
Contributions
Abstract: EP347
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Clinical
Background
Novel recurrent fusion gene types such as zinc finger protein 384 (ZNF384) fusions have been identified in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL) with the application of next-generation sequencing technologies. However, the comprehensive large-scale clinical cohort study for clarifying their prognostic significance remains scarce to date.
Aims
To comprehensively evaluate the prognostic role of ZNF384 fusions in adult BCP-ALL.
Methods
A total of 242 consecutive adult Ph-negative BCP-ALL patients treated in our institute were retrospectively screened ZNF384 fusions at diagnosis by multiplex real time quantitative PCR.
Results
ZNF384 fusions were identified in 47 patients (19.4%), 38 had EP300-ZNF384, 5 had CREBBP-ZNF384, 2 had TCF3-ZNF384, 1 had TAF15-ZNF384 and 1 had EWSR1-ZNF384. All patients with ZNF384 fusions belonged to B-other ALL (having no high hyperdiploid karyotype, BCR-ABL1, TCF3-PBX1, ETV6-RUNX1 or MLL rearrangement).
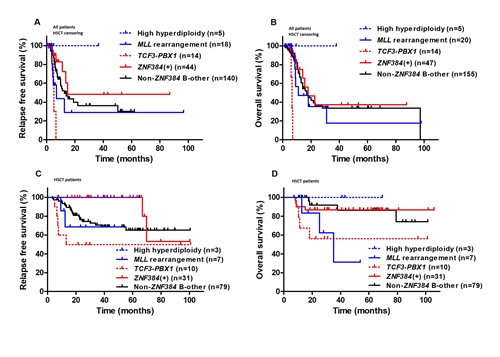
In the whole cohort, patients with ZNF384 fusions had significantly higher 3-year relapse-free-survival (RFS) and tended to have a higher 3-year overall survival (OS) than those with no ZNF384 fusions (80.1% vs 52.5%, P = 0.011; 67.6% vs 54.0%, P = 0.10). For both patients receiving chemotherapy alone and when patients who received allo-HSCT were censored at the time of transplantation (Figure A, B), patients with ZNF384 fusions had both similar RFS rate and similar OS rate to B-other ALL patients with no ZNF384 fusions (RFS: P =0.94 and 0.30; OS: P =0.94 and 0.51). Furthermore, for patients receiving chemotherapy alone, patients with ZNF384 fusions had both similar RFS and similar OS to those with MLL rearrangement and TCF3-PBX1 fusion transcript, respectively (RFS: P = 0.45 and 0.13; OS: P = 0.80 and 0.45). When patients who received allo-HSCT were censored at the time of transplantation, patients with ZNF384 fusions had significantly higher 3-year RFS and OS than those with TCF3-PBX1 fusion transcript (P=0.0093 and 0.0009), and significantly higher 3-year RFS than and similar 3-year OS to those with MLL rearrangement (P=0.036 and 0.80). For patients receiving transplantation (Figure C, D), those with ZNF384 fusions had significantly higher 3-year RFS than B-other ALL patients with no ZNF384 fusions and their OS were similar (P = 0.022 and 0.24). Furthermore, patients with ZNF384 fusions had significantly higher 3-year RFS and tended to have significant high OS than those with MLL rearrangement and TCF3-PBX1 fusion transcript, respectively (RFS: P = 0.0026 and 0.0038; OS: P = 0.062 and 0.065). In addition, ZNF384 fusion was not an independent prognostic factor for both RFS and OS in both adult Ph-negative BCP-ALL and B-other patients.
Conclusion
ZNF384 fusion is common in adult BCP-ALL, which may define a new group from BCP-ALL containing no classical fusion transcript with better prognosis through receiving allo-HSCT.
Keyword(s): Adult, B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Fusion, Prognostic factor
Abstract: EP347
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Clinical
Background
Novel recurrent fusion gene types such as zinc finger protein 384 (ZNF384) fusions have been identified in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL) with the application of next-generation sequencing technologies. However, the comprehensive large-scale clinical cohort study for clarifying their prognostic significance remains scarce to date.
Aims
To comprehensively evaluate the prognostic role of ZNF384 fusions in adult BCP-ALL.
Methods
A total of 242 consecutive adult Ph-negative BCP-ALL patients treated in our institute were retrospectively screened ZNF384 fusions at diagnosis by multiplex real time quantitative PCR.
Results
ZNF384 fusions were identified in 47 patients (19.4%), 38 had EP300-ZNF384, 5 had CREBBP-ZNF384, 2 had TCF3-ZNF384, 1 had TAF15-ZNF384 and 1 had EWSR1-ZNF384. All patients with ZNF384 fusions belonged to B-other ALL (having no high hyperdiploid karyotype, BCR-ABL1, TCF3-PBX1, ETV6-RUNX1 or MLL rearrangement).
In the whole cohort, patients with ZNF384 fusions had significantly higher 3-year relapse-free-survival (RFS) and tended to have a higher 3-year overall survival (OS) than those with no ZNF384 fusions (80.1% vs 52.5%, P = 0.011; 67.6% vs 54.0%, P = 0.10). For both patients receiving chemotherapy alone and when patients who received allo-HSCT were censored at the time of transplantation (Figure A, B), patients with ZNF384 fusions had both similar RFS rate and similar OS rate to B-other ALL patients with no ZNF384 fusions (RFS: P =0.94 and 0.30; OS: P =0.94 and 0.51). Furthermore, for patients receiving chemotherapy alone, patients with ZNF384 fusions had both similar RFS and similar OS to those with MLL rearrangement and TCF3-PBX1 fusion transcript, respectively (RFS: P = 0.45 and 0.13; OS: P = 0.80 and 0.45). When patients who received allo-HSCT were censored at the time of transplantation, patients with ZNF384 fusions had significantly higher 3-year RFS and OS than those with TCF3-PBX1 fusion transcript (P=0.0093 and 0.0009), and significantly higher 3-year RFS than and similar 3-year OS to those with MLL rearrangement (P=0.036 and 0.80). For patients receiving transplantation (Figure C, D), those with ZNF384 fusions had significantly higher 3-year RFS than B-other ALL patients with no ZNF384 fusions and their OS were similar (P = 0.022 and 0.24). Furthermore, patients with ZNF384 fusions had significantly higher 3-year RFS and tended to have significant high OS than those with MLL rearrangement and TCF3-PBX1 fusion transcript, respectively (RFS: P = 0.0026 and 0.0038; OS: P = 0.062 and 0.065). In addition, ZNF384 fusion was not an independent prognostic factor for both RFS and OS in both adult Ph-negative BCP-ALL and B-other patients.

Conclusion
ZNF384 fusion is common in adult BCP-ALL, which may define a new group from BCP-ALL containing no classical fusion transcript with better prognosis through receiving allo-HSCT.
Keyword(s): Adult, B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Fusion, Prognostic factor


