Contributions
Abstract: EP1316
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Thalassemias
Background
The National Hemoglobinopathy Registry of the Turkish Society of Hematology (TSH) records the data of hemoglobinopathy patients (pts) in Turkey. In the modern era, there has been a marked improvement in the standard of care in thalassemia.
Aims
We analyzed the conventional treatment indicators of disease to assess the delivery of high-quality care all over Turkey.
Methods
The registry has Ethical approval. Participating physicians recorded patients' data into the database after receiving informed consent from the patients/legal representatives. We extracted the data onto an Excel spreadsheet for analysis in January 2021.
Results
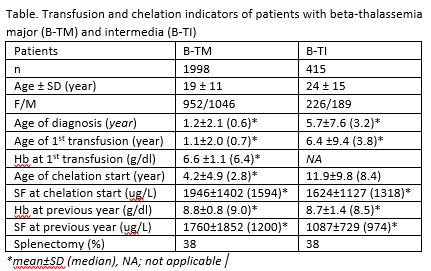
The register included 3554 pts' data entered by 56 thalassemia centers. There were 1998 pts with beta-thalassemia major (B-TM) and 415 pts with beta-thalassemia intermedia (B-TI).
The mean hemoglobin (Hb) at starting regular transfusion remained the same over the decades in B-TM pts. The mean Hb was 8.8±0.8 (median 9.0) g/dl in B-TM and 8.7±1.4 (range 6-13.5) g/dl in B-TI pts previous year. Overall, 4.6% and 7.0% of patients with B-TM and B-TI, respectively, were alloimmunized. 39% of non-immunized and 84.5% of alloimmunized pts were receiving ABO-RhEeDCc-Kell compatible pRBCs. Alloimmunization was significantly higher in patients who started regular Tx after the age of one year (3.9 vs. 10.0%) (p<0.0001). Transfusion transmitted infections affected 3% of the B-TM and 1% of the B-TI. Overall, 51 of 63 (80%) were HCV, in which 40% of those were reported as having chronic HCV infection. HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma was the cause of death in one.
Overall, 87% of pts with B-TM were on iron chelation therapy (ICT). Physicians prescribed ICT to 22% of pts with B-TI. Overall, 90% of pts were receiving chelator as monotherapy, and 90% of monotherapies were composed of Deferasirox (DFX). The combination was the choice in 1 of the 10th pts, and DFX & Deferiprone was the most prevalent (58.5% of the combined regimens). The data showed a gradually increasing trend towards monotherapy and the DFX use by each 10-year birth cohort. The median serum ferritin (SF) at starting ICT improved gradually by each 10-year birth cohort since 1960 from 2600 ug/L to as low as 1479 ug/L in the last cohort. Overall, median SF in B-TM pts settled down to 1200 ug/L in the previous year. Only 30% of B-TM patients had access to myocardial (T2*) MRI. The mean age of the first MRI assessment was 19±9 years. The majority (70%) had an mT2*of >20 ms, while 16.3% showed an mT2*of 10-20 ms and 6.7% an mT2* of <10 ms. Although SF was significantly correlated with the severity of cardiac siderosis, the pts' age was not.
In each 10-year birth cohort, 78% of pts with B-TM born between 1960-1990, and 54% of those born between 1990-2000 had a splenectomy. Further, half of those patients in each cohort had undergone splenectomy <10 years-old. The rate of splenectomy was lower (14%) in patients of the 2000-2010 cohort. It seems likely that the rate will less than that of the previous decades. Splenectomized patients showed less pRBC consumption than the non-splenectomized ones (median 125 vs. 173 ml/kg/y, p<0001). Although SF has not markedly differed in splenectomized and non-splenectomized patients, myocardial siderosis was higher in patients with splenectomy (25.7±11.0 vs. 29.2±8.5, p<0.001).
Conclusion
The register's data demonstrated the current status of a standard of care in thalassemia that still needs to achieve higher standards in this relatively young cohort in Turkey.
Keyword(s): Iron chelation, Splenectomy, Thalassemia, Transfusion
Abstract: EP1316
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Thalassemias
Background
The National Hemoglobinopathy Registry of the Turkish Society of Hematology (TSH) records the data of hemoglobinopathy patients (pts) in Turkey. In the modern era, there has been a marked improvement in the standard of care in thalassemia.
Aims
We analyzed the conventional treatment indicators of disease to assess the delivery of high-quality care all over Turkey.
Methods
The registry has Ethical approval. Participating physicians recorded patients' data into the database after receiving informed consent from the patients/legal representatives. We extracted the data onto an Excel spreadsheet for analysis in January 2021.
Results
The register included 3554 pts' data entered by 56 thalassemia centers. There were 1998 pts with beta-thalassemia major (B-TM) and 415 pts with beta-thalassemia intermedia (B-TI).
The mean hemoglobin (Hb) at starting regular transfusion remained the same over the decades in B-TM pts. The mean Hb was 8.8±0.8 (median 9.0) g/dl in B-TM and 8.7±1.4 (range 6-13.5) g/dl in B-TI pts previous year. Overall, 4.6% and 7.0% of patients with B-TM and B-TI, respectively, were alloimmunized. 39% of non-immunized and 84.5% of alloimmunized pts were receiving ABO-RhEeDCc-Kell compatible pRBCs. Alloimmunization was significantly higher in patients who started regular Tx after the age of one year (3.9 vs. 10.0%) (p<0.0001). Transfusion transmitted infections affected 3% of the B-TM and 1% of the B-TI. Overall, 51 of 63 (80%) were HCV, in which 40% of those were reported as having chronic HCV infection. HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma was the cause of death in one.
Overall, 87% of pts with B-TM were on iron chelation therapy (ICT). Physicians prescribed ICT to 22% of pts with B-TI. Overall, 90% of pts were receiving chelator as monotherapy, and 90% of monotherapies were composed of Deferasirox (DFX). The combination was the choice in 1 of the 10th pts, and DFX & Deferiprone was the most prevalent (58.5% of the combined regimens). The data showed a gradually increasing trend towards monotherapy and the DFX use by each 10-year birth cohort. The median serum ferritin (SF) at starting ICT improved gradually by each 10-year birth cohort since 1960 from 2600 ug/L to as low as 1479 ug/L in the last cohort. Overall, median SF in B-TM pts settled down to 1200 ug/L in the previous year. Only 30% of B-TM patients had access to myocardial (T2*) MRI. The mean age of the first MRI assessment was 19±9 years. The majority (70%) had an mT2*of >20 ms, while 16.3% showed an mT2*of 10-20 ms and 6.7% an mT2* of <10 ms. Although SF was significantly correlated with the severity of cardiac siderosis, the pts' age was not.
In each 10-year birth cohort, 78% of pts with B-TM born between 1960-1990, and 54% of those born between 1990-2000 had a splenectomy. Further, half of those patients in each cohort had undergone splenectomy <10 years-old. The rate of splenectomy was lower (14%) in patients of the 2000-2010 cohort. It seems likely that the rate will less than that of the previous decades. Splenectomized patients showed less pRBC consumption than the non-splenectomized ones (median 125 vs. 173 ml/kg/y, p<0001). Although SF has not markedly differed in splenectomized and non-splenectomized patients, myocardial siderosis was higher in patients with splenectomy (25.7±11.0 vs. 29.2±8.5, p<0.001).
Conclusion
The register's data demonstrated the current status of a standard of care in thalassemia that still needs to achieve higher standards in this relatively young cohort in Turkey.
Keyword(s): Iron chelation, Splenectomy, Thalassemia, Transfusion