
Contributions
Abstract: EP1085
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Background
The bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) family of proteins bind to chromatin to regulate the transcription of target genes involved in multiple pro-fibrotic pathways and is a potential novel therapeutic target for reducing fibrosis in myelofibrosis (MF). Pelabresib (CPI-0610), a first-in-class, oral, small-molecule inhibitor of BET proteins (BETi), has potential to promote disease-modifying activity through altered gene regulation of key oncogenic, fibrotic, and inflammatory factors in the clonal disease cells of origin in MF. Treatment with JAK inhibitor (JAKi) ruxolitinib (rux) or fedratinib in the frontline setting is associated with approximately 30-40% splenic response defined as spleen volume reduction ≥ 35% (SVR35) at 6 months (Verstovsek 2012, Pardanani 2015). The BETi pelabresib monotherapy demonstrated clinical activity in heavily pretreated MF patients (pts) (Talpaz, ASH 2020). In preclinical MF models, the combination of a BETi and rux demonstrated synergistic reduction of splenomegaly (Kleppe 2018). Therefore, combination of pelabresib with rux is expected to achieve higher SVR35 response rate in JAKi treatment naïve MF pts.
Aims
Evaluation of pelabresib in combination with rux in JAKi treatment naïve MF pts.
Methods
Pts with MF who were not previously treated with JAKi were enrolled in Arm 3 of the MANIFEST study. Primary endpoint is SVR35 response (≥35% reduction in spleen volume) at wk 24. Pts were treated with pelabresib 125 mg daily on days 1-14 in a 21-day cycle, in combination with rux which was dosed based on the baseline platelet count.
Results
As of 29 September 2020, 78 pts were treated, and 66 pts were ongoing. Baseline characteristics were mean age: 67 yo; 72% male; primary MF: 54% pts; DIPSS ≥Int-2: 76% pts; IPSS ≥Int-2: 83%; Hgb <10g/dL: 65%; median platelet: 294 x 109/L (range: 100, 1849); median spleen volume: 1719 cc (range: 451, 4782); median TSS: 16 (range: 0, 38); high-molecular-risk mutations: 55%, JAK2 mutation: 72%.
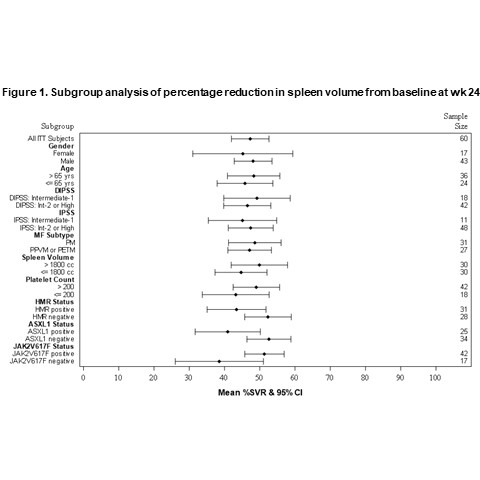
At wk 24, 67% (42/63) pts achieved SVR35 (median % change from baseline: -50%; range: -84.4%, 23.7%). Subgroup analysis showed that mean percentage change in spleen volume at wk 24 was consistent across subgroups based on gender, age, risk score, MF subtype, baseline platelet count and baseline spleen size (Fig. 1). Importantly, subgroup analysis based on molecular findings show a significant benefit regardless of the mutational status, including the presence of ASXL1 mutation which generally carries a poor prognosis.
Pelabresib was generally well tolerated. The most common treatment emergent adverse events include anemia (33%, ≥Gr3: 30%), thrombocytopenia (32%, ≥Gr3: 8%), diarrhea (30%, no ≥Gr3), dysgeusia (19%, no ≥Gr3), and asthenic conditions (19%, no ≥Gr3).
Conclusion
Pelabresib treatment in combination with rux in JAKi treatment naïve MF pts resulted in spleen volume reduction that was greater than what would be expected with rux alone, regardless of baseline patient disease and demographic characteristics.
Keyword(s): Epigenetic, Janus Kinase inhibitor, Myelofibrosis, Ruxolitinib
Abstract: EP1085
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Background
The bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) family of proteins bind to chromatin to regulate the transcription of target genes involved in multiple pro-fibrotic pathways and is a potential novel therapeutic target for reducing fibrosis in myelofibrosis (MF). Pelabresib (CPI-0610), a first-in-class, oral, small-molecule inhibitor of BET proteins (BETi), has potential to promote disease-modifying activity through altered gene regulation of key oncogenic, fibrotic, and inflammatory factors in the clonal disease cells of origin in MF. Treatment with JAK inhibitor (JAKi) ruxolitinib (rux) or fedratinib in the frontline setting is associated with approximately 30-40% splenic response defined as spleen volume reduction ≥ 35% (SVR35) at 6 months (Verstovsek 2012, Pardanani 2015). The BETi pelabresib monotherapy demonstrated clinical activity in heavily pretreated MF patients (pts) (Talpaz, ASH 2020). In preclinical MF models, the combination of a BETi and rux demonstrated synergistic reduction of splenomegaly (Kleppe 2018). Therefore, combination of pelabresib with rux is expected to achieve higher SVR35 response rate in JAKi treatment naïve MF pts.
Aims
Evaluation of pelabresib in combination with rux in JAKi treatment naïve MF pts.
Methods
Pts with MF who were not previously treated with JAKi were enrolled in Arm 3 of the MANIFEST study. Primary endpoint is SVR35 response (≥35% reduction in spleen volume) at wk 24. Pts were treated with pelabresib 125 mg daily on days 1-14 in a 21-day cycle, in combination with rux which was dosed based on the baseline platelet count.
Results
As of 29 September 2020, 78 pts were treated, and 66 pts were ongoing. Baseline characteristics were mean age: 67 yo; 72% male; primary MF: 54% pts; DIPSS ≥Int-2: 76% pts; IPSS ≥Int-2: 83%; Hgb <10g/dL: 65%; median platelet: 294 x 109/L (range: 100, 1849); median spleen volume: 1719 cc (range: 451, 4782); median TSS: 16 (range: 0, 38); high-molecular-risk mutations: 55%, JAK2 mutation: 72%.
At wk 24, 67% (42/63) pts achieved SVR35 (median % change from baseline: -50%; range: -84.4%, 23.7%). Subgroup analysis showed that mean percentage change in spleen volume at wk 24 was consistent across subgroups based on gender, age, risk score, MF subtype, baseline platelet count and baseline spleen size (Fig. 1). Importantly, subgroup analysis based on molecular findings show a significant benefit regardless of the mutational status, including the presence of ASXL1 mutation which generally carries a poor prognosis.
Pelabresib was generally well tolerated. The most common treatment emergent adverse events include anemia (33%, ≥Gr3: 30%), thrombocytopenia (32%, ≥Gr3: 8%), diarrhea (30%, no ≥Gr3), dysgeusia (19%, no ≥Gr3), and asthenic conditions (19%, no ≥Gr3).

Conclusion
Pelabresib treatment in combination with rux in JAKi treatment naïve MF pts resulted in spleen volume reduction that was greater than what would be expected with rux alone, regardless of baseline patient disease and demographic characteristics.
Keyword(s): Epigenetic, Janus Kinase inhibitor, Myelofibrosis, Ruxolitinib


