
Contributions
Abstract: EP1001
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Belantamab mafodotin (GSK2857916; belamaf) is a B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-targeting antibody–drug conjugate approved in the US and EU as a monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with RRMM. Ocular events (OEs) during the pivotal DREAMM-2 trial (NCT03525678) included corneal exam findings (punctate keratopathy and microcyst-like epithelial changes), BCVA changes, and ocular symptoms. Dose reductions or delays based on corneal exam findings and BCVA were used to manage OEs. Here we performed a post hoc investigation of relationships between corneal exam findings, BCVA changes, and patient-reported ocular symptoms to explore if BCVA changes and symptoms could guide dosing, rather than corneal exams.
Aims
.
Methods
Eye evaluations (including a corneal exam and BCVA assessment of Snellen visual acuity) were performed on all patients receiving single-agent belamaf (2.5 mg/kg) by ophthalmologists at baseline and prior to each belamaf dose. Changes in the corneal epithelium (Ker) and BCVA were both assessed as per protocol-defined criteria and assessment of grade (Gr) was based on the worse eye. BCVA grading was relative to baseline. Patient-reported ocular symptoms were reported as per the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events.
Results
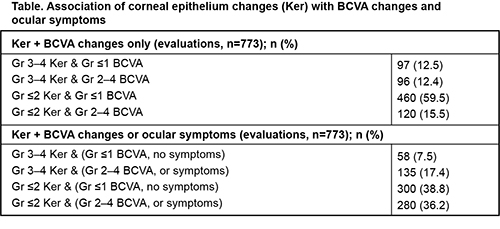
In 12.5% of eye evaluations Gr 3–4 Ker was associated with minimal or no (Gr ≤1) BCVA changes. When patient-reported ocular symptoms were also considered, only 7.5% of evaluations found Gr 3–4 Ker with Gr ≤1 BCVA changes or ocular symptoms. Mild or no (Gr ≤2) Ker was associated with Gr ≤1 BCVA changes in 59.5% of evaluations, or in 38.8% of evaluations with no ocular symptoms reported. Overall, Gr 3–4 Ker were found in 24.9% of evaluations; by contrast, patients had Gr 2–4 BCVA changes or ocular symptoms in 53.7% of evaluations.
Conclusion
These findings highlight that BCVA changes and ocular symptoms should be further investigated to determine if they can be used as alternatives (eg, frequency of eye examinations based on symptoms) for the management of belamaf dosing to potentially reduce the burden on patients and healthcare professionals.
Funding Source: GSK (205678; NCT03525678). Drug linker technology licensed from Seagen Inc.; mAb produced using POTELLIGENT Technology licensed from BioWa.
Encore statement: ©2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology, Inc. Reused with permission. All rights reserved. This abstract was previously submitted to the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, June 4–8, 2021, and is submitted on behalf of the original authors with their permission.
Keyword(s): B-cell maturation antigen, Multiple myeloma
Abstract: EP1001
Type: E-Poster Presentation
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Belantamab mafodotin (GSK2857916; belamaf) is a B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-targeting antibody–drug conjugate approved in the US and EU as a monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with RRMM. Ocular events (OEs) during the pivotal DREAMM-2 trial (NCT03525678) included corneal exam findings (punctate keratopathy and microcyst-like epithelial changes), BCVA changes, and ocular symptoms. Dose reductions or delays based on corneal exam findings and BCVA were used to manage OEs. Here we performed a post hoc investigation of relationships between corneal exam findings, BCVA changes, and patient-reported ocular symptoms to explore if BCVA changes and symptoms could guide dosing, rather than corneal exams.
Aims
.
Methods
Eye evaluations (including a corneal exam and BCVA assessment of Snellen visual acuity) were performed on all patients receiving single-agent belamaf (2.5 mg/kg) by ophthalmologists at baseline and prior to each belamaf dose. Changes in the corneal epithelium (Ker) and BCVA were both assessed as per protocol-defined criteria and assessment of grade (Gr) was based on the worse eye. BCVA grading was relative to baseline. Patient-reported ocular symptoms were reported as per the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events.
Results
In 12.5% of eye evaluations Gr 3–4 Ker was associated with minimal or no (Gr ≤1) BCVA changes. When patient-reported ocular symptoms were also considered, only 7.5% of evaluations found Gr 3–4 Ker with Gr ≤1 BCVA changes or ocular symptoms. Mild or no (Gr ≤2) Ker was associated with Gr ≤1 BCVA changes in 59.5% of evaluations, or in 38.8% of evaluations with no ocular symptoms reported. Overall, Gr 3–4 Ker were found in 24.9% of evaluations; by contrast, patients had Gr 2–4 BCVA changes or ocular symptoms in 53.7% of evaluations.

Conclusion
These findings highlight that BCVA changes and ocular symptoms should be further investigated to determine if they can be used as alternatives (eg, frequency of eye examinations based on symptoms) for the management of belamaf dosing to potentially reduce the burden on patients and healthcare professionals.
Funding Source: GSK (205678; NCT03525678). Drug linker technology licensed from Seagen Inc.; mAb produced using POTELLIGENT Technology licensed from BioWa.
Encore statement: ©2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology, Inc. Reused with permission. All rights reserved. This abstract was previously submitted to the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, June 4–8, 2021, and is submitted on behalf of the original authors with their permission.
Keyword(s): B-cell maturation antigen, Multiple myeloma


