
Contributions
Abstract: EP1156
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Platelet disorders
Background
Patient’s cirrhosis develops thrombocytopenia or other cytopenias from multiple factors, including hypersplenism, because it has no unique clinical or laboratory features to distinguish cytopenias is due cirrhosis or from other diseases.
Aims
This study was conducted to develop a diagnostic score for severe cytopenias in patients with hepatic cirrhosis.
Methods
In one referral center in Mexico City retrospective cohort of 95 patients with hepatitic cirrhosis of any etiology with thrombocytopenia or other cytopenia, (hematologic disease were excluded in hematologist evaluation and with bone marrow aspiration and biopsy), was used to construct the severe cytopenias in hepatic cirrhosis diagnostic score, called the C-score. We divide two groups according to severity of cytopenias: severe (absolute neutrophil count ≤1000 cells/µL or platelet count ≤ 50X10 /µL) and no severe cytopenias. Six variables were evaluated for their association with diagnosis of cytopenias in hepatic cirrhosis and logistic regression was used to calculate the weight of each criterion included in the score.
Results
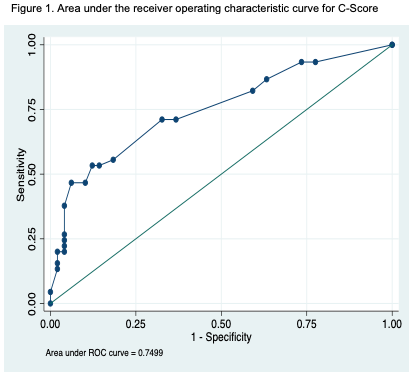
The group of severe cytopenias included 45 patients, no difference was observed in patient characteristics, included age, sex, etiology of cirrhosis, Child-Pugh Score, presence of esophageal varices, hemoglobin levels, lactate dehydrogenase, INR, creatinine. Six variables: 2 clinical (ascites and state of cirrhosis), 2 laboratory (lymphocytes and hemoglobin) and one radiological (spleen size, measured by the same radiologist) and one prognostic (MELD-Na), were used in the development the C-score. The possible number of points assigned to each variable ranged from 0 to – 3 for hemoglobin to 0-12 for spleen size and ascites (table 1). The area under the ROC curve for the C-Score was 0.74 (CI 95%, 0.65-0.84, P 0.05), indicating excellent discrimination (figure 1). The pseudo R2 statistic for the model was 0.15. The best cutoff value for de C-Score was ≥15, corresponding to a sensitivity of 71.11%, a specificity of 67.35%, positive predictive value of 66.67%, negative predictive value of 71.74% and accurate classification of 69.15% of the patients. The probability of having severe cytopenias in hepatic cirrhosis ranged from 30.22 % with a score of 5 to 89% with score of 40. We perform internal validation with the area under the ROC curve of 0.752 (min: 0.673, max 0.840).ç
Table 1. The C-Score
Parameter | Points |
Spleen Size (cm) <14 ≥14 |
0 12 |
Lymphocytes (cells/µL) >800 ≤800 |
0 6 |
Ascites No Mild Moderate/severe |
0 1 12 |
Hemoglobin (g/dl) ≤7 >7 |
0 -3 |
MELD-Na <14 ≥14 |
0 7 |
Cirrhosis stage Compensated Decompensated |
0 5 |
Conclusion
Discussion: Severe cytopenias are frequently in patients with cirrhosis, with multifactorial pathogenesis, difficult diagnosis and many of the times the patient undergoes unnecessary diagnostic workup. The C-Score is the first for the diagnosis of severe cytopenias in patients with cirrhosis, C-Score has limitations, was developed using a retrospective study population and in this initial study we focus on the development of the score, since we do not have a cohort for external validation, we perform internal validation by bootstrap, prospective validation of the score in other samples of patients is needed before it is recommended for widespread use.
Conclusion: The C-Score can be used to estimate the patients risks of having severe cytopenias in hepatic cirrhosis and it can help the clinician to make adequate diagnosis and treatment decisions in clinical practice.
Keyword(s): Cirrhosis, Diagnosis, Thrombocythemia
Abstract: EP1156
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Platelet disorders
Background
Patient’s cirrhosis develops thrombocytopenia or other cytopenias from multiple factors, including hypersplenism, because it has no unique clinical or laboratory features to distinguish cytopenias is due cirrhosis or from other diseases.
Aims
This study was conducted to develop a diagnostic score for severe cytopenias in patients with hepatic cirrhosis.
Methods
In one referral center in Mexico City retrospective cohort of 95 patients with hepatitic cirrhosis of any etiology with thrombocytopenia or other cytopenia, (hematologic disease were excluded in hematologist evaluation and with bone marrow aspiration and biopsy), was used to construct the severe cytopenias in hepatic cirrhosis diagnostic score, called the C-score. We divide two groups according to severity of cytopenias: severe (absolute neutrophil count ≤1000 cells/µL or platelet count ≤ 50X10 /µL) and no severe cytopenias. Six variables were evaluated for their association with diagnosis of cytopenias in hepatic cirrhosis and logistic regression was used to calculate the weight of each criterion included in the score.
Results
The group of severe cytopenias included 45 patients, no difference was observed in patient characteristics, included age, sex, etiology of cirrhosis, Child-Pugh Score, presence of esophageal varices, hemoglobin levels, lactate dehydrogenase, INR, creatinine. Six variables: 2 clinical (ascites and state of cirrhosis), 2 laboratory (lymphocytes and hemoglobin) and one radiological (spleen size, measured by the same radiologist) and one prognostic (MELD-Na), were used in the development the C-score. The possible number of points assigned to each variable ranged from 0 to – 3 for hemoglobin to 0-12 for spleen size and ascites (table 1). The area under the ROC curve for the C-Score was 0.74 (CI 95%, 0.65-0.84, P 0.05), indicating excellent discrimination (figure 1). The pseudo R2 statistic for the model was 0.15. The best cutoff value for de C-Score was ≥15, corresponding to a sensitivity of 71.11%, a specificity of 67.35%, positive predictive value of 66.67%, negative predictive value of 71.74% and accurate classification of 69.15% of the patients. The probability of having severe cytopenias in hepatic cirrhosis ranged from 30.22 % with a score of 5 to 89% with score of 40. We perform internal validation with the area under the ROC curve of 0.752 (min: 0.673, max 0.840).ç
Table 1. The C-Score
Parameter | Points |
Spleen Size (cm) <14 ≥14 |
0 12 |
Lymphocytes (cells/µL) >800 ≤800 |
0 6 |
Ascites No Mild Moderate/severe |
0 1 12 |
Hemoglobin (g/dl) ≤7 >7 |
0 -3 |
MELD-Na <14 ≥14 |
0 7 |
Cirrhosis stage Compensated Decompensated |
0 5 |

Conclusion
Discussion: Severe cytopenias are frequently in patients with cirrhosis, with multifactorial pathogenesis, difficult diagnosis and many of the times the patient undergoes unnecessary diagnostic workup. The C-Score is the first for the diagnosis of severe cytopenias in patients with cirrhosis, C-Score has limitations, was developed using a retrospective study population and in this initial study we focus on the development of the score, since we do not have a cohort for external validation, we perform internal validation by bootstrap, prospective validation of the score in other samples of patients is needed before it is recommended for widespread use.
Conclusion: The C-Score can be used to estimate the patients risks of having severe cytopenias in hepatic cirrhosis and it can help the clinician to make adequate diagnosis and treatment decisions in clinical practice.
Keyword(s): Cirrhosis, Diagnosis, Thrombocythemia


