
Contributions
Abstract: EP1271
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Background
For patients without HLA matched donor, PTCY in haploid stem cell transplantation has relatively higher risk of relapse and severe GVHD. Umbilical cord blood (UCB) are readily available and has helped expand the donor pool to almost all patients requiring a transplant. Meanwhile UCB transplant improves outcomes in leukaemia with lower risk of relapse and GVHD.However, the clinical application of UCB is limited due to their small cell numbers and lower implantation rate than other sources of hematopoietic stem cells(HSC).
Aims
This clinical study is to explore the feasibility and efficacy of post-transplantation fludarabine and cyclophosphamide to select and promote the unrelated UCB to engraft in combined transplantation of haploid and UCB stem cells for the treatment of childhood and adolescent leukemia.
Methods
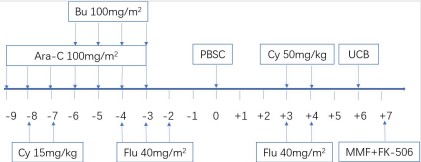
Total 27 children and adolescent patients with leukemia in Nanfang Hospital and Shenzhen Children's Hospital enrolled this study from Sept.2019 to Feb.2021. These patients were diagnosed as AML (3 secondary AML, 3 relapsed AML, 11 HR, 3 IR), ALL(2 relapsed, 2 HR) ,JMML(2) and MDS(1) with a median age of 10 years (range 1-17 years). Only one patient is BM PR before HSCT. The haploid stem cell was 5/10-9/10 mismatched and UCB was selected as 6/10-10/10 HLA matched or mismatched. The condition regimen was busulfan+fludarabine+CY+Ara-C. Haploid PBSC was infused in day0. All received PTCy 50 mg/kg and posttransplantation fludarabine 40mg/m2 on days 3 and 4 along with tacrolimus or cyclosporine and mycophenolate mofetil for prophylaxis of acute graft-versus-host disease(GVHD). UCB was infused in day6. A median of haploid stem cells of 11.08×106/kg(1.51-23.20) of CD34+ cells/kg was infused while a median of UCB cells of 1.80×105/kg(0.40-4.80) of CD34+ cells/kg was infused.
Results
At a median follow-up of 6 months (range 2-17), all patients are alive and leukemia free. Among these patients, 25/27(92.6%,95%CI: 0.820~1.032)of patients achieved complete chimerism of unrelated UCB cells and 2/27(7.4%,95%CI: -0.032~0.180) of patients achieved high-level mixed chimerism of unrelated UCB cells rather than haploid cells. Two recent patients had primary poor graft function around posttransplantation of 70days. Neutrophil reconstitution was achieved in 25/27 patients with a median time of 30 days (range 17-44 days)without G-CSF after transplantation. Platelet recovery was achieved in 25/27 patients with a median time of 39 days (range 8-92 days).The incidence of grade Ⅰ and grade Ⅱ GVHD was 37% and 37% respectively(95%CI: 0.176~0.565). There was no grade Ⅲ-Ⅳ GVHD and no extensive chronic GVHD. The incidence of chronic limited GVHD was 6/22(27.3%, 95%CI: 0.071~0.475). Fourteen of 27 (51.9%, 95%CI: 0.317~0.720) patients experienced clinically significant CMV reactivations or infections. One of 27(3.7%,95%CI: -0.039~0.113)patients experienced EB virus reactivation.
Conclusion
In our primary clinical study, post-transplantation fludarabine and cyclophosphamide could effectively selecte and promote the unrelated UCB to implant rather than haploid cells in combined transplantion of halpoid and UCB stem cells even if the dose of CD34+ cells of UCB as little as less than 1.00×105/kg . Although acute GVHD was common but just milder degree and with lower incidence of EB virus reactivation. This new strategy has the potential to promote the wilder clinical use of unrelated UCB in the treatment of leukemia.
Keyword(s): Adolescents, Children, Post-transplant, Umbilical cord blood transplant
Abstract: EP1271
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Background
For patients without HLA matched donor, PTCY in haploid stem cell transplantation has relatively higher risk of relapse and severe GVHD. Umbilical cord blood (UCB) are readily available and has helped expand the donor pool to almost all patients requiring a transplant. Meanwhile UCB transplant improves outcomes in leukaemia with lower risk of relapse and GVHD.However, the clinical application of UCB is limited due to their small cell numbers and lower implantation rate than other sources of hematopoietic stem cells(HSC).
Aims
This clinical study is to explore the feasibility and efficacy of post-transplantation fludarabine and cyclophosphamide to select and promote the unrelated UCB to engraft in combined transplantation of haploid and UCB stem cells for the treatment of childhood and adolescent leukemia.
Methods
Total 27 children and adolescent patients with leukemia in Nanfang Hospital and Shenzhen Children's Hospital enrolled this study from Sept.2019 to Feb.2021. These patients were diagnosed as AML (3 secondary AML, 3 relapsed AML, 11 HR, 3 IR), ALL(2 relapsed, 2 HR) ,JMML(2) and MDS(1) with a median age of 10 years (range 1-17 years). Only one patient is BM PR before HSCT. The haploid stem cell was 5/10-9/10 mismatched and UCB was selected as 6/10-10/10 HLA matched or mismatched. The condition regimen was busulfan+fludarabine+CY+Ara-C. Haploid PBSC was infused in day0. All received PTCy 50 mg/kg and posttransplantation fludarabine 40mg/m2 on days 3 and 4 along with tacrolimus or cyclosporine and mycophenolate mofetil for prophylaxis of acute graft-versus-host disease(GVHD). UCB was infused in day6. A median of haploid stem cells of 11.08×106/kg(1.51-23.20) of CD34+ cells/kg was infused while a median of UCB cells of 1.80×105/kg(0.40-4.80) of CD34+ cells/kg was infused.
Results
At a median follow-up of 6 months (range 2-17), all patients are alive and leukemia free. Among these patients, 25/27(92.6%,95%CI: 0.820~1.032)of patients achieved complete chimerism of unrelated UCB cells and 2/27(7.4%,95%CI: -0.032~0.180) of patients achieved high-level mixed chimerism of unrelated UCB cells rather than haploid cells. Two recent patients had primary poor graft function around posttransplantation of 70days. Neutrophil reconstitution was achieved in 25/27 patients with a median time of 30 days (range 17-44 days)without G-CSF after transplantation. Platelet recovery was achieved in 25/27 patients with a median time of 39 days (range 8-92 days).The incidence of grade Ⅰ and grade Ⅱ GVHD was 37% and 37% respectively(95%CI: 0.176~0.565). There was no grade Ⅲ-Ⅳ GVHD and no extensive chronic GVHD. The incidence of chronic limited GVHD was 6/22(27.3%, 95%CI: 0.071~0.475). Fourteen of 27 (51.9%, 95%CI: 0.317~0.720) patients experienced clinically significant CMV reactivations or infections. One of 27(3.7%,95%CI: -0.039~0.113)patients experienced EB virus reactivation.

Conclusion
In our primary clinical study, post-transplantation fludarabine and cyclophosphamide could effectively selecte and promote the unrelated UCB to implant rather than haploid cells in combined transplantion of halpoid and UCB stem cells even if the dose of CD34+ cells of UCB as little as less than 1.00×105/kg . Although acute GVHD was common but just milder degree and with lower incidence of EB virus reactivation. This new strategy has the potential to promote the wilder clinical use of unrelated UCB in the treatment of leukemia.
Keyword(s): Adolescents, Children, Post-transplant, Umbilical cord blood transplant


