
Contributions
Abstract: EP318
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Background
B cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL) is a molecularly heterogenous disease, characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of early lymphoid progenitor cells. As fusion-driven disease, it is further characterized by limited therapeutic options at relapse in adults. In recent years, it has been shown that non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) exhibit oncogenic properties. Especially, circular RNAs (circRNAs) are of increasing interest, as these are remarkably stable, covalently closed structures with tissue-specific expression and oncogenic potential.
Aims
Since their role in ALL remains largely uncharacterized, we investigated the expression pattern of circRNAs in BCP-ALL to identify and characterize new molecular markers for a deeper biological understanding.
Methods
We isolated ribosomal depleted RNA from a well-characterized cohort of 84 BCP-ALL samples from 63 patients (46 adults and 17 pediatric patients), consisting of 61 samples from initial diagnoses (ID) and 23 (21 paired) relapses (REL). RNA paired-end sequencing was performed on an Illumina HiSeq2500 with ~50 million reads per sample. Subgroup classification was based on mRNA expression and underlying driver fusion genes (FusionCatcher) in an established reference cohort of ~600 ALL samples. We used CIRCexplorer for circRNA detection and examined both individual circRNAs and circRNA variants condensed to their gene of origin. Differential expression analysis using DESeq2 was applied, and circRNA existence was confirmed by RT-PCR. All differentially expressed circRNAs were used for subsequent pathway analyses with ShinyGO.
Results
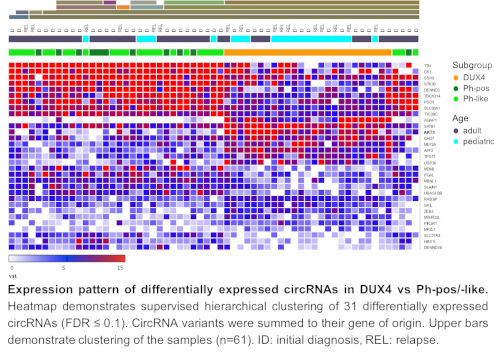
We identified a total of 79280 different circRNAs from 9400 genes in 84 analyzed samples. According to their mRNA expression, we defined molecular subgroups for all samples: DUX4 (ID n=15, REL n=10), Ph-pos (ID n=13), Ph-like (ID n=22, REL n=7) and others (ID n=11, REL n=6). To elucidate relapse specific circRNA expression, we compared paired samples from ID and REL in the subgroups of DUX4 and Ph-like, however found no significant change in circRNA expression. Due to minor difference in circRNA expression and the biological similarity of Ph-pos and Ph-like these samples were pooled and compared to DUX4 samples. Molecular BCP-ALL subgroups were classified by a unique circRNA expression pattern (Figure) with 259 differentially expressed circRNAs (FDR ≤ 0.05, log2 fold change ≥ 2) in DUX4 vs. Ph-pos/-like samples. We carried out pathway analyses and obtained over-represented pathways related to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance and cancer associated pathways involving known oncogenes like IGF1R, PIK3R1 and MDM2 (FDR ≤ 0.05). Of interest is the association to miRNAs in cancer, reflecting a potential sponge function of our identified circRNAs. Ph-pos/-like ALLs are characterized by deregulated JAK-STAT. In supervised analyses of circRNA expression of JAK-STAT members (DUX4 vs. Ph-pos/-like), we identified circAKT3 as potential target candidate (FDR ≤ 0.05, fold change 4.3).
Conclusion
We present a comprehensive analysis of circRNA expression in BCP-ALL in a well characterized cohort. Detected circRNA expression profiles discriminated BCP-ALL samples in molecular subgroups and remained stable between initial diagnosis and relapse. Moreover, we found differentially expressed circRNAs, corresponding to their gene of origin, enriched in different cancer pathways. Within JAK-STAT signaling, circAKT3 emerged as target candidate in BCP-ALL. These findings introduce circRNAs as new deregulated layer in BCP-ALL, warranting further exploration of potential therapeutic options.
Keyword(s): B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Gene expression profile, Molecular markers
Abstract: EP318
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Background
B cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL) is a molecularly heterogenous disease, characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of early lymphoid progenitor cells. As fusion-driven disease, it is further characterized by limited therapeutic options at relapse in adults. In recent years, it has been shown that non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) exhibit oncogenic properties. Especially, circular RNAs (circRNAs) are of increasing interest, as these are remarkably stable, covalently closed structures with tissue-specific expression and oncogenic potential.
Aims
Since their role in ALL remains largely uncharacterized, we investigated the expression pattern of circRNAs in BCP-ALL to identify and characterize new molecular markers for a deeper biological understanding.
Methods
We isolated ribosomal depleted RNA from a well-characterized cohort of 84 BCP-ALL samples from 63 patients (46 adults and 17 pediatric patients), consisting of 61 samples from initial diagnoses (ID) and 23 (21 paired) relapses (REL). RNA paired-end sequencing was performed on an Illumina HiSeq2500 with ~50 million reads per sample. Subgroup classification was based on mRNA expression and underlying driver fusion genes (FusionCatcher) in an established reference cohort of ~600 ALL samples. We used CIRCexplorer for circRNA detection and examined both individual circRNAs and circRNA variants condensed to their gene of origin. Differential expression analysis using DESeq2 was applied, and circRNA existence was confirmed by RT-PCR. All differentially expressed circRNAs were used for subsequent pathway analyses with ShinyGO.
Results
We identified a total of 79280 different circRNAs from 9400 genes in 84 analyzed samples. According to their mRNA expression, we defined molecular subgroups for all samples: DUX4 (ID n=15, REL n=10), Ph-pos (ID n=13), Ph-like (ID n=22, REL n=7) and others (ID n=11, REL n=6). To elucidate relapse specific circRNA expression, we compared paired samples from ID and REL in the subgroups of DUX4 and Ph-like, however found no significant change in circRNA expression. Due to minor difference in circRNA expression and the biological similarity of Ph-pos and Ph-like these samples were pooled and compared to DUX4 samples. Molecular BCP-ALL subgroups were classified by a unique circRNA expression pattern (Figure) with 259 differentially expressed circRNAs (FDR ≤ 0.05, log2 fold change ≥ 2) in DUX4 vs. Ph-pos/-like samples. We carried out pathway analyses and obtained over-represented pathways related to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance and cancer associated pathways involving known oncogenes like IGF1R, PIK3R1 and MDM2 (FDR ≤ 0.05). Of interest is the association to miRNAs in cancer, reflecting a potential sponge function of our identified circRNAs. Ph-pos/-like ALLs are characterized by deregulated JAK-STAT. In supervised analyses of circRNA expression of JAK-STAT members (DUX4 vs. Ph-pos/-like), we identified circAKT3 as potential target candidate (FDR ≤ 0.05, fold change 4.3).

Conclusion
We present a comprehensive analysis of circRNA expression in BCP-ALL in a well characterized cohort. Detected circRNA expression profiles discriminated BCP-ALL samples in molecular subgroups and remained stable between initial diagnosis and relapse. Moreover, we found differentially expressed circRNAs, corresponding to their gene of origin, enriched in different cancer pathways. Within JAK-STAT signaling, circAKT3 emerged as target candidate in BCP-ALL. These findings introduce circRNAs as new deregulated layer in BCP-ALL, warranting further exploration of potential therapeutic options.
Keyword(s): B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Gene expression profile, Molecular markers


