
Contributions
Abstract: EP1010
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
The addition of a monoclonal antibody to triplet induction regimens in patients (pts) with MM with intent for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) has resulted in higher overall and deep response rates.
Aims
In this MRD-guided treatment design, we are investigating the impact of the addition of Elo to KRd on complete response (CR) and/or MRD-negative rates in newly diagnosed MM regardless of transplant eligibility.
Methods
Enrollment was completed from four MM Research Consortium sites into this phase 2 study. All patients receive 12 cycles of Elo-KRd in 28-day cycles: Elo per standard dosing, K 20/56/70 mg/m2 days 1, 8 and 15, R 25 mg days 1-21, and dexamethasone 40 mg days 1, 8, 15, 22. ASCT eligible candidates can undergo stem cell collection after cycle 4 and then resume treatment; pts who elect to proceed to ASCT are censored for response at that time. Pts MRD(-) (<10-5) by NGS after cycles 8 (C8) and 12 (C12) proceed to Elo-Rd until progression. Patients who convert from MRD(+) to MRD(-) between C8 and C12 receive an additional 6 cycles of Elo-KRd (total 18 cycles) followed by Elo-Rd, and pts MRD(+) after C12 receive an additional 12 cycles of Elo-KRd (total 24) followed by Elo-Rd. The primary endpoint of the study is sCR and/or MRD(-) rate after C8 E-KRd. MRD status was determined by ClonoSEQ next generation sequencing (NGS, <10-5) [Adaptive Biotechnologies]. An improvement in the sCR and/or MRD(-) rate by NGS from a historical 30% to 50% at the end of C8 will be considered promising. Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (MS) was also performed (Bristol Myers Squibb) from peripheral blood samples on an experimental basis to help distinguish elotuzumab from IgG Kappa paraprotein seen on immunofixation (IFIX).
Results
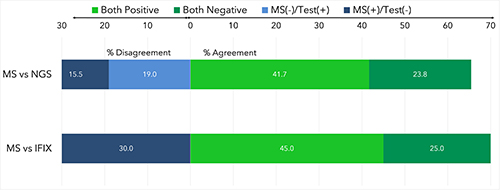
44 pts are enrolled, 39 of whom are evaluable for response (cutoff Jan 10 2021). 6 pts (14%) are Black, with 30 (68%) White pts and 8 (18%) with race unreported. Median age is 62 years (range 43-81, 23% age >70) and 23 (52%) have IMWG high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities (HRCA) including 13 (30%) with >2 high-risk abnormalities (6 pts unknown cytogenetics). 24 pts (55%) have a monoclonal IgG Kappa isotype at baseline. 34/39 (87%) have MRD trackable by clonoSEQ. The rate of sCR and/or MRD(-) by NGS at the end of C8 is 19/33 (58%), meeting the statistical threshold for efficacy (2 pts censored for elective ASCT before C8 and 4 pts on therapy but have not reached C8). For those reaching MRD(-), the median time to MRD(-) is 8 cycles (range 4-18). At the primary endpoint, there was 70% agreement between IFIX and MS amongst 20 paired samples with 6 discordant cases all MS(+)/IFIX(-). There was 65% agreement between MS and NGS across all timepoints, with 13/84 (15%) MS(+)/NGS(-) and 16/84 (19%) MS(-)/NGS(+). With a median follow-up of 24 months, estimated 2-year progression free survival is 87% (100% for standard risk, 79% for HRCA) and estimated 2-year overall survival is 89% (82% for HRCA). No pt who was MRD(-) by NGS after C8 has progressed, including 6 pts with HRCA. Serious adverse events occurred in 30 pts (68%). 89% experienced treatment emergent AEs, the most common (>10%) of which was pneumonia (14%). One pt had grade 5 myocardial infarction.
Conclusion
Elo-KRd demonstrates tolerability consistent with known toxicities of these agents and met the primary endpoint of sCR and/or MRD(-) of >50% after 8 cycles. MS and NGS are complementary in defining deep responses. With longer follow-up, the study may validate that an MRD-adaptive design for de-escalation of therapy in MM can generate deep responses while reducing treatment exposure.
Keyword(s): Clinical trial, Induction, Minimal residual disease (MRD), Multiple myeloma
Abstract: EP1010
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
The addition of a monoclonal antibody to triplet induction regimens in patients (pts) with MM with intent for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) has resulted in higher overall and deep response rates.
Aims
In this MRD-guided treatment design, we are investigating the impact of the addition of Elo to KRd on complete response (CR) and/or MRD-negative rates in newly diagnosed MM regardless of transplant eligibility.
Methods
Enrollment was completed from four MM Research Consortium sites into this phase 2 study. All patients receive 12 cycles of Elo-KRd in 28-day cycles: Elo per standard dosing, K 20/56/70 mg/m2 days 1, 8 and 15, R 25 mg days 1-21, and dexamethasone 40 mg days 1, 8, 15, 22. ASCT eligible candidates can undergo stem cell collection after cycle 4 and then resume treatment; pts who elect to proceed to ASCT are censored for response at that time. Pts MRD(-) (<10-5) by NGS after cycles 8 (C8) and 12 (C12) proceed to Elo-Rd until progression. Patients who convert from MRD(+) to MRD(-) between C8 and C12 receive an additional 6 cycles of Elo-KRd (total 18 cycles) followed by Elo-Rd, and pts MRD(+) after C12 receive an additional 12 cycles of Elo-KRd (total 24) followed by Elo-Rd. The primary endpoint of the study is sCR and/or MRD(-) rate after C8 E-KRd. MRD status was determined by ClonoSEQ next generation sequencing (NGS, <10-5) [Adaptive Biotechnologies]. An improvement in the sCR and/or MRD(-) rate by NGS from a historical 30% to 50% at the end of C8 will be considered promising. Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (MS) was also performed (Bristol Myers Squibb) from peripheral blood samples on an experimental basis to help distinguish elotuzumab from IgG Kappa paraprotein seen on immunofixation (IFIX).
Results
44 pts are enrolled, 39 of whom are evaluable for response (cutoff Jan 10 2021). 6 pts (14%) are Black, with 30 (68%) White pts and 8 (18%) with race unreported. Median age is 62 years (range 43-81, 23% age >70) and 23 (52%) have IMWG high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities (HRCA) including 13 (30%) with >2 high-risk abnormalities (6 pts unknown cytogenetics). 24 pts (55%) have a monoclonal IgG Kappa isotype at baseline. 34/39 (87%) have MRD trackable by clonoSEQ. The rate of sCR and/or MRD(-) by NGS at the end of C8 is 19/33 (58%), meeting the statistical threshold for efficacy (2 pts censored for elective ASCT before C8 and 4 pts on therapy but have not reached C8). For those reaching MRD(-), the median time to MRD(-) is 8 cycles (range 4-18). At the primary endpoint, there was 70% agreement between IFIX and MS amongst 20 paired samples with 6 discordant cases all MS(+)/IFIX(-). There was 65% agreement between MS and NGS across all timepoints, with 13/84 (15%) MS(+)/NGS(-) and 16/84 (19%) MS(-)/NGS(+). With a median follow-up of 24 months, estimated 2-year progression free survival is 87% (100% for standard risk, 79% for HRCA) and estimated 2-year overall survival is 89% (82% for HRCA). No pt who was MRD(-) by NGS after C8 has progressed, including 6 pts with HRCA. Serious adverse events occurred in 30 pts (68%). 89% experienced treatment emergent AEs, the most common (>10%) of which was pneumonia (14%). One pt had grade 5 myocardial infarction.

Conclusion
Elo-KRd demonstrates tolerability consistent with known toxicities of these agents and met the primary endpoint of sCR and/or MRD(-) of >50% after 8 cycles. MS and NGS are complementary in defining deep responses. With longer follow-up, the study may validate that an MRD-adaptive design for de-escalation of therapy in MM can generate deep responses while reducing treatment exposure.
Keyword(s): Clinical trial, Induction, Minimal residual disease (MRD), Multiple myeloma


