Contributions
Abstract: EP1051
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Subcutaneous daratumumab (DARA SC), which is approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma (MM), has efficacy comparable to intravenous (IV) DARA, but it takes only 3-5 min to administer vs 3-7 h for DARA IV and is associated with reduced rates of administration-related reactions (ARRs) in clinical studies. However, DARA IV to SC switch has not been studied, and ARR rates and patient management data (eg, time in/through clinic) associated with the switch are not well characterized.
Aims
To assess real-world evidence on chair time, post-administration observation time, and ARR rates in patients with MM switching from DARA IV to SC
Methods
Patients aged ≥18 years with an ICD-9/10 diagnosis code of MM and a first DARA treatment between April 1, 2017 and December 31, 2020 were identified in Mayo Clinic’s Electronic Health Records database. A scheduling and pharmacy software that tracked patient movement through appointments at a Mayo Clinic infusion center was used for data extraction. Data from patients initiating DARA by a single administration route (IV or SC) and patients who received DARA IV for ≥2 doses before switching to SC within 6-60 days were evaluated. The primary objective of the study was to describe the characteristics of DARA administration. The incidence of ARRs was determined in patients who switched from DARA IV to SC using ARR-associated events, including treatment, ICD codes, or admission to emergency department (ED).
Results
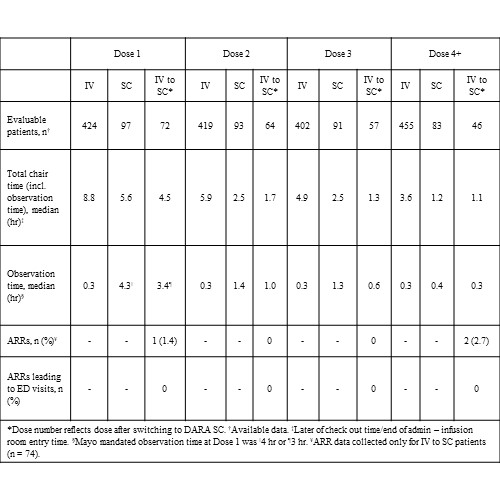
Overall, 737 patients initiated DARA treatment for MM (IV, n=640; SC, n=97); 74 patients who initiated DARA IV switched to SC. The median total chair time for DARA SC was 2.4 to 3.4 h shorter compared with DARA IV across all doses (Table). The median observation time decreased from Dose 1 to Dose 3 by 3.0 h (70%) in the SC group and by 2.8 h (82%) in the IV to SC switch group. Among patients who switched from IV to SC, the ARR rate was 1.4% for Dose 1 and 0% for both Doses 2 and 3, with no ARRs leading to ED visits for any dose. The analysis was limited in terms of data completeness, past treatments, and other temporal confounding factors.
Conclusion
A shorter median total chair time and low ARR rates were observed across all SC doses in this real-world study, based on which modification of the observation time after Dose 1 are being considered. This may lead to improved practice efficiency and support initiating DARA therapy with SC administration or switching from DARA IV to SC.
Keyword(s): Multiple myeloma, Subcutaneous
Abstract: EP1051
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Subcutaneous daratumumab (DARA SC), which is approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma (MM), has efficacy comparable to intravenous (IV) DARA, but it takes only 3-5 min to administer vs 3-7 h for DARA IV and is associated with reduced rates of administration-related reactions (ARRs) in clinical studies. However, DARA IV to SC switch has not been studied, and ARR rates and patient management data (eg, time in/through clinic) associated with the switch are not well characterized.
Aims
To assess real-world evidence on chair time, post-administration observation time, and ARR rates in patients with MM switching from DARA IV to SC
Methods
Patients aged ≥18 years with an ICD-9/10 diagnosis code of MM and a first DARA treatment between April 1, 2017 and December 31, 2020 were identified in Mayo Clinic’s Electronic Health Records database. A scheduling and pharmacy software that tracked patient movement through appointments at a Mayo Clinic infusion center was used for data extraction. Data from patients initiating DARA by a single administration route (IV or SC) and patients who received DARA IV for ≥2 doses before switching to SC within 6-60 days were evaluated. The primary objective of the study was to describe the characteristics of DARA administration. The incidence of ARRs was determined in patients who switched from DARA IV to SC using ARR-associated events, including treatment, ICD codes, or admission to emergency department (ED).
Results
Overall, 737 patients initiated DARA treatment for MM (IV, n=640; SC, n=97); 74 patients who initiated DARA IV switched to SC. The median total chair time for DARA SC was 2.4 to 3.4 h shorter compared with DARA IV across all doses (Table). The median observation time decreased from Dose 1 to Dose 3 by 3.0 h (70%) in the SC group and by 2.8 h (82%) in the IV to SC switch group. Among patients who switched from IV to SC, the ARR rate was 1.4% for Dose 1 and 0% for both Doses 2 and 3, with no ARRs leading to ED visits for any dose. The analysis was limited in terms of data completeness, past treatments, and other temporal confounding factors.
Conclusion
A shorter median total chair time and low ARR rates were observed across all SC doses in this real-world study, based on which modification of the observation time after Dose 1 are being considered. This may lead to improved practice efficiency and support initiating DARA therapy with SC administration or switching from DARA IV to SC.
Keyword(s): Multiple myeloma, Subcutaneous