
Contributions
Abstract: EP1074
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Background
Patients with myelofibrosis (MF) require treatment when the clinical benefits of JAK inhibitors are exhausted; there is a clear need for novel therapies. Lysine-specific demethylase-1 (LSD1) is an enzyme critical for malignant stem cells and the differentiation, e.g., LSD1 licenses maturation of megakaryocytes, a key cell in MF pathogenesis. IMG-7289 (bomedemstat) is an orally active LSD1 inhibitor that in mouse models of MPNs reduced peripheral cell counts, splenomegaly, inflammatory cytokines, marrow fibrosis and, importantly, mutant cell burdens (Jutzi et al. 2018).
Aims
IMG-7289-CTP-102 is an ongoing, multi-national, open-label, 24-week Phase 2 study of IMG-7289 taken once daily in MF patients resistant to all approved therapies. Key objectives are safety, and reduction a in spleen volume (SVR) and total symptoms scores (TSS). A platelet count ≥100k/μL is a key inclusion criterion. Bone marrow (BM) biopsies and imaging studies are read centrally. Dosing is individually tailored using platelet count as a biomarker targeting a platelet count of 50-100k/μL.
Methods
At the censoring date (15Feb2021), 62 patients had enrolled, 24 patients remain on study. The median duration of treatment is 98 days (14-567). Median age is 68 (35-88) with 50% males; 47% had PMF, 34%, PET-MF, 19%, PPV-MF. All but 6 patients were previously treated with ruxolitinib; 47% had received up to 3 additional treatments. 33% were transfusion-dependent. 58% were IPSS high-risk, 42% intermediate risk-2. Of driver mutations, 66% were JAK2, 27% CALR, 6% MPL and one triple-negative. Of a panel of 261 genes mutated in AML/MPN/MDS, 65% had ≥2 mutation, 46% had ≥1 HMR mutations, 94% were in ASXL1.
Results
Of all enrolled patients evaluable at 24 weeks for TSS (N=13), 85% recorded a reduction in TSS (mean change -31%; -81% to 21%) with 31% reporting >50% reduction. Of all patients evaluable for SVR after 24 weeks (N=19), 81% had a reduction in SV from baseline (mean SVR: -8%; -41% to +37%). 72% of evaluable patients (N=36) had stable or improved hemoglobin (>1 g/dL). 26% of evaluable patients had an improvement in fibrosis score by 1 grade while 43% were stable. Elevated serum LDH improved or resolved in 88%.
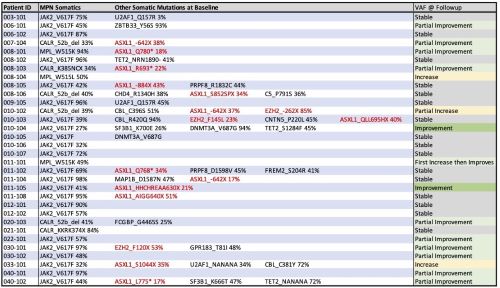
In 32 patients to date, mutant allele frequencies (MAF) in driver and HMR mutations were reduced in 42% and stable in 50%. All driver mutations showed sensitivity to bomedemstat; most ASXL1 clones were subject to purifying selection by treatment. When MAFs in driver mutations were stable or decreased, SV and/or TSS was stable (n=2) or improved (n= 17). In subjects with excess blasts (N=12), 8 (67%) improved or resolved during therapy. There has been no progression to AML at up to 550 days. There was no obvious relationship among mutations, final optimal dose or response rates. Germline variants will be discussed. CN-LOH remains a strong driver of mutant gene dosage.
55 patients (89%) reported 1001 AEs of which 63 were SAEs. Eight SAEs, 6 Grade 3 and 2 Grade 2, each occurring once, were deemed related by Investigators to IMG-7289: painful splenomegaly, rectal hemorrhage, cardiac failure, headache, vertigo, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, anaemia and pyoderma gangrenosum. There have been no safety signals, DLTs, or deaths related to drug.
Conclusion
In this first clinical study of an LSD1 inhibitor in MF patients, IMG-7289 as monotherapy was well-tolerated, improved symptom burdens and reduced spleen volume without safety signals. Additionally, improvements in fibrosis scores, anemia and MAF have been observed.
The study is active and is enrolling in the US, UK, EU and Hong Kong.
Keyword(s): Epigenetic, Myelofibrosis
Abstract: EP1074
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Background
Patients with myelofibrosis (MF) require treatment when the clinical benefits of JAK inhibitors are exhausted; there is a clear need for novel therapies. Lysine-specific demethylase-1 (LSD1) is an enzyme critical for malignant stem cells and the differentiation, e.g., LSD1 licenses maturation of megakaryocytes, a key cell in MF pathogenesis. IMG-7289 (bomedemstat) is an orally active LSD1 inhibitor that in mouse models of MPNs reduced peripheral cell counts, splenomegaly, inflammatory cytokines, marrow fibrosis and, importantly, mutant cell burdens (Jutzi et al. 2018).
Aims
IMG-7289-CTP-102 is an ongoing, multi-national, open-label, 24-week Phase 2 study of IMG-7289 taken once daily in MF patients resistant to all approved therapies. Key objectives are safety, and reduction a in spleen volume (SVR) and total symptoms scores (TSS). A platelet count ≥100k/μL is a key inclusion criterion. Bone marrow (BM) biopsies and imaging studies are read centrally. Dosing is individually tailored using platelet count as a biomarker targeting a platelet count of 50-100k/μL.
Methods
At the censoring date (15Feb2021), 62 patients had enrolled, 24 patients remain on study. The median duration of treatment is 98 days (14-567). Median age is 68 (35-88) with 50% males; 47% had PMF, 34%, PET-MF, 19%, PPV-MF. All but 6 patients were previously treated with ruxolitinib; 47% had received up to 3 additional treatments. 33% were transfusion-dependent. 58% were IPSS high-risk, 42% intermediate risk-2. Of driver mutations, 66% were JAK2, 27% CALR, 6% MPL and one triple-negative. Of a panel of 261 genes mutated in AML/MPN/MDS, 65% had ≥2 mutation, 46% had ≥1 HMR mutations, 94% were in ASXL1.
Results
Of all enrolled patients evaluable at 24 weeks for TSS (N=13), 85% recorded a reduction in TSS (mean change -31%; -81% to 21%) with 31% reporting >50% reduction. Of all patients evaluable for SVR after 24 weeks (N=19), 81% had a reduction in SV from baseline (mean SVR: -8%; -41% to +37%). 72% of evaluable patients (N=36) had stable or improved hemoglobin (>1 g/dL). 26% of evaluable patients had an improvement in fibrosis score by 1 grade while 43% were stable. Elevated serum LDH improved or resolved in 88%.
In 32 patients to date, mutant allele frequencies (MAF) in driver and HMR mutations were reduced in 42% and stable in 50%. All driver mutations showed sensitivity to bomedemstat; most ASXL1 clones were subject to purifying selection by treatment. When MAFs in driver mutations were stable or decreased, SV and/or TSS was stable (n=2) or improved (n= 17). In subjects with excess blasts (N=12), 8 (67%) improved or resolved during therapy. There has been no progression to AML at up to 550 days. There was no obvious relationship among mutations, final optimal dose or response rates. Germline variants will be discussed. CN-LOH remains a strong driver of mutant gene dosage.
55 patients (89%) reported 1001 AEs of which 63 were SAEs. Eight SAEs, 6 Grade 3 and 2 Grade 2, each occurring once, were deemed related by Investigators to IMG-7289: painful splenomegaly, rectal hemorrhage, cardiac failure, headache, vertigo, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, anaemia and pyoderma gangrenosum. There have been no safety signals, DLTs, or deaths related to drug.

Conclusion
In this first clinical study of an LSD1 inhibitor in MF patients, IMG-7289 as monotherapy was well-tolerated, improved symptom burdens and reduced spleen volume without safety signals. Additionally, improvements in fibrosis scores, anemia and MAF have been observed.
The study is active and is enrolling in the US, UK, EU and Hong Kong.
Keyword(s): Epigenetic, Myelofibrosis


