
Contributions
Abstract: EP1237
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Background
Maintenance treatment with lenalidomide (Len) after autologous SCT in MM patients has demonstrated 2.5 years improvement in overall survival(OS). Its role after alloSCT is controversial because of an increased risk of graft versus host disease (GVHD), and prospective trials are lacking. AlloSCT can be a curative option in MM patients, but relapse is the main cause of treatment failure, especially after reduced intensity conditioning regimens (RIC), although they are the preferred option due to lower non-relapse mortality (NRM). The use of Bz within the conditioning regimen was demonstrated to be safe and allowed to obtain a high response rate after RIC alloSCT in a previous phase I trial. In an attempt to decrease the risk of relapse, this phase II was planned adding maintenance with Bz and Len.
Aims
Evaluate the toxicity and efficacy of a RIC with Bz and postransplant maintenance with Bz and Len in HR MM patients. Updated analysis of relapse rate (RR), acute and chronic GVHD, event free survival (EFS) and OS. To analyse inmune subpopulations and the effect of Len in immune recovery.
Methods
Multicenter, phase II trial. All patients provided written informed consent. RIC included Bz 1.3 mg/m2 iv on days -9 and -2; fludarabine 30 mg/m2 iv on days −6 to −4 and melphalan 140 mg/m2 iv on d −3. GvHD prophylaxis was based on Bz 1.3 mg/m2 iv on d +1, +4 and +7 plus methotrexate 15 mg/m2 on d+1 and 10 mg/m2 on d +3, +6 and +11 and tacrolimus. For maintenance therapy, all patients received Bz 1,3 mg/m2 iv on d 1, 8 and 15 in 28 days cycles starting on d+70 postransplant. Based on disease status at d +100, patients received six cycles of Bz (1.3 mg/m2 iv on d 1, 8, 15) every 56 days (if complete response(CR) or nCR) or four cycles of Bz (1.3 mg/m2 iv on d 1, 8, 15), Len (15 mg on days 1 to 21) and dex (10 mg on d 1 to 4 and 8 to 11) followed by same treatment regimen specified for patients in CR. Len was started on day +180 (5 mg pd until relapse or toxicity).Different subpopulations of the immune system were evaluated on peripheral blood by flow cytometry (FC) on days +100, +180, +270, and +365.
Results
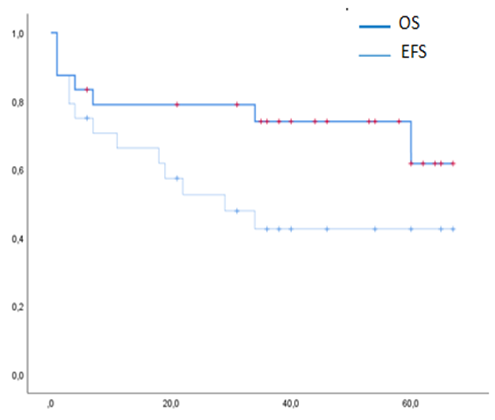
24 patients were included. All had previously received treatment with proteasome inhibitors and immunomodulatory drugs, 87% had received a previous autoSCT. Cumulative incidence (CI) of grade 2-4 and 3-4 aGvHD at 100d was 39% (CI 95%: 15.5%>56.1%) and 21.7% (CI 95%: 7.7%>40.4%). CI of overall cGVHD at 1y was 22.7% (CI 95%: 7.9%>42%) and moderate-severe 18.1% (CI 95%: 5.4%>36.8%). 7 patients died (5 due to aGvHD), CI NRM was 21.1% (95% CI 0.074-0.394) at 1y. With a median follow up of 39m (range 1-67), median EFS was 29m (95% CI 8.1%>49.8) (not reached for patients with at least VGPR at d100 postransplant); median OS was not reached. EFS and OS at 3y were 42,48% (95% CI 21.9%>61.7%) and 74% (95% CI 50.8%>87.45%). CI of relapse was 13.6% (95% CI: 3.2%>31.3%) at 1y. Out of 20 patients evaluable for maintenance therapy, 15 patients stopped it before relapse or death due to GvHD (9), infection (1), citopenia (1), neuropathy (2) and patient/physician´s choice (2). Upon comparing inmune recovery between patients included in the phase II or the phase I trial (who did not received maintenance), several differences emerged in different immune cell sub-populations (non classical monocytes, lymphocytes).
Conclusion
Combination of alloSCT with novel drugs could improve the efficacy of the procedure in MM.
Maintenance treatment with Len and Bz leads to a low risk of relapse. Although the risk of cGVHD did not increase, Len was stopped in a significant proportion of patients.
Keyword(s): Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, Maintenance, Multiple myeloma
Abstract: EP1237
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Background
Maintenance treatment with lenalidomide (Len) after autologous SCT in MM patients has demonstrated 2.5 years improvement in overall survival(OS). Its role after alloSCT is controversial because of an increased risk of graft versus host disease (GVHD), and prospective trials are lacking. AlloSCT can be a curative option in MM patients, but relapse is the main cause of treatment failure, especially after reduced intensity conditioning regimens (RIC), although they are the preferred option due to lower non-relapse mortality (NRM). The use of Bz within the conditioning regimen was demonstrated to be safe and allowed to obtain a high response rate after RIC alloSCT in a previous phase I trial. In an attempt to decrease the risk of relapse, this phase II was planned adding maintenance with Bz and Len.
Aims
Evaluate the toxicity and efficacy of a RIC with Bz and postransplant maintenance with Bz and Len in HR MM patients. Updated analysis of relapse rate (RR), acute and chronic GVHD, event free survival (EFS) and OS. To analyse inmune subpopulations and the effect of Len in immune recovery.
Methods
Multicenter, phase II trial. All patients provided written informed consent. RIC included Bz 1.3 mg/m2 iv on days -9 and -2; fludarabine 30 mg/m2 iv on days −6 to −4 and melphalan 140 mg/m2 iv on d −3. GvHD prophylaxis was based on Bz 1.3 mg/m2 iv on d +1, +4 and +7 plus methotrexate 15 mg/m2 on d+1 and 10 mg/m2 on d +3, +6 and +11 and tacrolimus. For maintenance therapy, all patients received Bz 1,3 mg/m2 iv on d 1, 8 and 15 in 28 days cycles starting on d+70 postransplant. Based on disease status at d +100, patients received six cycles of Bz (1.3 mg/m2 iv on d 1, 8, 15) every 56 days (if complete response(CR) or nCR) or four cycles of Bz (1.3 mg/m2 iv on d 1, 8, 15), Len (15 mg on days 1 to 21) and dex (10 mg on d 1 to 4 and 8 to 11) followed by same treatment regimen specified for patients in CR. Len was started on day +180 (5 mg pd until relapse or toxicity).Different subpopulations of the immune system were evaluated on peripheral blood by flow cytometry (FC) on days +100, +180, +270, and +365.
Results
24 patients were included. All had previously received treatment with proteasome inhibitors and immunomodulatory drugs, 87% had received a previous autoSCT. Cumulative incidence (CI) of grade 2-4 and 3-4 aGvHD at 100d was 39% (CI 95%: 15.5%>56.1%) and 21.7% (CI 95%: 7.7%>40.4%). CI of overall cGVHD at 1y was 22.7% (CI 95%: 7.9%>42%) and moderate-severe 18.1% (CI 95%: 5.4%>36.8%). 7 patients died (5 due to aGvHD), CI NRM was 21.1% (95% CI 0.074-0.394) at 1y. With a median follow up of 39m (range 1-67), median EFS was 29m (95% CI 8.1%>49.8) (not reached for patients with at least VGPR at d100 postransplant); median OS was not reached. EFS and OS at 3y were 42,48% (95% CI 21.9%>61.7%) and 74% (95% CI 50.8%>87.45%). CI of relapse was 13.6% (95% CI: 3.2%>31.3%) at 1y. Out of 20 patients evaluable for maintenance therapy, 15 patients stopped it before relapse or death due to GvHD (9), infection (1), citopenia (1), neuropathy (2) and patient/physician´s choice (2). Upon comparing inmune recovery between patients included in the phase II or the phase I trial (who did not received maintenance), several differences emerged in different immune cell sub-populations (non classical monocytes, lymphocytes).

Conclusion
Combination of alloSCT with novel drugs could improve the efficacy of the procedure in MM.
Maintenance treatment with Len and Bz leads to a low risk of relapse. Although the risk of cGVHD did not increase, Len was stopped in a significant proportion of patients.
Keyword(s): Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, Maintenance, Multiple myeloma


