
Contributions
Abstract: EP1202
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Sickle cell disease
Background
Polymerization of deoxygenated hemoglobin S (HbS) is the precipitating event leading to red blood cell (RBC) sickling, hemolysis, and vaso-occlusion. The pathogenesis of sickle cell disease (SCD) is exacerbated by increased levels of 2,3-DPG, which decrease O2 affinity, and decreased levels of ATP, which impact RBC function. FT-4202 is a small molecule activator of erythrocyte pyruvate kinase (PKR) that decreases 2,3-DPG and increases ATP in RBCs. In healthy volunteers (HVs), FT-4202 was well tolerated in both single ascending dose (SD) and 14-day (2wk) once daily (QD) multiple ascending dose (MD) cohorts (Kalfa, 2019). In patients (pts) with SCD, a SD of FT-4202 was well tolerated and demonstrated similar pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) responses as in HVs (Estepp, 2020). Based on these initial results, two 2wk SCD MD cohorts (SCD MD1 [300mg FT-4202/placebo (P)] and SCD MD2 [600mg FT-4202/P]) were initiated in pts with SCD. The unblinded results of the SCD MD1 cohort are described here; data from the ongoing SCD MD2 and 12wk open label SCD MD (400mg FT-4202 QD) cohorts will be presented [NCT03815695].
Aims
To evaluate the safety and PK/PD of FT‑4202 in HVs and pts with SCD.
Methods
In each 2wk SCD MD cohort, a minimum of 9 pts, randomized 7:2 to FT-4202:P, were required for safety/dose escalation decisions. Safety included treatment (Tx)-emergent adverse events (AEs), vital signs, ECGs and laboratory parameters. Blood sampling for PK and PD (RBC 2,3-DPG and ATP) was performed for up to 7 days after end of treatment (EOT). Exploratory studies included P50 and RBC deformability with controlled deoxygenation/reoxygenation and varying osmolality (Lorrca® oxygenscan and osmoscan).
Results
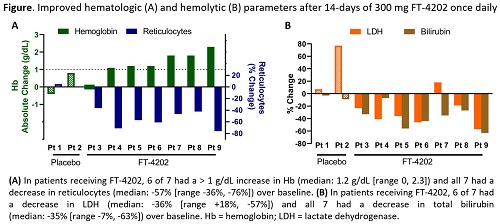
In the SCD MD1 cohort, of 9 pts (8 Hb SS; 1 SB+ thal) randomized 7:2 to FT-4202:P, 6 pts were on hydroxyurea. Eighteen AEs were reported in 7 pts (6 FT-4202, 1 P) with 16/18 AEs unrelated to study Tx; related AEs were headache and nausea (n=1 each). All AEs occurring in FT-4202 pts were ≤ grade 2. Three uncomplicated sickle pain events reported in 2 FT-4202 pts were consistent with SCD history and managed with standard home pain medications (no SAE/no hospitalization). Consistent with expected PD effects of PKR activation, rapid and sustained pharmacological activity was observed. In FT-4202 pts, 2,3-DPG levels decreased within 24h (p=0.031), while ATP levels increased through Tx day 7 (p=0.031). Both effects were sustained through the 2wk Tx period. In FT-4202 pts, Hb O2 affinity was increased as demonstrated by decreased P50 (p=0.031), reaching comparable values to untreated HVs. The increased O2 affinity and ATP were associated with improved sickle RBC deformability across an O2 or osmotic gradient; this improvement persisted for up to 7 days post-Tx in some pts. After 2wks, Hb increased (median +1.2 g/dL, p=0.031), with 6/7 pts having a maximum increase of >1 g/dL, occurring at EOT in 5/6 pts. Significant decreases in reticulocyte count (median -57%, p=0.016), LDH (median -36%, p=0.031), and bilirubin (median -35%, p=0.016) were also observed (Figure).
Conclusion
FT-4202 demonstrated a favorable safety profile in SCD pts when dosed at 300mg QD for 2wks. Consistent with PKR activation, FT-4202 decreased 2,3-DPG and increased ATP in RBCs, which correlated with increased RBC O2 affinity and improved RBC deformability. FT-4202 improved hematologic and hemolytic parameters, with best responses often observed at the end of the 2wk Tx period. Data from the ongoing 2wk SCD MD2 (600mg FT-4202/P) and 12wk open label SCD MD (400mg FT-4202) cohorts will be presented.
Keyword(s): Hemoglobin, Red blood cell, Sickle cell disease, Vasoocclusive crisis
Abstract: EP1202
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Sickle cell disease
Background
Polymerization of deoxygenated hemoglobin S (HbS) is the precipitating event leading to red blood cell (RBC) sickling, hemolysis, and vaso-occlusion. The pathogenesis of sickle cell disease (SCD) is exacerbated by increased levels of 2,3-DPG, which decrease O2 affinity, and decreased levels of ATP, which impact RBC function. FT-4202 is a small molecule activator of erythrocyte pyruvate kinase (PKR) that decreases 2,3-DPG and increases ATP in RBCs. In healthy volunteers (HVs), FT-4202 was well tolerated in both single ascending dose (SD) and 14-day (2wk) once daily (QD) multiple ascending dose (MD) cohorts (Kalfa, 2019). In patients (pts) with SCD, a SD of FT-4202 was well tolerated and demonstrated similar pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) responses as in HVs (Estepp, 2020). Based on these initial results, two 2wk SCD MD cohorts (SCD MD1 [300mg FT-4202/placebo (P)] and SCD MD2 [600mg FT-4202/P]) were initiated in pts with SCD. The unblinded results of the SCD MD1 cohort are described here; data from the ongoing SCD MD2 and 12wk open label SCD MD (400mg FT-4202 QD) cohorts will be presented [NCT03815695].
Aims
To evaluate the safety and PK/PD of FT‑4202 in HVs and pts with SCD.
Methods
In each 2wk SCD MD cohort, a minimum of 9 pts, randomized 7:2 to FT-4202:P, were required for safety/dose escalation decisions. Safety included treatment (Tx)-emergent adverse events (AEs), vital signs, ECGs and laboratory parameters. Blood sampling for PK and PD (RBC 2,3-DPG and ATP) was performed for up to 7 days after end of treatment (EOT). Exploratory studies included P50 and RBC deformability with controlled deoxygenation/reoxygenation and varying osmolality (Lorrca® oxygenscan and osmoscan).
Results
In the SCD MD1 cohort, of 9 pts (8 Hb SS; 1 SB+ thal) randomized 7:2 to FT-4202:P, 6 pts were on hydroxyurea. Eighteen AEs were reported in 7 pts (6 FT-4202, 1 P) with 16/18 AEs unrelated to study Tx; related AEs were headache and nausea (n=1 each). All AEs occurring in FT-4202 pts were ≤ grade 2. Three uncomplicated sickle pain events reported in 2 FT-4202 pts were consistent with SCD history and managed with standard home pain medications (no SAE/no hospitalization). Consistent with expected PD effects of PKR activation, rapid and sustained pharmacological activity was observed. In FT-4202 pts, 2,3-DPG levels decreased within 24h (p=0.031), while ATP levels increased through Tx day 7 (p=0.031). Both effects were sustained through the 2wk Tx period. In FT-4202 pts, Hb O2 affinity was increased as demonstrated by decreased P50 (p=0.031), reaching comparable values to untreated HVs. The increased O2 affinity and ATP were associated with improved sickle RBC deformability across an O2 or osmotic gradient; this improvement persisted for up to 7 days post-Tx in some pts. After 2wks, Hb increased (median +1.2 g/dL, p=0.031), with 6/7 pts having a maximum increase of >1 g/dL, occurring at EOT in 5/6 pts. Significant decreases in reticulocyte count (median -57%, p=0.016), LDH (median -36%, p=0.031), and bilirubin (median -35%, p=0.016) were also observed (Figure).

Conclusion
FT-4202 demonstrated a favorable safety profile in SCD pts when dosed at 300mg QD for 2wks. Consistent with PKR activation, FT-4202 decreased 2,3-DPG and increased ATP in RBCs, which correlated with increased RBC O2 affinity and improved RBC deformability. FT-4202 improved hematologic and hemolytic parameters, with best responses often observed at the end of the 2wk Tx period. Data from the ongoing 2wk SCD MD2 (600mg FT-4202/P) and 12wk open label SCD MD (400mg FT-4202) cohorts will be presented.
Keyword(s): Hemoglobin, Red blood cell, Sickle cell disease, Vasoocclusive crisis


