
Contributions
Abstract: EP343
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Clinical
Background
EORTC-CLG 58081 was designed as a translational-observational study for the identification of prognostic factors in children >1 year with Ph-negative ALL. Treatment recommendations were built on the best arms of the randomized phase 3 trial EORTC-CLG 58951: prednisolone (PRED) 60 mg/m² in induction for all risk groups but for average risk (AR) T-ALL (dexamethasone (DEX) 10 mg/m²) and AR2 B cell precursor (BCP)-ALL (DEX 6mg/m2). The AR2 group comprised patients (pts) with BCP-ALL (≥100x109/L WBC or CNS or extramedullary involvement at diagnosis) and pts with T-ALL (no CNS involvement or VHR features). Very low risk (VLR) pts had high-hyperdiploïdy, WBC<10x109/l, age <10 years, and no very high risk (VHR) features (D8 blood blasts>1x109/l, adverse genetic features, no CR or MRD≥10-2 at end of induction (EOI)). The risk stratification was left unchanged, except that MRD≥10-3 at the end of consolidation was added to VHR criterion in the 58081 study.
Aims
To evaluate event-free survival (EFS), (1) overall and according to each risk group in the 58081 as compared with the 58951 study (reference arm with PRED), and (2) from CR according to the EOI MRD level.
Methods
Between 2011 and 2017, 833 pts were enrolled in the 58081 study. The median follow-up was 5.5 yrs. Primary endpoint was EFS from date of first CR until relapse or death in CR; lack of CR achievement was an EFS event at T0.
Results
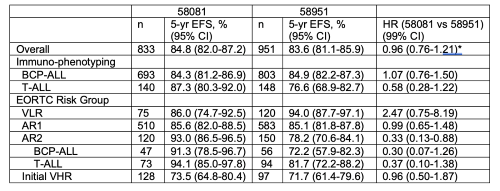
Results are presented in the Table. The 5-yr EFS rate were similar in the 2 studies, overall and in the BCP ALL subgroup, but in the T-ALL pts it was significantly higher in the 58081 study than in the 58951 study. Comparable EFS were obtained in both studies for AR1 and VHR pts (76.5% of the total). The EFS of VLR group was shorter in the 58081 study. In contrast, the EFS of AR2 pts significantly increased in the 58081 study, overall, and similarly in both subgroups, as same as the overall survival of AR2 patients which was 95.4% for the 58081 vs 88.3% for the 58951 (HR: 0.35; 95%CI 0.09-1.27, P=0.02). The 5-yr EFS for pts who reached CR was shorter for those with MRD≥10-2 at EOI (68.4%, HR=3.23) and those with 10-3<MRD<10-2 (55.2%, HR=5.63) as compared to pts with MRD<10-3 (89.8%).
Table
*: 95% CI
Conclusion
The poor EFS of patients with intermediate MRD at EOI confirm the value of this early timepoint to distinguish patients with high relapse risk. The disappointing results obtained for patients in the VLR group despite unchanged therapy and a more stringent definition of risk (age 1-9 yrs) are difficult to interpret but should prompt caution about therapeutic de-escalation. The improved EFS in the AR2 group is most likely due to the use of DXM, in induction for all pts and in VCR-DEX pulses in pts with BCP-ALL, together with improved MRD-based stratification. This allowed a dramatic EFS improvement in T-ALL subgroup, which for the first time and although using a risk stratification based solely on response to treatment outperforms that of BCP-ALL.
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Childhood, MRD, Outcome
Abstract: EP343
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Clinical
Background
EORTC-CLG 58081 was designed as a translational-observational study for the identification of prognostic factors in children >1 year with Ph-negative ALL. Treatment recommendations were built on the best arms of the randomized phase 3 trial EORTC-CLG 58951: prednisolone (PRED) 60 mg/m² in induction for all risk groups but for average risk (AR) T-ALL (dexamethasone (DEX) 10 mg/m²) and AR2 B cell precursor (BCP)-ALL (DEX 6mg/m2). The AR2 group comprised patients (pts) with BCP-ALL (≥100x109/L WBC or CNS or extramedullary involvement at diagnosis) and pts with T-ALL (no CNS involvement or VHR features). Very low risk (VLR) pts had high-hyperdiploïdy, WBC<10x109/l, age <10 years, and no very high risk (VHR) features (D8 blood blasts>1x109/l, adverse genetic features, no CR or MRD≥10-2 at end of induction (EOI)). The risk stratification was left unchanged, except that MRD≥10-3 at the end of consolidation was added to VHR criterion in the 58081 study.
Aims
To evaluate event-free survival (EFS), (1) overall and according to each risk group in the 58081 as compared with the 58951 study (reference arm with PRED), and (2) from CR according to the EOI MRD level.
Methods
Between 2011 and 2017, 833 pts were enrolled in the 58081 study. The median follow-up was 5.5 yrs. Primary endpoint was EFS from date of first CR until relapse or death in CR; lack of CR achievement was an EFS event at T0.
Results
Results are presented in the Table. The 5-yr EFS rate were similar in the 2 studies, overall and in the BCP ALL subgroup, but in the T-ALL pts it was significantly higher in the 58081 study than in the 58951 study. Comparable EFS were obtained in both studies for AR1 and VHR pts (76.5% of the total). The EFS of VLR group was shorter in the 58081 study. In contrast, the EFS of AR2 pts significantly increased in the 58081 study, overall, and similarly in both subgroups, as same as the overall survival of AR2 patients which was 95.4% for the 58081 vs 88.3% for the 58951 (HR: 0.35; 95%CI 0.09-1.27, P=0.02). The 5-yr EFS for pts who reached CR was shorter for those with MRD≥10-2 at EOI (68.4%, HR=3.23) and those with 10-3<MRD<10-2 (55.2%, HR=5.63) as compared to pts with MRD<10-3 (89.8%).
Table
*: 95% CI

Conclusion
The poor EFS of patients with intermediate MRD at EOI confirm the value of this early timepoint to distinguish patients with high relapse risk. The disappointing results obtained for patients in the VLR group despite unchanged therapy and a more stringent definition of risk (age 1-9 yrs) are difficult to interpret but should prompt caution about therapeutic de-escalation. The improved EFS in the AR2 group is most likely due to the use of DXM, in induction for all pts and in VCR-DEX pulses in pts with BCP-ALL, together with improved MRD-based stratification. This allowed a dramatic EFS improvement in T-ALL subgroup, which for the first time and although using a risk stratification based solely on response to treatment outperforms that of BCP-ALL.
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Childhood, MRD, Outcome


