Contributions
Abstract: EP1046
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Patients with MM experience treatment and disease-related symptoms that impact their daily living and health-related quality of life. Among patients with MM the commonly reported disease symptoms that impact patient daily life include pain, and fatigue (Gonzalez-McQuire, MDM Policy Pract. 2019). BELLINI (M14-031, NCT01794520) phase 3 double-blind randomized clinical trial compared venetoclax (ven) in combination with bortezomib (bort) and dexamethasone (dex) compared with placebo (pbo), bort and dex. The primary study results readout in 2019 reported that the primary endpoint of PFS (HR 0.63, 95% CI=0.44-0.89) was achieved but higher risk of death (HR 2.027, 95% CI=1.04-3.95) was observed in the treatment (trt) arm compared with pbo arm (survival data not yet mature; Kumar, S et al. EHA Library. Jun 16 2019;273254:LB2601).
Aims
The current analysis compared time to deterioration (TTD) in patient-reported outcomes (PROs) as measured by the EORTC QLQ-C30 and EORTC QLQ-MY20 questionnaires (PROs assessed at Cycles 1, 3, 5, 7 and every other cycle starting cycle 9) between the M14-031 study groups
Methods
BELLINI enrolled adult patients with RR MM with exposure to 1-3 prior lines of therapy. For current analysis, meaningful change thresholds (MCTs) for the EORTC-QLQ-C30 (Osoba et al 1998), and EORTC-QLQ-MY20 (Sully et. al 2019) measures were defined using published literature. For each PRO domain, meaningful deterioration was defined as a change of at least one unit of the scale specific MCT at any time point after the baseline observation. Kaplan-Meier (KM) curves and corresponding nominal log-rank P-value were used to assess differences between trt arms (reported for the overall and t(11;14) positive sub-group).
Results
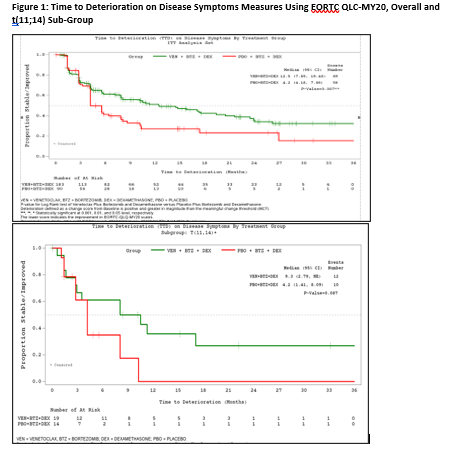
The intention-to-treat (ITT) dataset included 194 pts (≥65 years: 56%; 2-3 prior lines: 46.1%) in the trt group and 97 pts (≥65 years: 54%; 2-3 prior lines: 51.5%) in the pbo group. The t(11;14) positive sub-group included 35 patients of which 20 were in the ven arm and 15 in the pbo arm. For the ITT population, delay in TTD was observed for the EORTC QLQ-MY20 disease symptom domain (e.g., bone aches or pain, back pain, hip pain) in the trt group compared with the pbo group (12.5 vs. 4.2 Months; P = 0.042; Figure 1). TTD in EORTC QLQ-MY20 disease symptom domain was longer but not statistically significantly in the trt group compared with the pbo group in the t(11;14) MM sub-group (Figure 1). KM analysis for the EORTC QLQ-C30 domains indicated delay in cognitive functioning deterioration for the trt group versus the pbo group (4.6 vs. 4.2 months; P = 0.042). No statistically significant differences were observed in TTD between the two study groups for the EORTC QLQ-C30 emotional (P = 0.437), physical (P = 0.754), role (P = 0.623) functioning domains, fatigue (P = 0.829) and global health status/quality of life (P = 0.623) domains.. In multivariate Cox proportional hazard model, reduction in the risk of deterioration in EORTC QLQ-MY20 disease symptoms domain was estimated at 38% (hazard ratio;95% CI: 0.62; 0.44 - 0.88) in the trt group compared with the pbo group.
Conclusion
In this analysis of the M14-031 PRO data, delays in TTD were observed in in the ven-based trt arm compared with the pbo group for the myeloma-specific disease symptom domain. This finding was consistent in the overall ITT population and positive trend in the t(11;14) sub-group. Smaller sample size for the t(11;14) positive sub-group likely limits drawing meaningful inferences.
Keyword(s):
Abstract: EP1046
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Patients with MM experience treatment and disease-related symptoms that impact their daily living and health-related quality of life. Among patients with MM the commonly reported disease symptoms that impact patient daily life include pain, and fatigue (Gonzalez-McQuire, MDM Policy Pract. 2019). BELLINI (M14-031, NCT01794520) phase 3 double-blind randomized clinical trial compared venetoclax (ven) in combination with bortezomib (bort) and dexamethasone (dex) compared with placebo (pbo), bort and dex. The primary study results readout in 2019 reported that the primary endpoint of PFS (HR 0.63, 95% CI=0.44-0.89) was achieved but higher risk of death (HR 2.027, 95% CI=1.04-3.95) was observed in the treatment (trt) arm compared with pbo arm (survival data not yet mature; Kumar, S et al. EHA Library. Jun 16 2019;273254:LB2601).
Aims
The current analysis compared time to deterioration (TTD) in patient-reported outcomes (PROs) as measured by the EORTC QLQ-C30 and EORTC QLQ-MY20 questionnaires (PROs assessed at Cycles 1, 3, 5, 7 and every other cycle starting cycle 9) between the M14-031 study groups
Methods
BELLINI enrolled adult patients with RR MM with exposure to 1-3 prior lines of therapy. For current analysis, meaningful change thresholds (MCTs) for the EORTC-QLQ-C30 (Osoba et al 1998), and EORTC-QLQ-MY20 (Sully et. al 2019) measures were defined using published literature. For each PRO domain, meaningful deterioration was defined as a change of at least one unit of the scale specific MCT at any time point after the baseline observation. Kaplan-Meier (KM) curves and corresponding nominal log-rank P-value were used to assess differences between trt arms (reported for the overall and t(11;14) positive sub-group).
Results
The intention-to-treat (ITT) dataset included 194 pts (≥65 years: 56%; 2-3 prior lines: 46.1%) in the trt group and 97 pts (≥65 years: 54%; 2-3 prior lines: 51.5%) in the pbo group. The t(11;14) positive sub-group included 35 patients of which 20 were in the ven arm and 15 in the pbo arm. For the ITT population, delay in TTD was observed for the EORTC QLQ-MY20 disease symptom domain (e.g., bone aches or pain, back pain, hip pain) in the trt group compared with the pbo group (12.5 vs. 4.2 Months; P = 0.042; Figure 1). TTD in EORTC QLQ-MY20 disease symptom domain was longer but not statistically significantly in the trt group compared with the pbo group in the t(11;14) MM sub-group (Figure 1). KM analysis for the EORTC QLQ-C30 domains indicated delay in cognitive functioning deterioration for the trt group versus the pbo group (4.6 vs. 4.2 months; P = 0.042). No statistically significant differences were observed in TTD between the two study groups for the EORTC QLQ-C30 emotional (P = 0.437), physical (P = 0.754), role (P = 0.623) functioning domains, fatigue (P = 0.829) and global health status/quality of life (P = 0.623) domains.. In multivariate Cox proportional hazard model, reduction in the risk of deterioration in EORTC QLQ-MY20 disease symptoms domain was estimated at 38% (hazard ratio;95% CI: 0.62; 0.44 - 0.88) in the trt group compared with the pbo group.
Conclusion
In this analysis of the M14-031 PRO data, delays in TTD were observed in in the ven-based trt arm compared with the pbo group for the myeloma-specific disease symptom domain. This finding was consistent in the overall ITT population and positive trend in the t(11;14) sub-group. Smaller sample size for the t(11;14) positive sub-group likely limits drawing meaningful inferences.
Keyword(s):