Contributions
Abstract: EP1320
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Thrombosis and vascular biology - Biology & Translational Research
Background
The identification of ambulatory patients with cancer at a high-risk of thrombosis and candidates for thromboprophylaxis remains challenging as several risk assessments models (RAMs) have been developed but none of them are routinely used in clinical practice by oncologists.
Aims
To evaluate in a prospective validation cohort (Oncothromb12-01) the predictive capacity of the Khorana, PROTECHT, CONKO, Vienna-CATS modified without P-selectin and Pabinger’s nomogram risk scores.
Methods
Multicenter, prospective, observational cohort study in Spain. The second cohort started in 2018 and includes outpatients with lung, central nervous system, colorectal, pancreatic, biliary tract, and gastric cancer naïve for systemic anti-tumor therapy and scheduled for initial treatment. The primary endpoint was the diagnosis of a symptomatic or incidental VTE episode within 12 months of follow up. The predictive power of each RAMs was analyzed by means of calculation of sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), positive and negative likelihood ratios, and area under the ROC curve (AUC).
Results
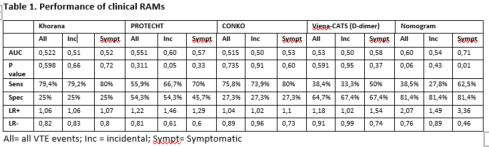
126 patients, median age 64 y.o. Gender male/female 54/72. Tumor types: pancreas 42,1 %, colorectal 21,4%, gastric 11,9%, biliary tract 9,5%, lung 9,5%, CNS 3,2%, esophagus 1,6% and pancreas + colorectal 0,8%. 57,9% stage IV, 10,3% ECOG ≥ 2. Thirty-four (27%) developed VTE during follow-up. PE 12 (35,3%), DVT 8(23,5%), central venous catheter thrombosis 1 (35,3%), visceral VTE 15 (44,1%). Incidental VTE 24 (70,5%). Overall mortality rate at 12 months 43%. Mortality rate of patients with VTE 65%. 79% of patients with VTE had tumor persistence within 12 months. The positive threshold of 3 points was determined for high-risk category in the RAMs (> 10% for Nomogram). Performance of clinical RAMs is summarized in Table 1.
Conclusion
All clinical RAMs tested in this study performed poorly in this high-risk population. We suggest the inclusion of other parameters in the RAMs as genomic o molecular variables to improve the predictive capacity.
Keyword(s): Chemotherapy, Prophylaxis, Risk factor, Thrombosis
Abstract: EP1320
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Thrombosis and vascular biology - Biology & Translational Research
Background
The identification of ambulatory patients with cancer at a high-risk of thrombosis and candidates for thromboprophylaxis remains challenging as several risk assessments models (RAMs) have been developed but none of them are routinely used in clinical practice by oncologists.
Aims
To evaluate in a prospective validation cohort (Oncothromb12-01) the predictive capacity of the Khorana, PROTECHT, CONKO, Vienna-CATS modified without P-selectin and Pabinger’s nomogram risk scores.
Methods
Multicenter, prospective, observational cohort study in Spain. The second cohort started in 2018 and includes outpatients with lung, central nervous system, colorectal, pancreatic, biliary tract, and gastric cancer naïve for systemic anti-tumor therapy and scheduled for initial treatment. The primary endpoint was the diagnosis of a symptomatic or incidental VTE episode within 12 months of follow up. The predictive power of each RAMs was analyzed by means of calculation of sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), positive and negative likelihood ratios, and area under the ROC curve (AUC).
Results
126 patients, median age 64 y.o. Gender male/female 54/72. Tumor types: pancreas 42,1 %, colorectal 21,4%, gastric 11,9%, biliary tract 9,5%, lung 9,5%, CNS 3,2%, esophagus 1,6% and pancreas + colorectal 0,8%. 57,9% stage IV, 10,3% ECOG ≥ 2. Thirty-four (27%) developed VTE during follow-up. PE 12 (35,3%), DVT 8(23,5%), central venous catheter thrombosis 1 (35,3%), visceral VTE 15 (44,1%). Incidental VTE 24 (70,5%). Overall mortality rate at 12 months 43%. Mortality rate of patients with VTE 65%. 79% of patients with VTE had tumor persistence within 12 months. The positive threshold of 3 points was determined for high-risk category in the RAMs (> 10% for Nomogram). Performance of clinical RAMs is summarized in Table 1.
Conclusion
All clinical RAMs tested in this study performed poorly in this high-risk population. We suggest the inclusion of other parameters in the RAMs as genomic o molecular variables to improve the predictive capacity.
Keyword(s): Chemotherapy, Prophylaxis, Risk factor, Thrombosis