
Contributions
Abstract: EP1012
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Various studies have demonstrated that Mass Spectrometry (MS) could be a more sensitive method than protein electrophoresis (SPEP) and immunofixation (IFE) for detecting the monoclonal component (MC) in serum in multiple myeloma (MM) patients.
Aims
To compare MS performance against conventional techniques (SPEP and IFE) for the detection of the MC in MM patients enrolled in the PETHEMA/GEM2012MENOS65 clinical trial.
Methods
Newly diagnosed MM patients enrolled in the PETHEMA/GEM2012MENOS65 received six induction cycles of bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRD), high-dose therapy (melphalan 200 or busulfan and melphalan) followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and two further cycles of consolidation with VRD. MC in serum was evaluated by conventional techniques (SPEP and IFE) and by Quantitative Immunoprecipitation Mass Spectrometry (QIP-MS) using IgG/A/M, kappa, lambda, free kappa and free lambda isotypic specific beads, both after induction (post-Ind), at day 100 after ASCT (post-ASCT), and after consolidation (post-Cons). The first 186 patients out of the 458 recruited were included in this study.
Results
QIP-MS identified the MC in 118/186 (63%) patients post-Ind, 80/173 (46%) post-ASCT and 61/168 (36%) post-Cons. By contrast, SPEP/IFE detected the MC in 97/186 (52%) post-Ind, 62/173 (36%) post-ASCT and 41/168 (24%) post-Cons. The percentage of discordant cases decreased from 18% post-Ind to 14% post-ASCT and 13% post-Cons. Most discordances were due to samples positive by QIP-MS and negative by SPEP/IFE (15% post-Ind, 12% post-ASCT and 13% post-Cons). In a minority of cases, the MC was exclusively detected by SPEP/IFE: 6/186 (3%) post-Ind, 3/173 (2%) post-ASCT, and 1/168 (1%) post-Cons. Most discrepancies occurred early during monitoring or after ASCT, and could represent false-positives due to gel interpretation issues and/or the presence of oligoclonal bands. Of note, none of these latter discrepant cases (QIP-MS neg/SPEP/IFE+) have relapsed so far.
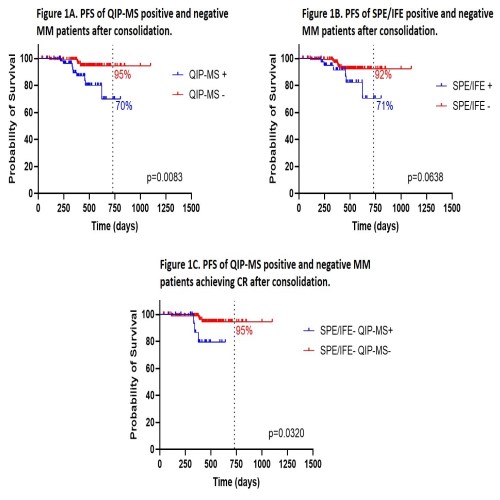
Once confirmed the higher ability of MS to detect the MC as compared to standard methods, we decided to compare their respective clinical value in terms of progression free survival (PFS) at the completion of the treatment (post-Cons, Figure 1). The probability of PFS at 2 years post-Cons was 95% for QIP-MS- patients vs 70% for those QIP-MS+ (p=0.0083, HR=4.677; fig. 1A). By contrast, the differences in PFS at 2 years post-Cons between SPEP/IFE- vs SPEP/IFE+ cases did not reach statistical significance (92% vs 71%, p=0.0638; fig. 1B). Investigating the 127 patients achieving CR post-Cons, we found out that QIP-MS was able to identify the presence of a MC in 21 of them (16.5%); further, the identification of the MC by QIP-MS in this group of patients in standard CR (SPEP/IFE-) was associated with a significantly shorter PFS (p=0.0320; HR=10.07; fig. 1C).
Conclusion
As compared to standard methods to detect the MC in serum, in this study QIP-MS: 1) identified the presence of the paraprotein in a higher proportion of cases throughout monitoring; 2) was able to discriminate 2 groups of patients with different PFS at treatment completion and 3) identified residual disease in a cohort of patients in standard CR but at increased risk of progression.
Keyword(s): Minimal residual disease (MRD), Myeloma
Abstract: EP1012
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Various studies have demonstrated that Mass Spectrometry (MS) could be a more sensitive method than protein electrophoresis (SPEP) and immunofixation (IFE) for detecting the monoclonal component (MC) in serum in multiple myeloma (MM) patients.
Aims
To compare MS performance against conventional techniques (SPEP and IFE) for the detection of the MC in MM patients enrolled in the PETHEMA/GEM2012MENOS65 clinical trial.
Methods
Newly diagnosed MM patients enrolled in the PETHEMA/GEM2012MENOS65 received six induction cycles of bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRD), high-dose therapy (melphalan 200 or busulfan and melphalan) followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and two further cycles of consolidation with VRD. MC in serum was evaluated by conventional techniques (SPEP and IFE) and by Quantitative Immunoprecipitation Mass Spectrometry (QIP-MS) using IgG/A/M, kappa, lambda, free kappa and free lambda isotypic specific beads, both after induction (post-Ind), at day 100 after ASCT (post-ASCT), and after consolidation (post-Cons). The first 186 patients out of the 458 recruited were included in this study.
Results
QIP-MS identified the MC in 118/186 (63%) patients post-Ind, 80/173 (46%) post-ASCT and 61/168 (36%) post-Cons. By contrast, SPEP/IFE detected the MC in 97/186 (52%) post-Ind, 62/173 (36%) post-ASCT and 41/168 (24%) post-Cons. The percentage of discordant cases decreased from 18% post-Ind to 14% post-ASCT and 13% post-Cons. Most discordances were due to samples positive by QIP-MS and negative by SPEP/IFE (15% post-Ind, 12% post-ASCT and 13% post-Cons). In a minority of cases, the MC was exclusively detected by SPEP/IFE: 6/186 (3%) post-Ind, 3/173 (2%) post-ASCT, and 1/168 (1%) post-Cons. Most discrepancies occurred early during monitoring or after ASCT, and could represent false-positives due to gel interpretation issues and/or the presence of oligoclonal bands. Of note, none of these latter discrepant cases (QIP-MS neg/SPEP/IFE+) have relapsed so far.
Once confirmed the higher ability of MS to detect the MC as compared to standard methods, we decided to compare their respective clinical value in terms of progression free survival (PFS) at the completion of the treatment (post-Cons, Figure 1). The probability of PFS at 2 years post-Cons was 95% for QIP-MS- patients vs 70% for those QIP-MS+ (p=0.0083, HR=4.677; fig. 1A). By contrast, the differences in PFS at 2 years post-Cons between SPEP/IFE- vs SPEP/IFE+ cases did not reach statistical significance (92% vs 71%, p=0.0638; fig. 1B). Investigating the 127 patients achieving CR post-Cons, we found out that QIP-MS was able to identify the presence of a MC in 21 of them (16.5%); further, the identification of the MC by QIP-MS in this group of patients in standard CR (SPEP/IFE-) was associated with a significantly shorter PFS (p=0.0320; HR=10.07; fig. 1C).

Conclusion
As compared to standard methods to detect the MC in serum, in this study QIP-MS: 1) identified the presence of the paraprotein in a higher proportion of cases throughout monitoring; 2) was able to discriminate 2 groups of patients with different PFS at treatment completion and 3) identified residual disease in a cohort of patients in standard CR but at increased risk of progression.
Keyword(s): Minimal residual disease (MRD), Myeloma


