
Contributions
Abstract: EP1210
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Sickle cell disease
Background
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is an inherited, autosomal recessive disorder that leads to hemolytic anemia and vascular disease, with a range of acute and chronic complications driven by self-perpetuating cycle of vaso-occlusion and vaso-occlusive crises (VOCs).
Aims
CSL889, a human plasma derived hemopexin, is being developed as a novel pharmacologic therapy to scavenge cell free toxic heme in patients with VOC, with the goal of reducing the duration and severity of acute VOC in adults and children with SCD.
Methods
In order to evaluate the pharmacokinetics (PK) of CSL889, single-dose PK studies were performed following intravenous (IV) administration in Townes HbSS mice, a model for sickle cell disease, (Hbbtm2(HBG1,HBB*)Tow), wild type C57BL6 (WT) mice and rats at a dose of 35 mg/kg, and in cynomolgus monkeys at doses of 50, 150 and 500 mg/kg BW. Additionally, a PK following repeated dosing (up to 3 repeat doses each 4 hours apart at a dose of 500 mg/kg IV) in Townes HbSS mice was conducted. In addition to CSL889, the concentration-time profiles of hemopexin:heme complex and total heme were described. Townes HbSS mice were used because they express the human HbSS and mimic the major features of the human SCD (eg. sickled red blood cells (RBCs) with a half-life of 2.4 days vs normal RBCs with a half-life of 15.7 days in healthy mice). Quantification of total human hemopexin (CSL889) in mouse, rat and cynomolgus monkey was performed using LC-MS/MS.
Results
In comparison to WT mice, Townes HbSS mice showed a markedly decreased Cmax (0.41 mg/mL vs 0.70 mg/mL) associated with a markedly increased clearance (23.0 vs 1.6 mL/kg/h) and consequently decreased half-life (7 vs 58 h) and mean residence time (MRT; 5 vs 81 h) following IV administration of CSL889. Similarly, the area under the curve (AUC0-inf) was 14-fold higher in WT- compared to Townes HbSS mice (21.8 vs. 1.52 h*mg/mL). PK parameters of CSL889 in rats were comparable to that in WT mice - Cmax (0.74 mg/mL), clearance (1.78 mL/kg/h), half-life (58 h) and AUC0-inf (19.6 h*mg/mL).
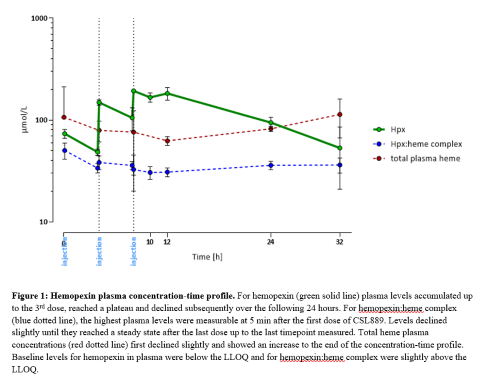
For hemopexin, following repeated IV administration, plasma levels accumulated up to the 3rd dose, reached a plateau and declined subsequently over the following 24 hours. AUC0-inf was 345 h*mg/mL, MRT 21.4 h, half-life 13.7 h and IVR 93%. For hemopexin:heme complex, the highest plasma levels were measurable at 5 min after the first dose of CSL889. Levels declined slightly until they reached a steady state after the last dose up to the last timepoint measured. Total heme plasma concentrations first declined slightly and showed an increase to the end of the concentration-time profile (Figure 1).
In monkeys, Cmax and AUC of CSL889 increased slightly less than dose-proportionally over the dose range of 50-500 mg/kg (Cmax from 1.6 to 10.4 mg/mL and AUC0-inf from 84.4 to 587 h*mg/mL). A slightly higher total clearance (Cl) [0.85 vs 0.66 vs. 0.61 mL/h/kg] was observed at the high dose compared to the intermediate and low dose. The terminal half-life following IV administration increased with dose from 80 to 103 h.
Conclusion
Townes HbSS mice tested at 35 mg/kg showed a shorter half-life compared to the healthy rodent species (7 h vs. 58 h) suggesting an increased binding of CSL889 to accessible heme in SCD. Following repeated dosing in Townes HbSS mice increasing hemopexin concentration levels correlate with decreasing total heme plasma levels. The increase of total heme towards the end is most probably due to the saturation of the clearance mechanism and ongoing hemolysis.
Keyword(s): Pharmacokinetic, Sickle cell disease
Abstract: EP1210
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Sickle cell disease
Background
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is an inherited, autosomal recessive disorder that leads to hemolytic anemia and vascular disease, with a range of acute and chronic complications driven by self-perpetuating cycle of vaso-occlusion and vaso-occlusive crises (VOCs).
Aims
CSL889, a human plasma derived hemopexin, is being developed as a novel pharmacologic therapy to scavenge cell free toxic heme in patients with VOC, with the goal of reducing the duration and severity of acute VOC in adults and children with SCD.
Methods
In order to evaluate the pharmacokinetics (PK) of CSL889, single-dose PK studies were performed following intravenous (IV) administration in Townes HbSS mice, a model for sickle cell disease, (Hbbtm2(HBG1,HBB*)Tow), wild type C57BL6 (WT) mice and rats at a dose of 35 mg/kg, and in cynomolgus monkeys at doses of 50, 150 and 500 mg/kg BW. Additionally, a PK following repeated dosing (up to 3 repeat doses each 4 hours apart at a dose of 500 mg/kg IV) in Townes HbSS mice was conducted. In addition to CSL889, the concentration-time profiles of hemopexin:heme complex and total heme were described. Townes HbSS mice were used because they express the human HbSS and mimic the major features of the human SCD (eg. sickled red blood cells (RBCs) with a half-life of 2.4 days vs normal RBCs with a half-life of 15.7 days in healthy mice). Quantification of total human hemopexin (CSL889) in mouse, rat and cynomolgus monkey was performed using LC-MS/MS.
Results
In comparison to WT mice, Townes HbSS mice showed a markedly decreased Cmax (0.41 mg/mL vs 0.70 mg/mL) associated with a markedly increased clearance (23.0 vs 1.6 mL/kg/h) and consequently decreased half-life (7 vs 58 h) and mean residence time (MRT; 5 vs 81 h) following IV administration of CSL889. Similarly, the area under the curve (AUC0-inf) was 14-fold higher in WT- compared to Townes HbSS mice (21.8 vs. 1.52 h*mg/mL). PK parameters of CSL889 in rats were comparable to that in WT mice - Cmax (0.74 mg/mL), clearance (1.78 mL/kg/h), half-life (58 h) and AUC0-inf (19.6 h*mg/mL).
For hemopexin, following repeated IV administration, plasma levels accumulated up to the 3rd dose, reached a plateau and declined subsequently over the following 24 hours. AUC0-inf was 345 h*mg/mL, MRT 21.4 h, half-life 13.7 h and IVR 93%. For hemopexin:heme complex, the highest plasma levels were measurable at 5 min after the first dose of CSL889. Levels declined slightly until they reached a steady state after the last dose up to the last timepoint measured. Total heme plasma concentrations first declined slightly and showed an increase to the end of the concentration-time profile (Figure 1).
In monkeys, Cmax and AUC of CSL889 increased slightly less than dose-proportionally over the dose range of 50-500 mg/kg (Cmax from 1.6 to 10.4 mg/mL and AUC0-inf from 84.4 to 587 h*mg/mL). A slightly higher total clearance (Cl) [0.85 vs 0.66 vs. 0.61 mL/h/kg] was observed at the high dose compared to the intermediate and low dose. The terminal half-life following IV administration increased with dose from 80 to 103 h.

Conclusion
Townes HbSS mice tested at 35 mg/kg showed a shorter half-life compared to the healthy rodent species (7 h vs. 58 h) suggesting an increased binding of CSL889 to accessible heme in SCD. Following repeated dosing in Townes HbSS mice increasing hemopexin concentration levels correlate with decreasing total heme plasma levels. The increase of total heme towards the end is most probably due to the saturation of the clearance mechanism and ongoing hemolysis.
Keyword(s): Pharmacokinetic, Sickle cell disease


