
Contributions
Abstract: EP1006
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
The Phase 3 IKEMA study (NCT03275285) demonstrated that isatuximab (Isa) plus carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd) significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) compared with Kd in patients (pts) with relapsed multiple myeloma (RMM) (hazard ratio [HR] 0.53; 99% confidence interval [CI] 0.32–0.89; P=0.0007).
Aims
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of Isa-Kd in the East Asian patients (19 Japanese, 27 Korean).
Methods
RMM pts who received 1-3 prior lines of therapy were stratified to receive Isa-Kd or Kd. Isa-Kd arm received Isa (10 mg/kg intravenously) weekly for 4 weeks, then every 2 weeks. Both arms received K (20 mg/m2 days 1-2, 56 mg/m2 thereafter) twice-weekly for 3 of 4 weeks, and d (20 mg) twice-weekly. Treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable adverse events (AE). The primary endpoint was prolongation of PFS. Key secondary endpoints included; very good partial response or better (≥VGPR), complete response (CR) rate and minimal residual disease negativity (MRD–) rate.
Results
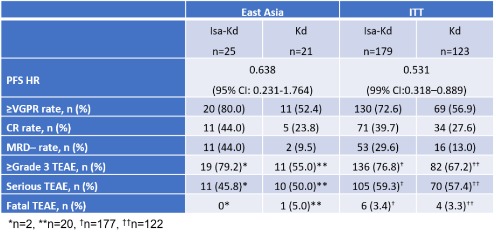
East Asian pts (25 Isa-Kd, 21 Kd) were randomized. Pt characteristics were similar in the East Asian subgroup compared with the intent to treat (ITT) population (N=302). Median age (Isa-Kd 64.0 [range 45–83] years vs Kd 60.0 [range 33–73] years); median prior lines Isa-Kd 2.0 (range 1–3) vs Kd 1.0 (range 1–3); refractory to lenalidomide 16.0% Isa-Kd vs 47.6% Kd; refractory to PI 20.0% Isa-Kd vs 33.3% Kd; high-risk cytogenetics 48.0% Isa-Kd vs 42.9% Kd. After a median follow-up of 20.7 months, the addition of Isa to Kd improved ≥VGPR, CR and MRD– rates (Table). The HR 0.64 (95%CI: 0.231-1.764) for disease progression or death favored Isa-Kd. Grade ≥3 AEs were observed in 79.2% Isa-Kd vs 55.0% Kd pts, serious TEAEs in 45.8% Isa-Kd vs 50.0% Kd; TEAEs leading to treatment discontinuation were lower in the Isa-Kd group (4.2% Isa-Kd vs 10.0% Kd). Overall, 64.0% Isa-Kd vs 42.9% Kd pts were still receiving treatment.
Conclusion
Efficacy and safety results of Isa-Kd in East Asian pts are consistent with the results of the overall IKEMA population, in which significantly better efficacy (PFS, CR, ≥VGPR and MRD– rate) was reported in favor of Isa-Kd without an increase in the number of patients with serious TEAEs or discontinuations. Isa-Kd is a potential treatment option for East Asian pts with RMM.
Keyword(s): Immunotherapy, Monoclonal antibody, Multiple myeloma
Abstract: EP1006
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
The Phase 3 IKEMA study (NCT03275285) demonstrated that isatuximab (Isa) plus carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd) significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) compared with Kd in patients (pts) with relapsed multiple myeloma (RMM) (hazard ratio [HR] 0.53; 99% confidence interval [CI] 0.32–0.89; P=0.0007).
Aims
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of Isa-Kd in the East Asian patients (19 Japanese, 27 Korean).
Methods
RMM pts who received 1-3 prior lines of therapy were stratified to receive Isa-Kd or Kd. Isa-Kd arm received Isa (10 mg/kg intravenously) weekly for 4 weeks, then every 2 weeks. Both arms received K (20 mg/m2 days 1-2, 56 mg/m2 thereafter) twice-weekly for 3 of 4 weeks, and d (20 mg) twice-weekly. Treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable adverse events (AE). The primary endpoint was prolongation of PFS. Key secondary endpoints included; very good partial response or better (≥VGPR), complete response (CR) rate and minimal residual disease negativity (MRD–) rate.
Results
East Asian pts (25 Isa-Kd, 21 Kd) were randomized. Pt characteristics were similar in the East Asian subgroup compared with the intent to treat (ITT) population (N=302). Median age (Isa-Kd 64.0 [range 45–83] years vs Kd 60.0 [range 33–73] years); median prior lines Isa-Kd 2.0 (range 1–3) vs Kd 1.0 (range 1–3); refractory to lenalidomide 16.0% Isa-Kd vs 47.6% Kd; refractory to PI 20.0% Isa-Kd vs 33.3% Kd; high-risk cytogenetics 48.0% Isa-Kd vs 42.9% Kd. After a median follow-up of 20.7 months, the addition of Isa to Kd improved ≥VGPR, CR and MRD– rates (Table). The HR 0.64 (95%CI: 0.231-1.764) for disease progression or death favored Isa-Kd. Grade ≥3 AEs were observed in 79.2% Isa-Kd vs 55.0% Kd pts, serious TEAEs in 45.8% Isa-Kd vs 50.0% Kd; TEAEs leading to treatment discontinuation were lower in the Isa-Kd group (4.2% Isa-Kd vs 10.0% Kd). Overall, 64.0% Isa-Kd vs 42.9% Kd pts were still receiving treatment.

Conclusion
Efficacy and safety results of Isa-Kd in East Asian pts are consistent with the results of the overall IKEMA population, in which significantly better efficacy (PFS, CR, ≥VGPR and MRD– rate) was reported in favor of Isa-Kd without an increase in the number of patients with serious TEAEs or discontinuations. Isa-Kd is a potential treatment option for East Asian pts with RMM.
Keyword(s): Immunotherapy, Monoclonal antibody, Multiple myeloma


