-responders and 5 responders to treatment based on ELN2017 response criteria had available samples and were analyzed. Bone marrow samples were collected prior to and at end of second treatment cycle. A total Polyfunctional T cells co-secreting 2+ cytokines were assessed with the 32-plex proteomics. The polyfunctional strength Index (PSI) of single T cells was computed as the percentage of polyfunctional cells, multiplied by mean fluorescence intensity of the proteins secreted by those cells.
Results
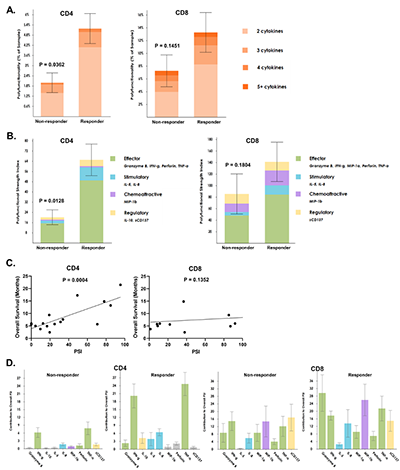
A total of 16 patients (5 CR/CRi and 11 non-responders) with R/R AML who received a median of 3 (range 2-17) cycles and a median of 11 (range 3-33) doses of nivolumab were analyzed (Table 1). The pretreatment bone marrow CD4+ but not CD8+ T cells had significantly higher frequency of polyfunctional cells (p=0.04 and 0.15, respectively) and significantly higher PSI (p=0.01 and 0.18, respectively) in responders compared with non-responders (Figure 1A-B). Also, pretreatment bone marrow PSI of CD4+ (P<0.001) but not CD8+ (P=0.14) subsets demonstrated a significant positive association with overall survival (OS) across all patients, likely partly driven by response enrichment, suggesting that the degree of polyfunctional state of CD4+ cells may potentially also predict outcomes in AML patients treated with azacitidine/nivolumab (Figure 1C). Further evaluation of the PSI composition across cell types revealed that IFN-g and TNF-a were the major drivers of enhanced PSI of pretherapy CD4+ subset, whereas Granzyme B, IFN-g, MIP-1b and TNF-a drove the non-significantly enhanced pretreatment PSI of CD8+ subset in the responders (Figure 1D). Using t-SNE dimension reduction, CD4+ and CD8+ cells from responders and non-responders had distinct clustering patterns. Highly polyfunctional groups clustered together in both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. The most dominant functional group across CD4+ and CD8+ cells was the effector protein pattern, which was more notable in the pretreatment bone marrows of responders compared to non-responders and also corresponded to the highly polyfunctional group. Compared to non-responders, the pretherapy CD4+ T cells of responders had more distinct and unique polyfunctional groups (green rectangles) such as co-expression of TNF-a/IFN-g/IL-8, TNF-a/IFN-g/Granzyme B or TNF-a/IFN-g/Perforin/IL-8 proteins.
Conclusion
The single-cell multiplexed functional proteomics precision profiling demonstrated that the pretreatment PSI of CD4+ cells was significantly associated with response and OS in relapsed patients treated with azacitidine/nivolumab and should be evaluated prospectively to ascertain whether this could be an effective biomarker to select AML patients for PD-1 based therapies. Pretreatment PSI may have a potential role as a biomarker in the wider sphere of immunotherapy in AML. Such analyses are warranted and encouraged.
Keyword(s):
Abstract: EP401
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute myeloid leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Background
In a phase 2 clinical trial in patients with relapsed/refractory AML, combining azacitidine with nivolumab demonstrated encouraging response rates (33%), median event-free and overall survival, compared with a historical cohort of contemporary patients treated with azacitidine-based therapies. Biomarkers of response are yet to be determined.
Aims
In this sudy, we aimed to identify biomarkers of response to nivolumab-based therapy using single cell polyfunctional proteomic assays.
Methods
Eleven non-responders and 5 responders to treatment based on ELN2017 response criteria had available samples and were analyzed. Bone marrow samples were collected prior to and at end of second treatment cycle. A total Polyfunctional T cells co-secreting 2+ cytokines were assessed with the 32-plex proteomics. The polyfunctional strength Index (PSI) of single T cells was computed as the percentage of polyfunctional cells, multiplied by mean fluorescence intensity of the proteins secreted by those cells.
Results
A total of 16 patients (5 CR/CRi and 11 non-responders) with R/R AML who received a median of 3 (range 2-17) cycles and a median of 11 (range 3-33) doses of nivolumab were analyzed (Table 1). The pretreatment bone marrow CD4+ but not CD8+ T cells had significantly higher frequency of polyfunctional cells (p=0.04 and 0.15, respectively) and significantly higher PSI (p=0.01 and 0.18, respectively) in responders compared with non-responders (Figure 1A-B). Also, pretreatment bone marrow PSI of CD4+ (P<0.001) but not CD8+ (P=0.14) subsets demonstrated a significant positive association with overall survival (OS) across all patients, likely partly driven by response enrichment, suggesting that the degree of polyfunctional state of CD4+ cells may potentially also predict outcomes in AML patients treated with azacitidine/nivolumab (Figure 1C). Further evaluation of the PSI composition across cell types revealed that IFN-g and TNF-a were the major drivers of enhanced PSI of pretherapy CD4+ subset, whereas Granzyme B, IFN-g, MIP-1b and TNF-a drove the non-significantly enhanced pretreatment PSI of CD8+ subset in the responders (Figure 1D). Using t-SNE dimension reduction, CD4+ and CD8+ cells from responders and non-responders had distinct clustering patterns. Highly polyfunctional groups clustered together in both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. The most dominant functional group across CD4+ and CD8+ cells was the effector protein pattern, which was more notable in the pretreatment bone marrows of responders compared to non-responders and also corresponded to the highly polyfunctional group. Compared to non-responders, the pretherapy CD4+ T cells of responders had more distinct and unique polyfunctional groups (green rectangles) such as co-expression of TNF-a/IFN-g/IL-8, TNF-a/IFN-g/Granzyme B or TNF-a/IFN-g/Perforin/IL-8 proteins.

Conclusion
The single-cell multiplexed functional proteomics precision profiling demonstrated that the pretreatment PSI of CD4+ cells was significantly associated with response and OS in relapsed patients treated with azacitidine/nivolumab and should be evaluated prospectively to ascertain whether this could be an effective biomarker to select AML patients for PD-1 based therapies. Pretreatment PSI may have a potential role as a biomarker in the wider sphere of immunotherapy in AML. Such analyses are warranted and encouraged.
Keyword(s):


